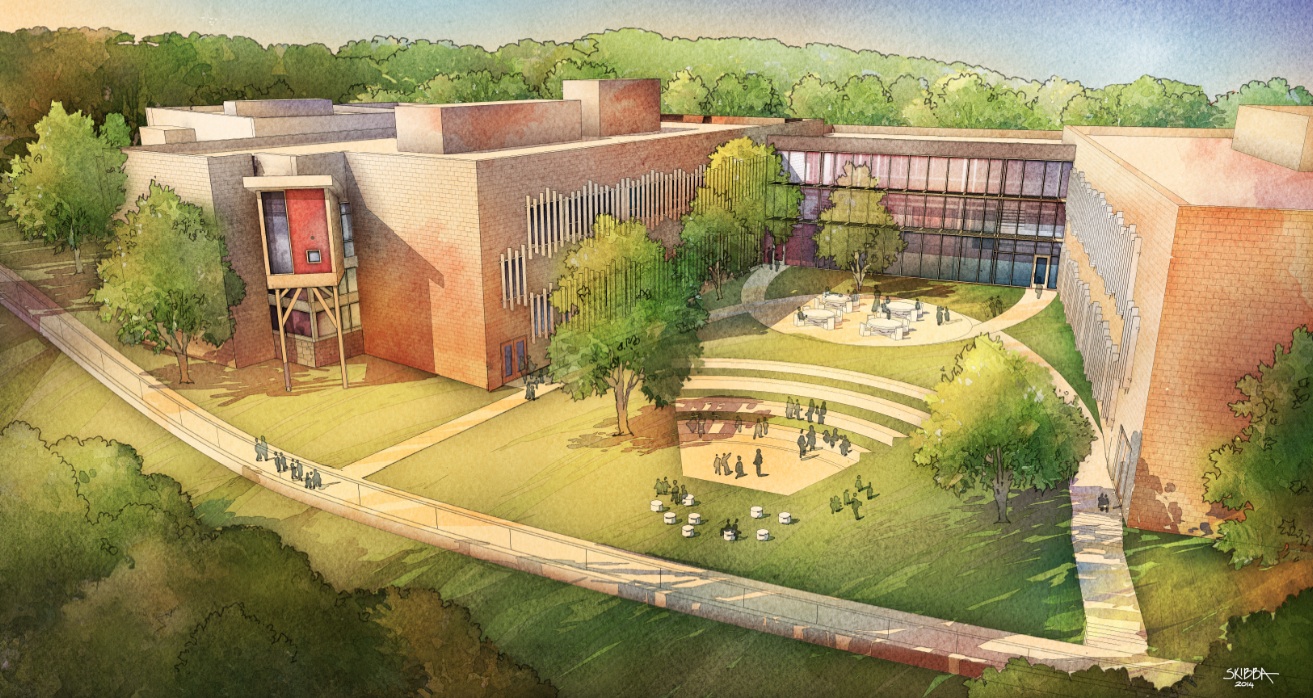
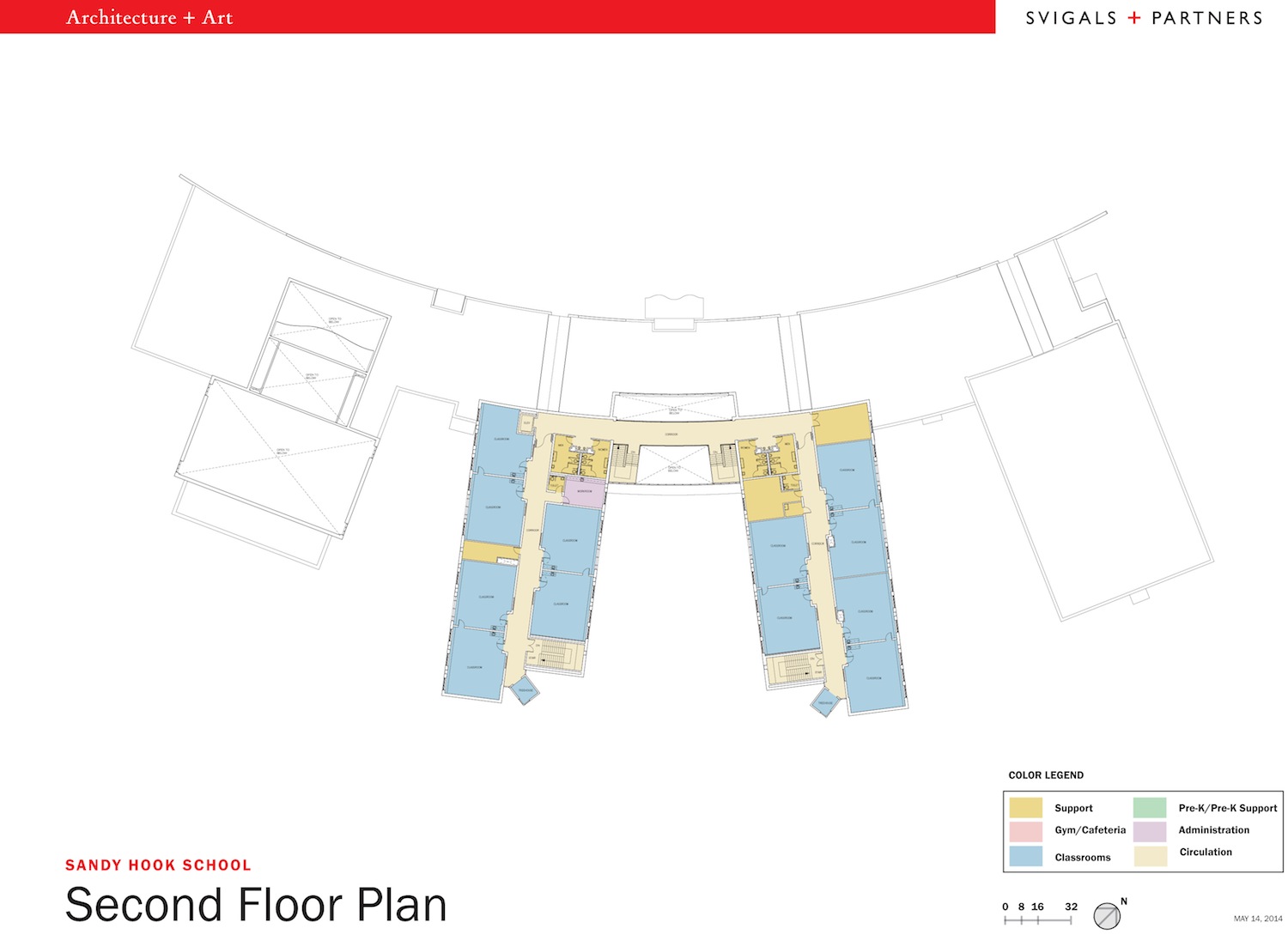
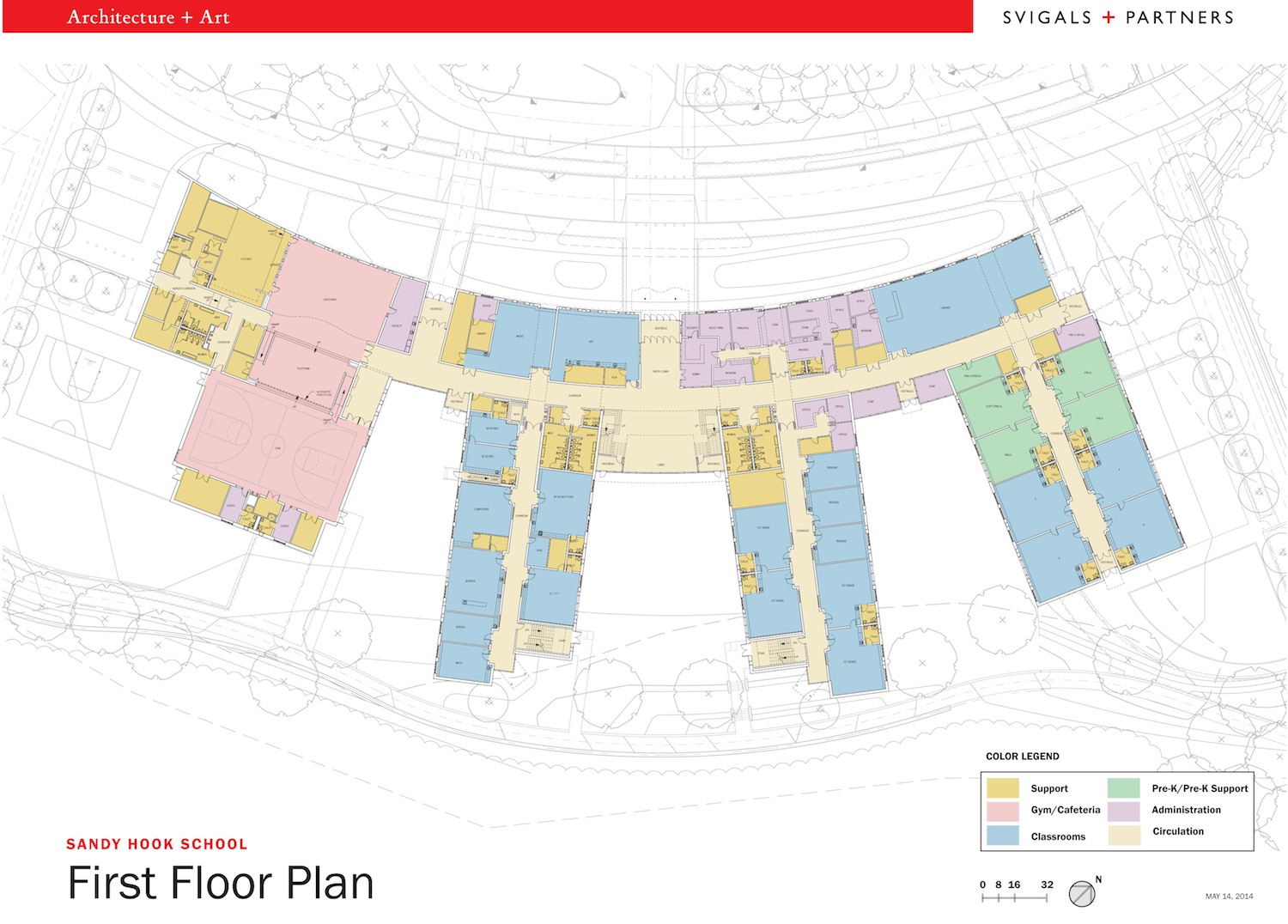
The design of the new Sandy Hook Elementary School on the site of the 2012 Newtown, Conn., school shooting features enhanced security measures—some subtle and others more prominent. Given the setting, this project is bound to get much attention and could influence school security standards on other projects.
Design firm Svigals + Partners used various measures to tighten security while avoiding heavy-handed features. The school is sited far back from the road and surrounding wooded areas, giving teachers and administrators more time to spot potential intruders. A rain garden spanning the school façade creates a buffer between the drop off point and school entrance.
Layered security doors and entry areas offer additional protection. Visitors must be screened through an intercom system before entering a security vestibule, where they will have to be checked in by school personnel.
A set of doors at each of the school wings can be automatically closed to block an intruder from reaching classroom areas. During a lockdown emergency, any doors that are propped open will be triggered electronically to swing shut. Classroom doors have dead bolts that automatically lock when closed, but release when a student or teacher needs to leave the room. The exterior features ample fenestration for daylighting and avoids a prison-like look.
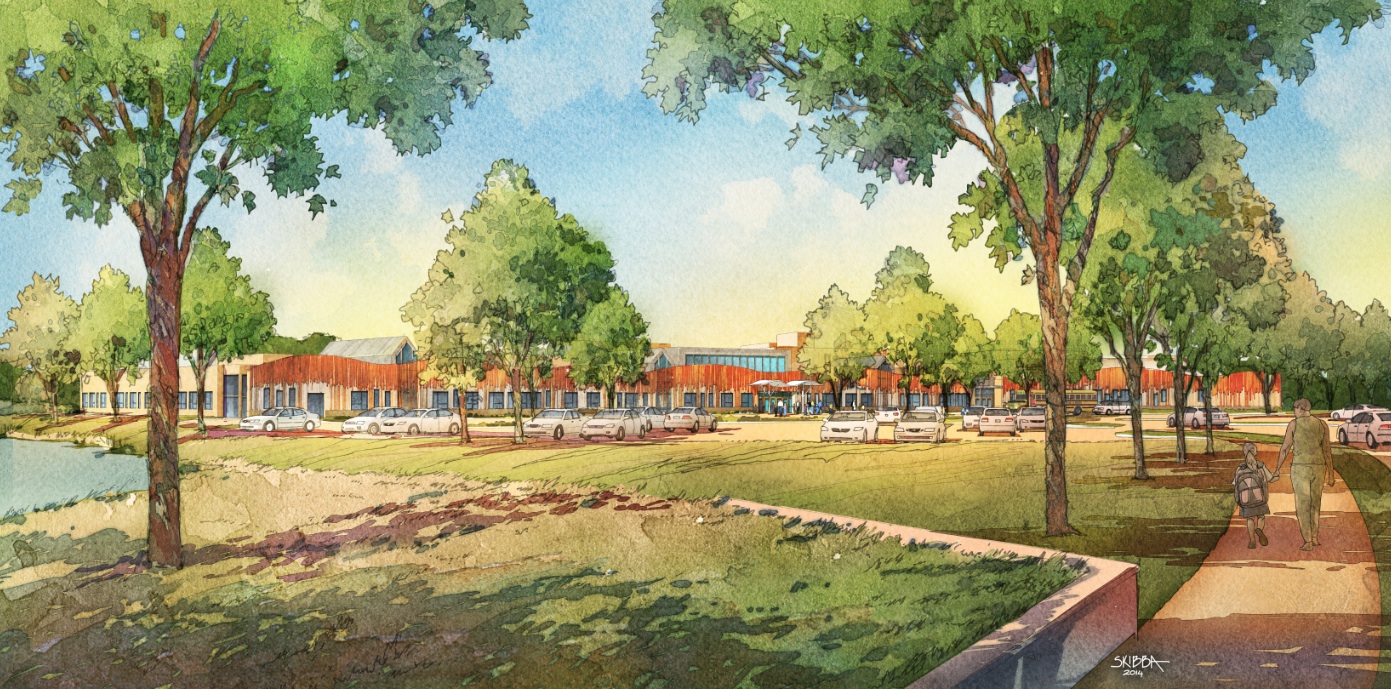

The re-design of Dickinson Drive brings traffic in at the very north and center of the site, allowing a clear panoramic view as you enter.
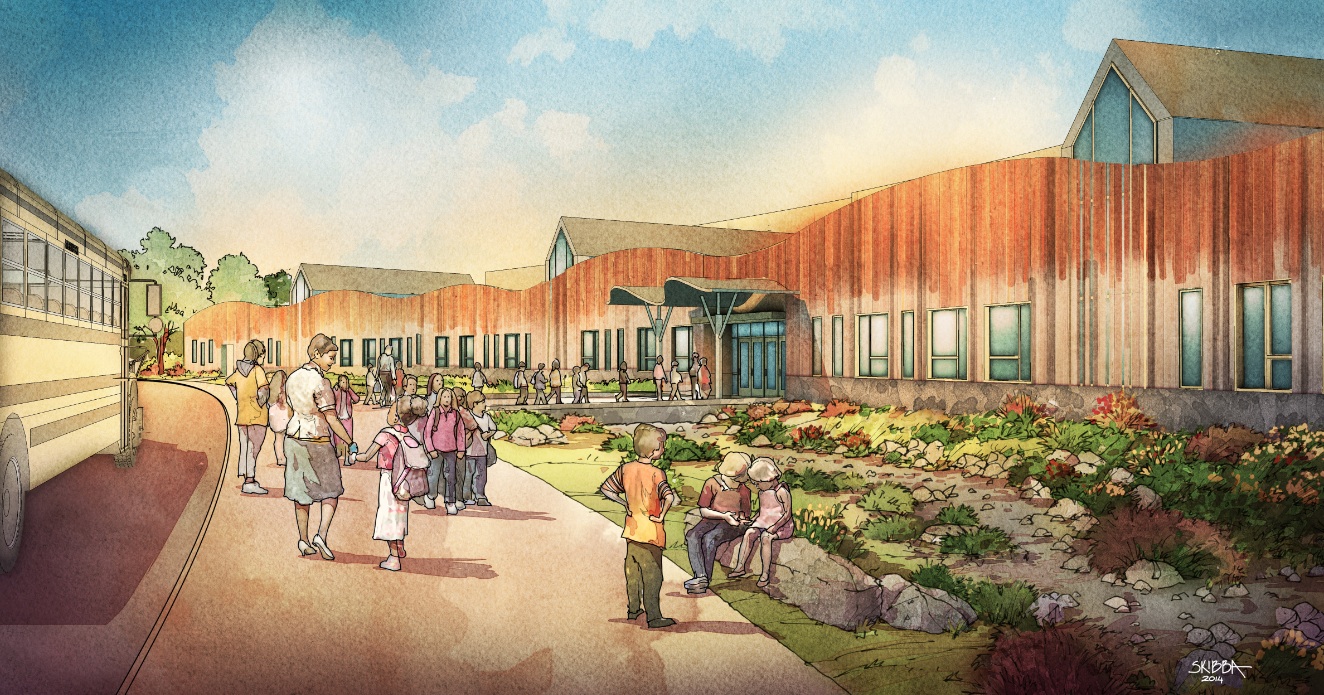

Several compelling themes surfaced amidst discussions of the qualities of Newtown and Sandy Hook. One was the view of the Town from a distance, buildings and spires appearing above an undulating horizon of trees. The other was how the geology of water courses created the “sandy hook” after which the area was named.
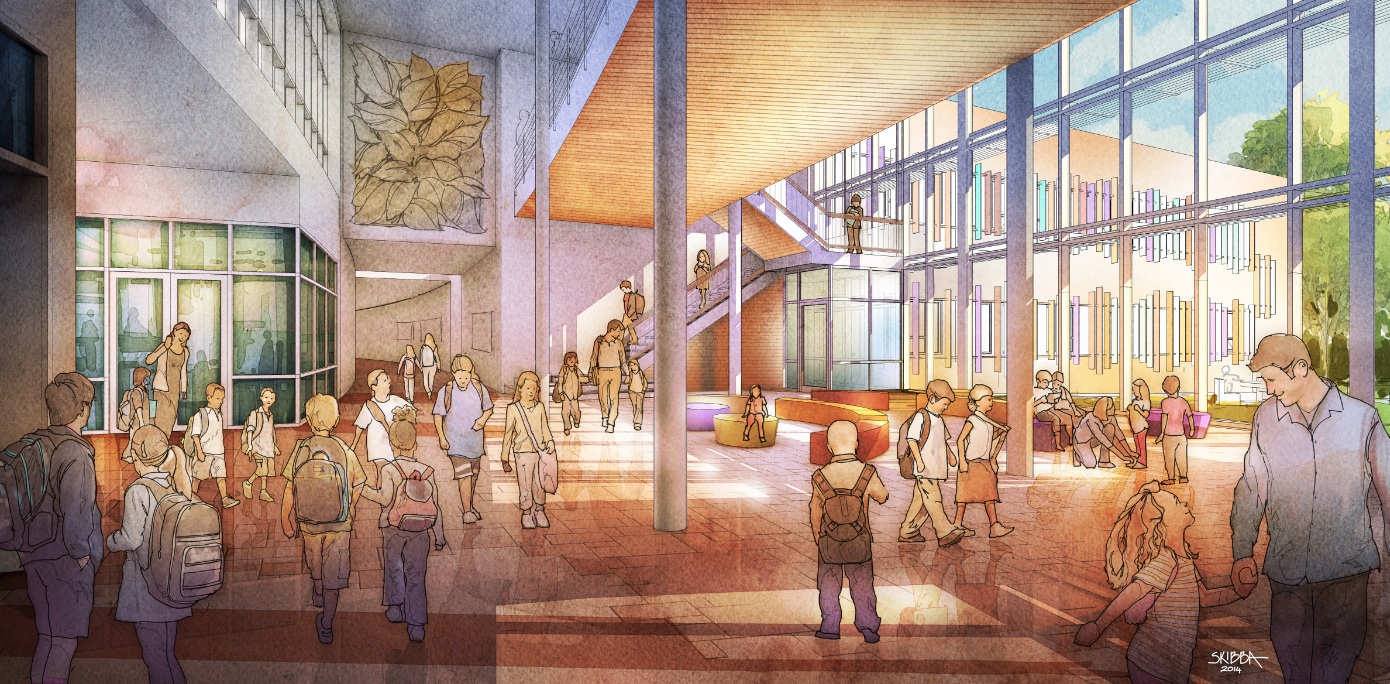
From the main central lobby, vistas of nature appear between the classroom wings connecting the inside and outside with tree-like columns. (More on the design.)
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Joint-Use Facilities Where Everybody Benefits
Shouldn’t major financial investments in new schools benefit both the students and the greater community? Conventional wisdom says yes, of course. That logic explains the growing interest in joint-use schools—innovative facilities designed with shared spaces that address the education needs of students and the community’s need for social, recreation, and civic spaces.
| Aug 11, 2010
Education's Big Upgrade
Forty-five percent of the country's elementary, middle, and high schools were built between 1950 and 1969 and will soon reach the end of their usefulness, according to the 2005–2008 K-12 School Market for Design & Construction Firms, published by ZweigWhite, a Massachusetts-based market-research firm.
| Aug 11, 2010
Burr Elementary School
In planning the Burr Elementary School in Fairfield, Conn., the school's building committee heeded the words of William Wordsworth: Come forth into the light of things, let nature be your teacher. They selected construction manager Turner Construction Company, New York, and the New York office of A/E firm Skidmore, Owings & Merrill to integrate nature on the heavily wooded 15.
| Aug 11, 2010
Bronze Award: Trenton Daylight/Twilight High School Trenton, N.J.
The story of the Trenton Daylight/Twilight High School is one of renewal and rebirth—both of the classic buildings that symbolize the city's past and the youth that represent its future. The $39 million, 101,000-sf urban infill project locates the high school—which serves recent dropouts and students who are at risk of dropping out—within three existing vacant buildings.
| Aug 11, 2010
New school designs don't go by the book
America needs more schools. Forty-five percent of the nation's elementary, middle, and high schools were built between 1950 and 1969, according market research firm ZweigWhite, Natick, Mass. Yet even as the stock of K-12 schools ages and declines, school enrollments continue to climb. The National Center for Education Statistics predicts that enrollment in public K-12 schools will keep rising...
| Aug 11, 2010
Bronze Award: Lincoln High School Tacoma, Wash.
Lincoln High School in Tacoma, Wash., was built in 1913 and spent nearly a century morphing into a patchwork of outdated and confusing additions. A few years ago, the Tacoma School District picked Lincoln High School, dubbed “Old Main,” to be the first high school in the district to be part of its newly launched Small Learning Communities program.
| Aug 11, 2010
Bronze Award: Hawthorne Elementary School, Elmhurst, Ill.
At 121 years, Hawthorne School is the oldest elementary school building in the Elmhurst, Ill., school district and a source of pride for the community. Unfortunately, decades of modifications and short-sighted planning had rendered it dysfunctional in terms of modern educational delivery. At the same time, increasing enrollment was leading to overcrowding, with the result that the library, for ...