Marking the beginning of a new era of transparency around energy use in buildings, New York City has publicly posted 2011 energy benchmarking results for 2,065 large commercial properties, which together cover more than 530 million square feet.
This is the first time that any U.S. city, state, or county has disclosed private-sector building energy data from a mandatory benchmarking policy.
The 2011 results are posted on the Greener, Greater Buildings Plan website, along with a letter giving a more detailed explanation of the output scores. The posting of benchmarking results will now be an annual occurrence for all large buildings in New York City. Results for large residential buildings will be posted for the first time in the fall of 2013, along with those for commercial and municipal buildings.
Energy use in buildings is responsible for roughly 75% of New York City’s emissions. The benchmarking, or measuring, and disclosure of energy use in buildings is the cornerstone of the city’s Greener, Greater Buildings Plan -- the most comprehensive policy in the nation addressing energy use in existing buildings -- and it is key to achieving the ambitious PlaNYC goal of reducing citywide carbon emissions 30 percent by 2030.
The benchmarking data can be used to assess where cost-effective building improvements can be made and to allow the market to find those opportunities. And since New York City’s benchmarking requirement is annual, the city and the market will be able to reward buildings that improve their performance year on year.
The benchmarking data also enabled the city to analyze for the first time how building energy use varies with building age, location, size, fuel mix, and an assortment of other factors.
Benchmarking data from 2010, released last month, showed that energy-use intensity varies dramatically among the same types of buildings, with the worst-performing buildings using three to five times the amount of energy per square foot as the best. Consequently, there is potential to save tremendous amounts of energy by improving the efficiency of the poor performers.
Under New York’s benchmarking ordinance, building owners annually enter energy and water use data and other pertinent information about their buildings, such as square footage and hours of operation, into the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) free online benchmarking tool, ENERGY STAR Portfolio Manager.
From this information, Portfolio Manager calculates the benchmarking results, including the energy and water use per square foot, the carbon emissions, and for some types of buildings, a 1-to-100 ENERGY STAR rating comparing the building’s relative energy performance with other similar buildings, normalized for building occupancy factors. The city’s posting includes these outputs.
However, even if all the input data were correct, the benchmarking results still require interpretation. There are many reasons why a building might have a high energy intensity. Sometimes that could be due to inefficient operations or outmoded equipment, but it also could be due to a high occupant density or longer hours of operation. High energy intensity does not always mean energy waste. +
Related Stories
Green | Apr 27, 2016
Top 10 green building projects for 2016
The Exploratorium at Pier 15 in San Francisco and the West Branch of the Berkeley Public Library are two of the projects recognized by AIA COTE as the top green buildings of 2016.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Apr 17, 2016
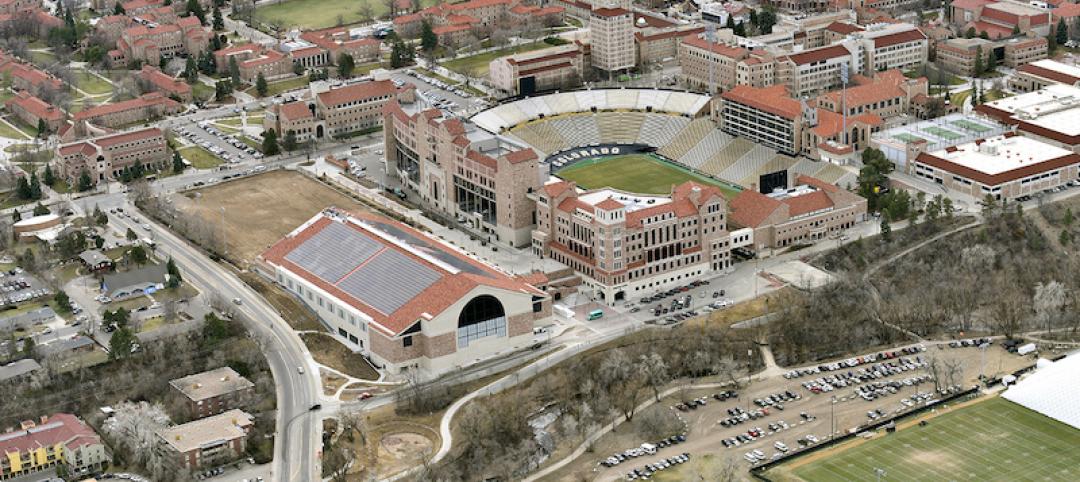
An expanded and renovated complex brings together U. of Colorado’s sports programs
This two-year project enhances the experiences of athletes and fans alike.
Building Technology | Apr 11, 2016
A nascent commercial wireless sensor market is poised to ascend in the next decade
Europe and Asia will propel that growth, according to a new report from Navigant.
Multifamily Housing | Mar 10, 2016
Access and energy control app clicks with student housing developers and managers
Ease of installation is one of StratIS’s selling features.
BIM and Information Technology | Mar 2, 2016
Thanks to MIT researchers, Boston now has its very own citywide building energy model
The most detailed model ever for a city this size will help Boston meet its long-term energy use goals.
Energy Efficiency | Feb 23, 2016
Economists, energy efficiency practitioners need to work together for better cost/benefit studies
Flawed energy efficiency research yields misleading, confusing results.
Green | Feb 18, 2016
Best laid plans: Masdar City’s dreams of being the first net-zero city may have disappeared
The $22 billion experiment, to this point, has produced less than stellar results.
Green | Feb 1, 2016
Supreme Court ruling on demand response expected to benefit smart grid
Ruling allows PV owners and other small energy generators to continue to be paid wholesale rates for power they generate.
Codes and Standards | Jan 22, 2016
State Savings Calculator analyzes savings associated with energy codes
The calculator breaks down the cost-effectiveness of energy codes on a state-by-state basis.
Green | Nov 17, 2015
DOE launches new data collaborative to help cities and states boost building efficiency
The SEED Standard will help manage, standardize, share performance data.