Global management consulting firm McKinsey recently launched the Net Zero Built Environment Council, a cross-sector coalition of industry stakeholders aiming to decarbonize the built world.
The council’s chief goal is to collaboratively create new pathways to cut greenhouse gas emissions from buildings.
The Council will support stakeholders to create and commercialize new green innovations, create global sustainability metrics and research, and promote cost-effective pathways to “decarbonizing everything from construction methods to materials,” according to McKinsey.
The council will work to align siloed supply chains, construction projects and markets, and help industry players tap into an estimated $800 billion to $1.9 trillion in potential green markets. The launch of the Net Zero Built Environment Council comes alongside the release of a new McKinsey report that identifies a lack of collaboration within the built environment ecosystem as a key obstacle to decarbonization.

McKinsey’s research found that 76% of emissions from an average building are caused by operations, demonstrating a need for collaborative decarbonization across the entire built environment life cycle, not just during construction.
The report found that half of all emissions across the built environment could be eliminated with little extra cost, while 20% will be more costly and complex to decarbonize, such as cement and steel, requiring more industry partnerships to reduce costs and risks for all new materials and technologies.
3 goals of the Net Zero Built Environment Council
To help facilitate the critical elements for change, we are launching the Net Zero Built Environment Council, which brings together many of the leading incumbents and new scale-ups across the built-environment ecosystem. Along the lines of the three ingredients covered in this article, the council’s ambitions can help with the following actions:
- Create transparency. Establish a fact-based perspective on a possible cost-effective recipe (translate the most powerful technology and other levers into a simplified playbook that applies to major building archetypes).
- Raise awareness of what is doable. Remove perceived barriers to decarbonization, capture the interest of decision makers, and spur “positive pressure” and acceleration to act.
- Stimulate partnerships and encourage initiative. Enable execution via innovative financial models, deployment of technologies, and scaling of efforts by bringing together stakeholders from across the built environment, whether by jointly commercializing technologies at scale or by identifying and creating lighthouse projects.
All contributors along the value chain must come together to overcome systematic challenges and increase transparency on cost-effective pathways to reach decarbonization goals and spread awareness to the entire sector. In this sense, the Net Zero Built Environment Council represents an important step forward in uniting industries and sectors—not only to achieve their climate ambitions but also to create green growth in the built environment.
Related Stories
Codes and Standards | Mar 29, 2015
Elevator shafts a major source of heat loss in New York City
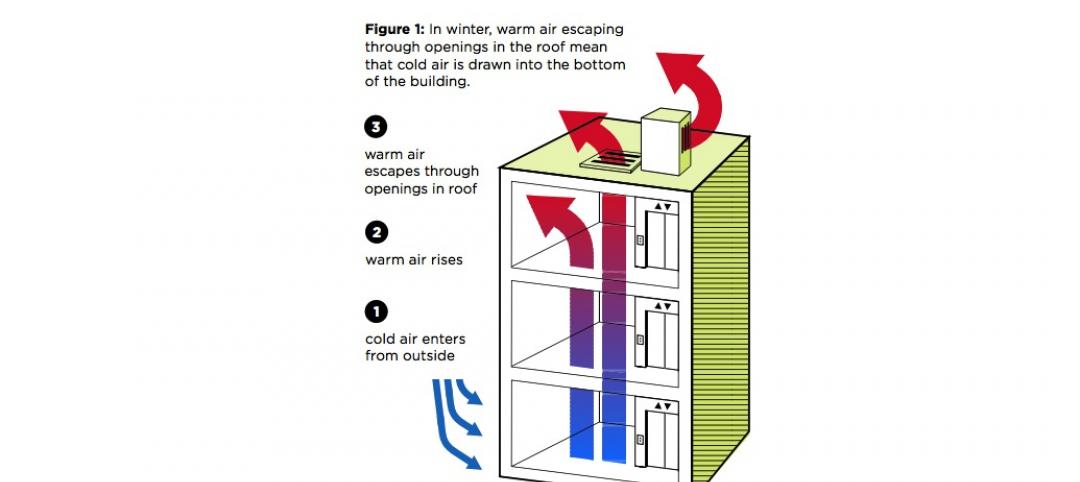
A typical New York apartment building loses thousands of dollars worth of energy every year from leaky elevator shafts that vent warm air at the top of the building and draw in cold air at the bottom, according to a new Urban Green Council report.
Green | Mar 29, 2015
Passive House Institute launches ‘cost-effective’ passive building standard
The group says the building energy performance target is in the “sweet spot” where cost effectiveness overlaps with aggressive energy and carbon reduction.
Sponsored | Walls and Partitions | Mar 25, 2015
Metl-Span systems meet design needs in cost effective manner
The goal from the beginning was to construct an energy efficient building with insulated metal panels.
Green | Mar 25, 2015
WELL Building Standard introduced in China
The WELL Building Standard is a performance-based system for measuring, certifying and monitoring features that impact human health and wellbeing, through air, water, nourishment, light, fitness, comfort, and mind.
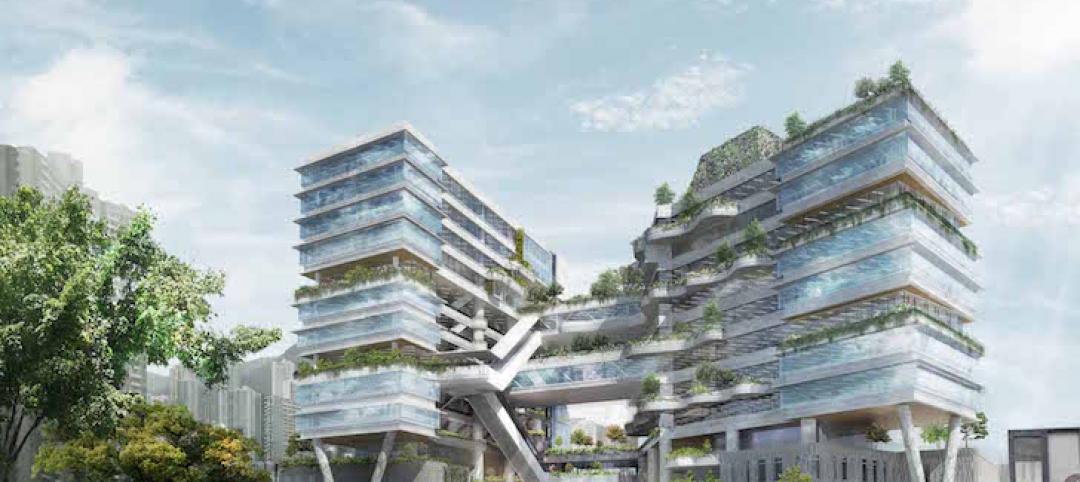
Higher Education | Mar 23, 2015
Hong Kong university building will feature bioclimatic façade
The project's twin-tower design opens the campus up to the neighboring public green space, while maximizing the use of summer winds for natural ventilation.
Green | Mar 22, 2015
6 myths holding back green building
Sustainable design has proven benefits, so why isn’t it more widely adopted?
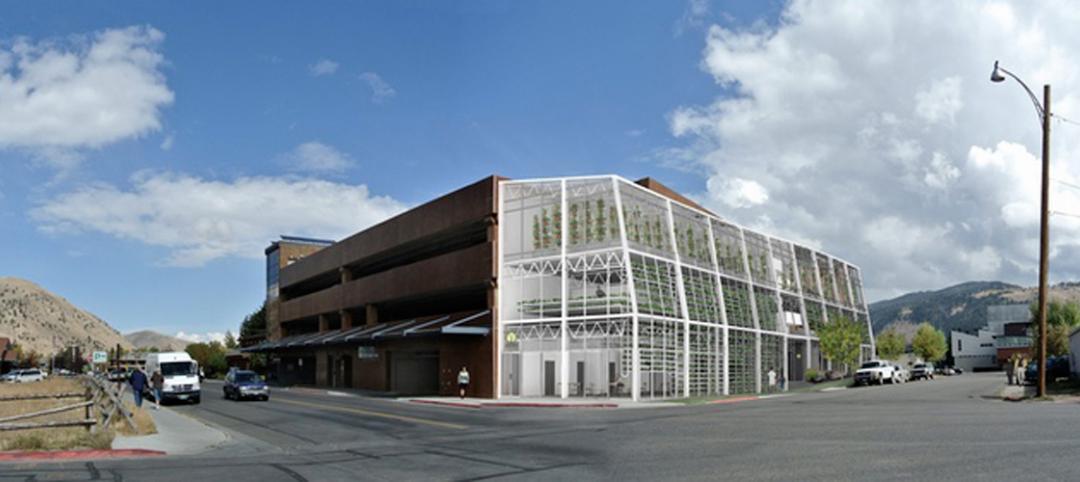
Green | Mar 18, 2015
Vertical urban greenhouses will feed import-reliant Jackson Hole, Wyo.
A Jackson Hole, Wyo., start up aims to reduce the city’s susceptibility to food deficits by building vertical greenhouses.
Sponsored | Energy Efficiency | Mar 16, 2015
California cuts its carbon footprint with solar
Spanning four locations in Central Valley, the California Renewable Energy Small Tariff projects pack a lot of power and are prime examples of the real-life benefits of going solar.
Codes and Standards | Mar 12, 2015
Energy Trust of Oregon offers financial incentives for net-zero buildings
The organization is offering technical assistance along with financial benefits.
Codes and Standards | Mar 5, 2015
AEC industry groups look to harmonize green building standards, codes
The USGBC, ASHRAE, ICC, IES, and AIA are collaborating on a single green code.