One-quarter of city dwellers draws a line that connects the economic and environmental challenges of urban living with negative impacts on their mental health and well-being, and nearly as many urbanites say the challenges can affect them physically.
Those are some of the key findings in an “Architects of Change” report, based on an 11-question survey of 4,024 city dwellers in the U.S., United Kingdom, Germany, and Italy, commissioned by Chaos, a global leader in 3D visualization tools, and conducted on January 3-8, 2024, by Censuswide.
The report combines a rather bleak portrayal of city living with analysis—by John M. Cays, Associate Dean for Academic Affairs at New Jersey Institute of Technology’s Hillier College of Architecture and Design—that offers suggestions about how architects and designers might visualize the city of the future in ways that make urban living more palatable for residents, especially those age 35 to 44 who are most likely to purchase a house and become parents.
Climate change is adding stress to urban living
 While the respondents were pretty evenly divided among age, income, and geographic cohorts, the “common” respondent lives in a three-person household. Ten percent lives alone, and 13 percent lives in a household of five or more people. The respondents ranged from 16 to 55-plus years old, with the greatest portion falling within 35 and 44. Fifty-six percent of respondents—and 70 percent in the U.S. and Italy—owns homes outright.
While the respondents were pretty evenly divided among age, income, and geographic cohorts, the “common” respondent lives in a three-person household. Ten percent lives alone, and 13 percent lives in a household of five or more people. The respondents ranged from 16 to 55-plus years old, with the greatest portion falling within 35 and 44. Fifty-six percent of respondents—and 70 percent in the U.S. and Italy—owns homes outright.
Nearly three-quarters, 73 percent, of the survey’s respondents have lived in cities for at least five years. But that number drops to 28 percent when so-called nonnatives—people who were born in cities and have lived there all their lives—are excluded.
(The report links mobility and income. Among respondents with incomes of more than $45,501, the number of nonnatives who have lived in cities five years or fewer exceeds those who have lived in cities five years or more.)
The urban living experience can be stressful, especially when now when housing prices and rents are escalating. Sixty-three percent of respondents connect how much they pay for housing with declines in their quality of life. Nearly half, 47 percent, were considering moving to less-expensive housing markets. And 73 percent worry about the rising cost of energy.
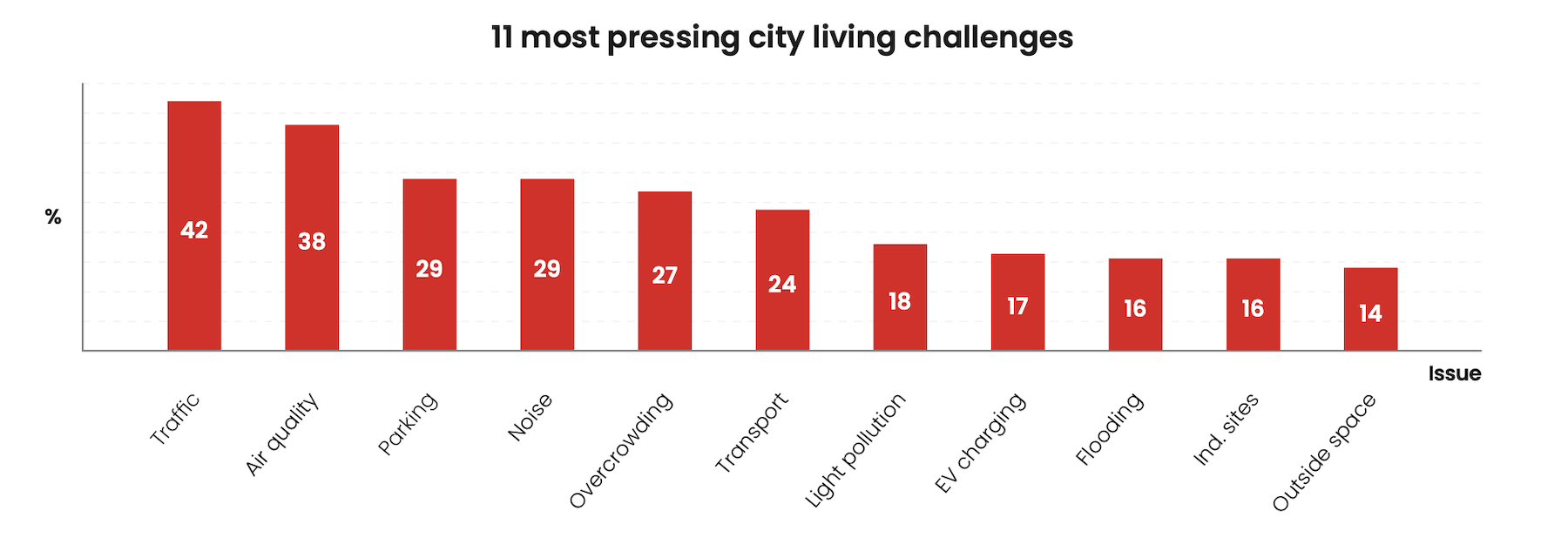
City dwellers must put up with all kinds of annoyances, too. Forty-two percent of respondents cited traffic congestion, followed by access to parking (29 percent) and noise pollution (29 percent). The good news for AEC firms is that these complaints leave open the door for building improvements in soundproofing and in-home air filtration.
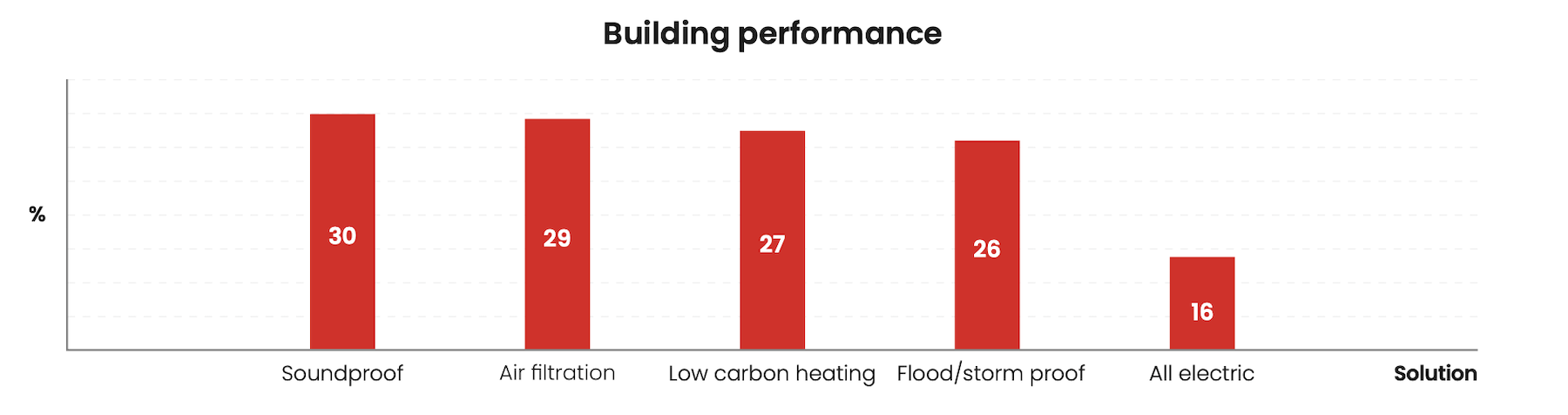
Cities are also at the doorstep of climate change, and their residents are noticing. Fifty-seven percent of respondents said they feel temperate extremes that affect their mental health and well-being. Another 21 percent cited weather extremes as a reason for moving. Three-fifths of respondents said they are willing to pay for solar panels that would lessen the impact of environmental change. And more than one-quarter of those survey sees climate change as a driver for storm- and floodproofing their homes.
(One finding that’s hard to explain: households with six or more people expressed the least concern for environmental design changes.)
Does urban living reinforce enduring home qualities?
More than three-fifths of those polled say that urban living places more economic pressure on them. Not surprisingly, lower-income city dwellers are feeling that pressure more acutely; however, energy costs are palpable as well for higher-income residents who are likely to be living in larger homes that consume more energy.
Cays, the Hillier College dean, observed the rise in micro housing units as one solution to housing inflation. And while the enduring qualities of a home—as a place of refuge, gathering, and repose—will remain constant, Cays can also envision tomorrow’s homes as “simply bathing and sleeping hubs,” with additional needs, like cooking and recreation, more external communal services.
On the climate change front, Cays’ analysis was more general and obvious. He said that any solutions must reflect geographic diversity, and that understanding building performance can make cities more adaptable to change.
Millennials are vulnerable to urban living pressures
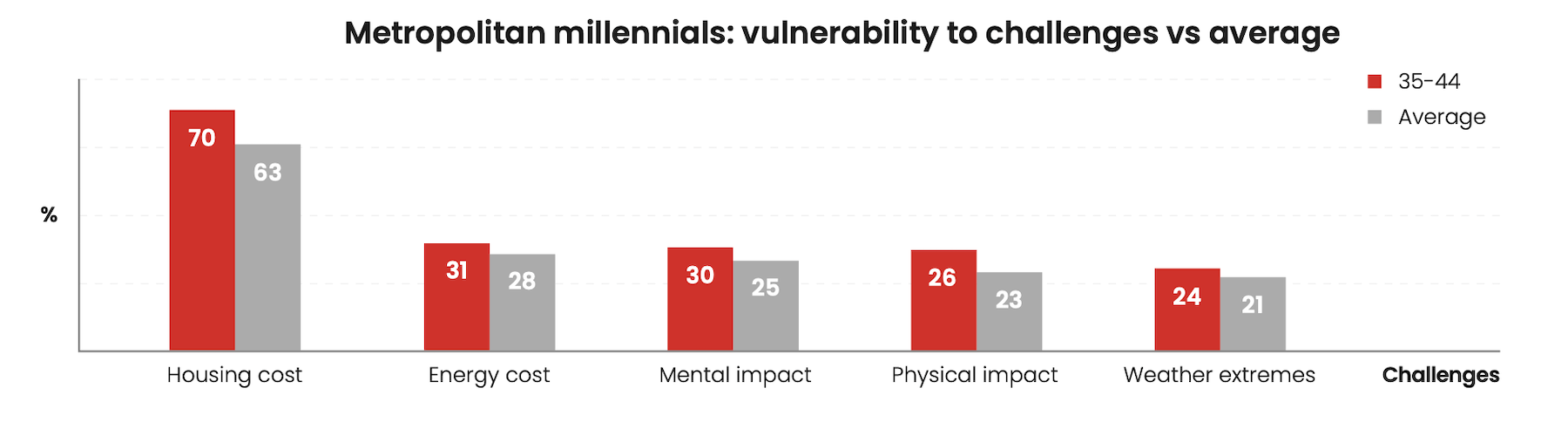 The report presents Millennials as the lifeblood of cities, but also as the age group most vulnerable to the pressures of urban living. Their biggest reason for leaving cities is rising housing costs. And if cities can’t hold onto their Millennial residents and attract new ones, those cities are likely to close schools, lose small businesses and entertainment venues, and see declines in the arts, healthcare, and open spaces.
The report presents Millennials as the lifeblood of cities, but also as the age group most vulnerable to the pressures of urban living. Their biggest reason for leaving cities is rising housing costs. And if cities can’t hold onto their Millennial residents and attract new ones, those cities are likely to close schools, lose small businesses and entertainment venues, and see declines in the arts, healthcare, and open spaces.
Cays said that architects can visualize urban design that supports families, provides schools and open spaces, and “incentivizes the protection and promotion of communities.”
Related Stories
Urban Planning | Dec 4, 2017
Can you spark an urban renaissance?
Thoughtful design, architecture, and planning can accelerate and even create an urban renaissance.
Urban Planning | Nov 20, 2017
Creating safer streets: Solutions for high-crash locations
While there has been an emphasis on improving safety along corridors, it is equally important to focus on identifying potential safety issues at intersections.
Urban Planning | Nov 16, 2017
Business groups present a new vision of Downtown Houston as that city’s unavoidable hub
The plan, which took 18 months to complete, emphasizes the centrality of downtown to the metro’s eight counties.
Architects | Oct 30, 2017
City 2050: What will your city look like in 2050?
What do we think the future will look like 30 years or so from now? And what will City: 2050 be like?
Great Solutions | Oct 17, 2017
Loop NYC would reclaim 24 miles of park space from Manhattan’s street grid
A new proposal leverages driverless cars to free up almost all of Manhattan’s Park Avenue and Broadway for pedestrian paths.
Mixed-Use | Aug 2, 2017
Redevelopment of Newark’s Bears Stadium site receives team of architects
Lotus Equity Group selected Michael Green Architecture, TEN Aquitectos, Practice for Architecture and Urbanism, and Minno & Wasko Architects and Planners to work on the project.
Urban Planning | Jul 21, 2017
Streets as storytellers: Defining places and connecting people
“In a city the street must be supreme. It is the first institution of the city. The street is a room by agreement, a community room, the walls of which belong to the donors, dedicated to the city for common use.” – Louis Kahn
Urban Planning | Jun 26, 2017
Convenience and community lead the suburban shift
As the demand for well-connected urban locales increases, so too has the cost of property and monthly rent; and as suburbs typically offer a bargain on both, more people are looking for a compromise.
Office Buildings | Jun 12, 2017
At 11.8 million-sf, LG Science Park is the largest new corporate research campus in the world
The project is currently 75% complete and on schedule to open in 2018.
Architects | May 26, 2017
Innovations in addressing homelessness
Parks departments and designers find new approaches to ameliorate homelessness.