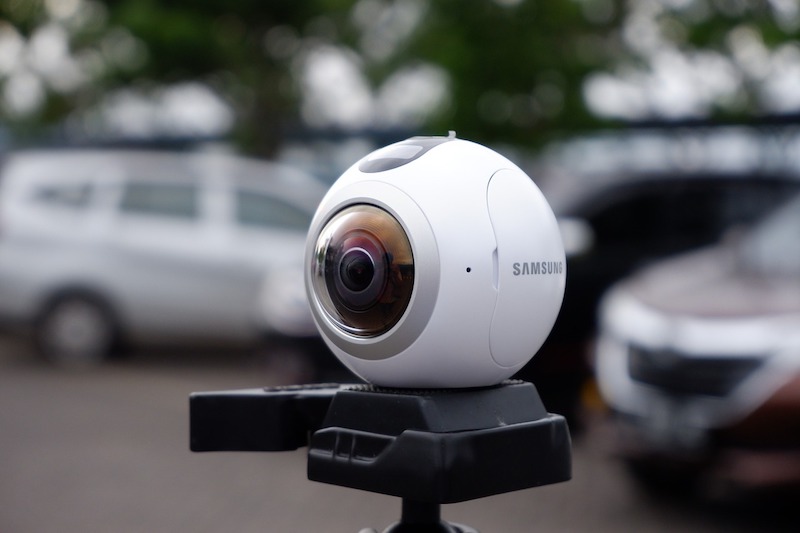
Stationary laser scanners continue to be the most popular building documentation hardware that AEC firms and service providers use for jobsite reality capture and photography. But 360° cameras are rapidly gaining ground on scanners, and unmanned aerial vehicles are steadily expanding their user base.
These are among the key findings in the latest Cornerstone report released by the U.S. Institute of Building Documentation, its first on the subject of hardware since 2013.
The report analyzes responses from a survey of 256 companies, of which 143 were Contractors and 27 were Surveyors. Project managers accounted for 108 of the respondents, and technology managers 59. One hundred and sixty-one companies polled have more than 500 employees, and 80% have been in business at least 20 years.
The report looks at the relative uses of five hardware groups.
Stationary laser scanners: More than three quarters of respondents use them, and most say they prefer to own, rather than rent, the equipment.
Most companies own at least two scanners, and 11 contractor respondents said they owned more than 10. On the other hand, most service providers and architecture firms reported owning only a single scanner.
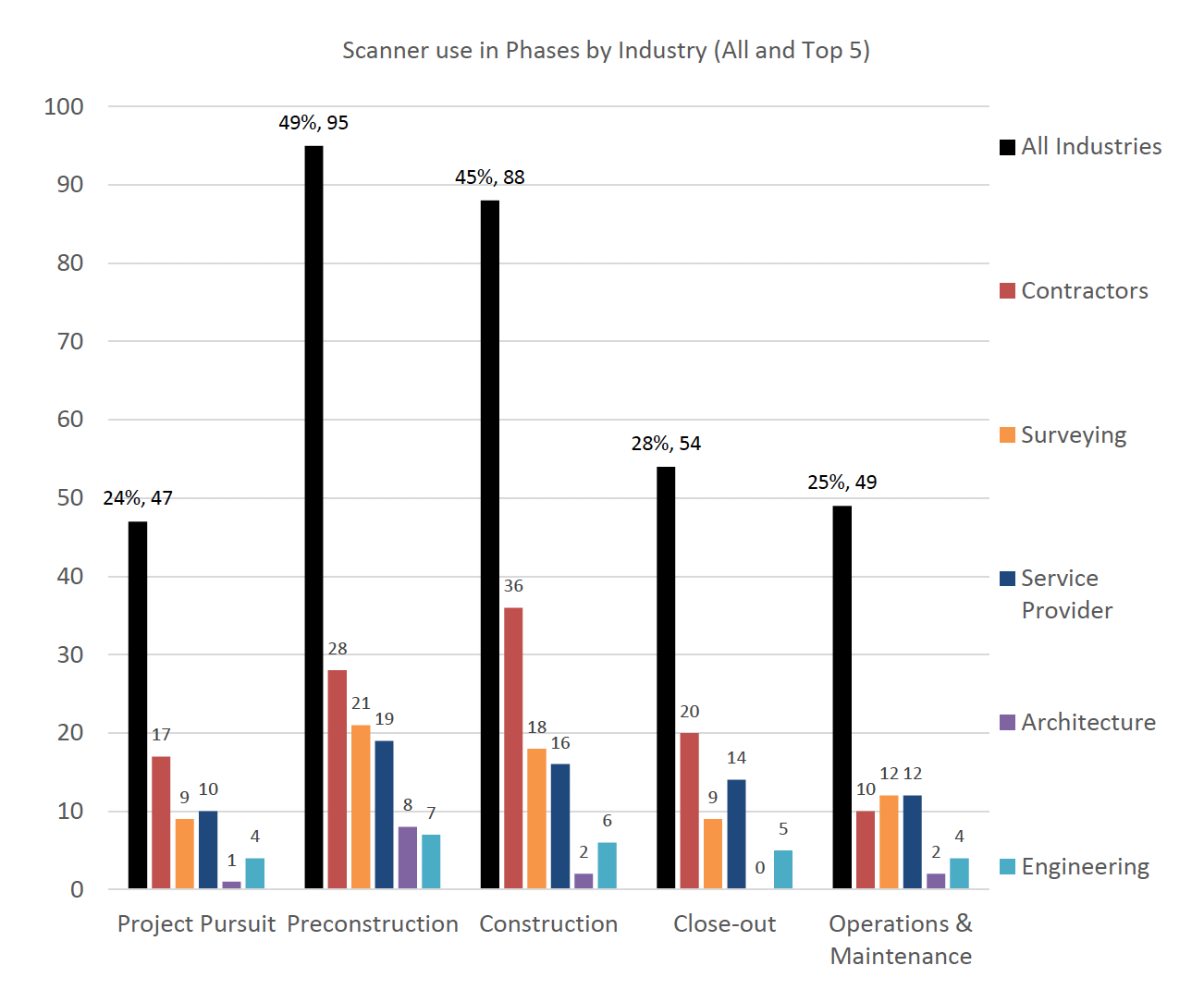
Stationary laser scanners are the most commonly used building documentation tools, particularly at the preconstruction and construction phases. (The numbers in the chart above indicate the respondents.) Image: U.S. Institute of Building Documentation.
Accuracy ranks highest as a criterion for renting or purchases stationary laser scanners, followed by range, size, and weight.
Stationary laser scanners are being deployed on all phases of construction projects, and most often in preconstruction and construction. “Heavier use by contractors in the construction phase is likely due to the relatively recent introductions of analysis and comparison software, which enable using reality capture data for advanced [quality assurance/quality control] of work in place,” the report states.
Architecture and Engineering firms use scanners most frequently during preconstruction design. But unlike architecture firms, engineering firms maintain usage throughout the remainder of the project.
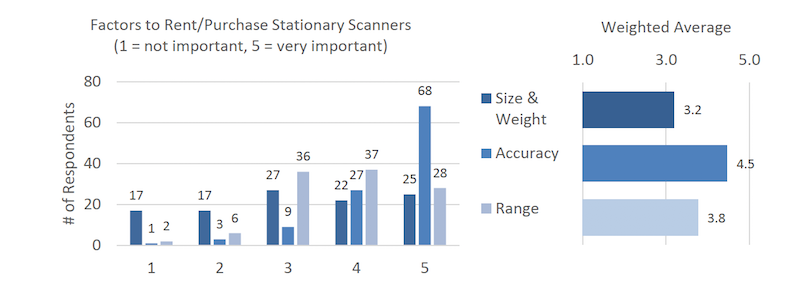
Accuracy is the most important measure when renting or purchasing a stationary laser scanner. Image: U.S. Institute of Building Documentation.
360° cameras: The report finds that 360° cameras are the second-most-used of the five hardware types, and represent a significant shift in the market over the last two years.
“While these devices existed when the last survey was put out, they played no significant role in our industry,” the report states. “Even three years ago, it would have been a novelty item in our survey.” U.S. Institute of Building Documentation predicts that 360° cameras will surpass stationary laser scanners as the most used documentation tool within the next year.
Three fifths of respondents use these cameras on their projects. One-quarter own three to five cameras, and 15% own more than 20, as large construction firms pursue enterprise implementation of the technology across multiple sites.
Forty percent of respondents upgrade their 360° cameras every one or two years, and owning them is the “clear choice,” the report finds. 360° cameras are delivering the strongest results for ROI of all the hardware devices; 87% of respondents filling out this section of the survey had already achieved their ROI on these products.
Image resolution was rated the most important factor for renting or purchasing 360° cameras, with lighting responsiveness close behind. Contractors also place a higher importance than any other group on 360° video capture.
Seventeen percent of respondents plan to add 360 photography services to their portfolios.
Mobile laser scanners: Mobile scanners aren’t nearly as popular as their stationary brethren. Less than one-quarter of respondents answered the survey’s question about mobile-scanner usage, and of these only 37% answered affirmatively. A majority of respondents either rents mobile scanners or owns only one. “This suggests that the actual usage of mobile scanning in those firms is infrequent,” the report infers.
Accuracy and speed are the most important factors when renting or purchasing a mobile laser scanner, but fewer than one-third of respondents thought that having the latest equipment was essential. These scanners’ most important attributes are RGB (red, blue, green) photo mapping and the ability to tie into survey controls.
Still, more than one-quarter (26%) of respondents said they intend to add mobile scanning services to their portfolios.
Unmanned aerial vehicles: Nearly 30% of the survey’s total respondents filled out this part of the questionnaire, and 49% of these use UAVs on their projects.
Just under two fifths of respondents own one or two drones, and a surprising 17% said they own more than 20. The report notes that most construction firms participating in the survey own more than 10 UAVs. Interestingly, few construction firms report owning three-to-five or five-to-10, “which suggests that once the value is proven on a few projects with one or two drones, these firms are rapidly adopting the technology across their projects,” the report observes.
 Drones are becoming more widely used to document jobsite activities, especially at the preconstruction phase. Image: Pixabay
Drones are becoming more widely used to document jobsite activities, especially at the preconstruction phase. Image: Pixabay
Respondents are using drones across all phases of their projects, though the heaviest use appears to be happening during preconstruction. Highly accurate geopositioning with RTK (real-time kinematic) or other GPS methods is very important to service providers, which also show a fairly strong preference towards customizable sensor packages.
Twenty-two percent of respondents intend to add UAVs to their service portfolios.
“It is exciting to see that UAVs have moved beyond the pursuit phase already and are providing value to the operational phases of respondents’ projects this early in the adoption curve,” the report states. Most respondents (67%) report a positive ROI on their investment in UAVs, with another 22% expecting to achieve sufficient ROI to justify the cost of the equipment. But respondents also feel that manufacturers need to do better in such areas as fail-safes and other safety features.
Fixed site cameras. Only one-third of the 57% of companies that responded to this part of the survey use fixed site cameras on jobsites. And most respondents prefer to rent these cameras rather than own them. Fixed site cameras are used primarily during the construction phase to track progress.
Related Stories
Concrete Technology | Apr 19, 2022
SGH’s Applied Science & Research Center achieves ISO 17025 accreditation for concrete testing procedures
Simpson Gumpertz & Heger’s (SGH) Applied Science & Research Center recently received ISO/IEC17025 accreditation from the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA) for several concrete testing methods.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Apr 19, 2022
Multi-story building systems and selection criteria
This course outlines the attributes, functions, benefits, limits, and acoustic qualities of composite deck slabs. It reviews the three primary types of composite systems that represent the full range of long-span composite floor systems and examines the criteria for their selection, design, and engineering.
Wood | Apr 13, 2022
Mass timber: Multifamily’s next big building system
Mass timber construction experts offer advice on how to use prefabricated wood systems to help you reach for the heights with your next apartment or condominium project.
AEC Tech | Apr 13, 2022
Morphosis designs EV charging station for automaker Genesis
LA-based design and architecture firm Morphosis has partnered with automotive luxury brand Genesis to bring their signature brand and styling, attention-to-detail, and seamless customer experience to the design of Electric Vehicle Charging (EVC) Stations.
AEC Tech | Apr 13, 2022
A robot automates elevator installation
Schindler—which manufactures and installs elevators, escalators, and moving walkways—has created a robot called R.I.S.E. (robotic installation system for elevators) to help install lifts in high-rise buildings.
Modular Building | Mar 31, 2022
Rick Murdock’s dream multifamily housing factory
Modular housing leader Rick Murdock had a vision: Why not use robotic systems to automate the production of affordable modular housing? Now that vision is a reality.
Building Technology | Feb 28, 2022
BIPV and solar technology is making its mark in the industry
Increasingly, building teams are comparing the use of building-integrated photovoltaic (BIPV) systems for façades, roofs, and other architectural assemblies with a promising and much easier alternative: conventional solar panel arrays, either on their building or off-site, to supplement their resiliency and decarbonization efforts
M/E/P Systems | Jan 27, 2022
Top 5 building HVAC system problems and how to fix them
When your HVAC system was new, it was designed to keep the indoor environment comfortable, functional, and safe. Over time, that system can drift out of alignment, leading to wasted resources, excessive energy consumption, and reduced occupant comfort.
Sponsored | Voice of the Brand | Jan 27, 2022
A Modern Approach to Labor in the Construction Industry
The COVID-19 pandemic disrupted and reshaped norms in the workforce and the ongoing labor shortage can be felt in every industry. Innovations to go faster, maintain safety, minimize learning curves, and drive down costs are becoming imperatives for companies to stay competitive in the construction industry.
Sponsored | Reconstruction & Renovation | Jan 25, 2022
Concrete buildings: Effective solutions for restorations and major repairs
Architectural concrete as we know it today was invented in the 19th century. It reached new heights in the U.S. after World War II when mid-century modernism was in vogue, following in the footsteps of a European aesthetic that expressed structure and permanent surfaces through this exposed material. Concrete was treated as a monolithic miracle, waterproof and structurally and visually versatile.
















