The construction and design industries are witnessing a significant shift towards energy-efficient spaces, driven by more stringent building energy codes, increased initiatives and legislation focused on reducing carbon in materials used for building projects and a growing public interest in environmental impact.
While energy efficiency and operational carbon are significant factors in environmentally conscious construction, it’s important to underscore the importance of embodied carbon emissions, which continue to gain traction as a major focus in today’s sustainable design landscape. Architects are increasingly opting for products with low embodied carbon, a term that refers to emissions caused by the manufacturing and installation of construction materials. When assessing the embodied carbon in building products, including glass, the industry standard metric is Global Warming Potential (GWP), measured in kilograms of equivalent carbon dioxide per metric ton (CO2-eq). GWP is used to evaluate the environmental impact of a product's life cycle.
Previously, there was no standard for “low embodied carbon” (LEC) building products; however, there is now. The U.S. Federal Government’s Federal Buy Clean Initiative was established to promote using and developing low-carbon, made-in-America construction materials. In establishing best practices for the U.S. building products industry, standards for LEC products were set by the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) under the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 and related guidance from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. By these standards, LEC products can fall into three different product categories according to embodied carbon content: Top 20%, Top 40%, and exceeds the industry average.
As the market shifts towards eco-friendly spaces that increase energy efficiency and lower carbon emissions that promote occupant health and well-being, the availability of high-performance architectural glass configurations that significantly boost thermal capabilities and reduce the building's carbon footprint is also on the rise.
Measuring Energy Performance
When assessing the energy efficiency of glass, the U-value, also known as the U-factor, stands out as one of the most critical performance indicators. This metric is a pivotal indicator of the insulating properties of the glass, or in simpler terms, it gauges the amount of heat flow or heat loss that occurs through the glass due to the temperature difference between the interior and exterior. U-values typically span from 0.1 to 1.0. The lower the U-value, the more efficient the insulation. The U-value of a window is determined by the number of British thermal units (Btus) that traverse each square foot of area per degree of temperature difference from one side of the window to the other.
Alongside U-value, R-value is another important metric in thermal performance. U-value is used to measure the performance assemblies of insulating glass units (IGUs), while R-value is used to measure the capabilities of most other parts of the building envelope, such as walls, floors, and roofs. These two values are mathematical reciprocals of each other. Lower U-values indicate better insulating performance, whereas higher R-values indicate better thermal resistance.
More Options than Ever to Enhance U-value
Thanks to the advent of low-emissivity (low-e) coatings and technologies for IGUs, architects now have diverse options to enhance U-values wherever enhanced thermal performance is needed. These cutting-edge choices can enhance thermal potential by two or even three times, leading to substantial annual energy savings and surpassing sustainable design objectives for reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
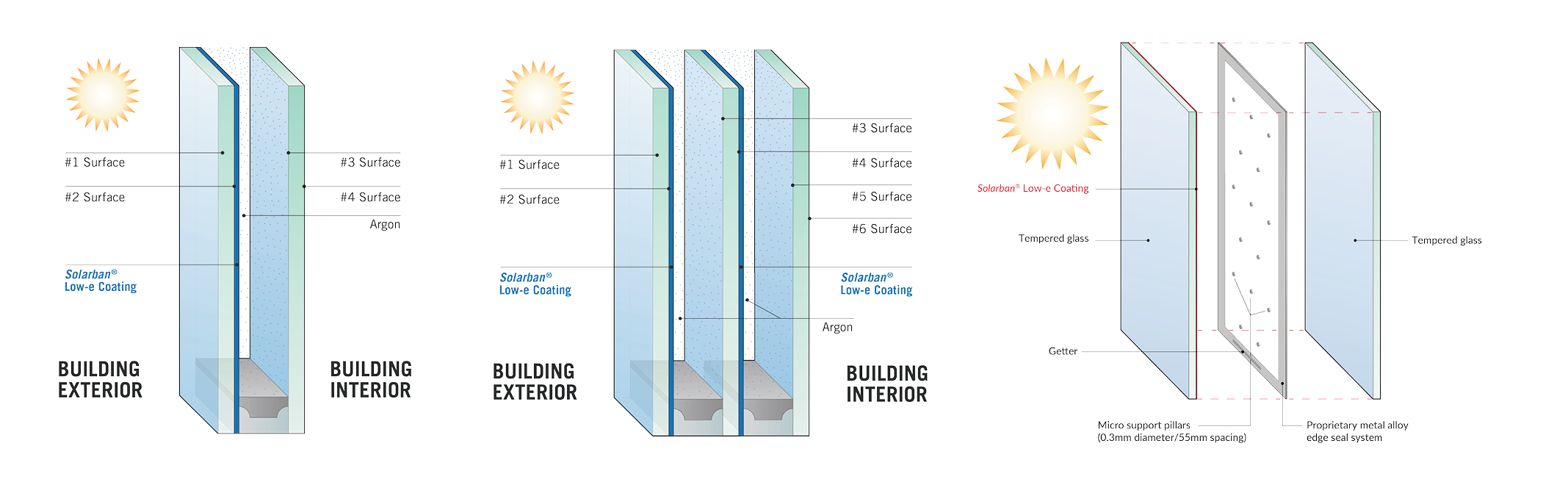
Along with traditional methods to improve U-values, such as using low-e coatings and dual- or triple-pane IGUs with argon gas or warm-edge spacers, new technologies like fourth-surface low-e coatings and vacuum insulating glass (VIG) are transforming the thermal capacity of buildings, offering exceptional improvements in durability and insulation without changing the visual characteristics of the IGU.
Fourth-Surface Low-e Coatings
Fourth-surface low-e coatings are designed to be used on the inside surface of an IGU, and when combined with solar control low-e glass on the second surface, they can significantly improve U-values while still allowing a high rate of visible light transmittance (VLT). These coatings effectively retain indoor temperatures by slowing heat transfer through the IGU. This can help reduce summer cooling costs and winter heating costs, resulting in up to a 20% improvement in the U-value compared to using solar control low-e glass alone on the second surface.
Vacuum Insulating Glass (VIG)
VIG is an innovative high-performance glass that utilizes vacuum technology and a low-e coating in an IGU to provide exceptional thermal capabilities comparable to traditional walls. VIG units typically can be used on their own to replace single-pane glass without replacing the framing system, or they can be used as a substitute for the interior lite in a dual-paned IGU, forming a hybrid IGU. VIG units with a low-e coating can have R-values up to R-20, offering thermal capabilities five times better than conventional insulating glass and up to 20 times better than monolithic glass. They can be incorporated into virtually any traditional glazing system, window frame or curtain wall application.
Advanced Technologies Substantially Improve Thermal Performance
Below is a chart of U-value comparisons for various glass configurations calculated using a baseline of a Dual-Pane Low-e 1” IGU Solarban® 70 (2) Clear + Clear with argon from Vitro Architectural Glass, with a U-value of 0.24. Based on these configurations, the overall thermal performance of a building can be improved by up to 79%. If expressed as R-values, the percentage of improvement would be even more substantial.
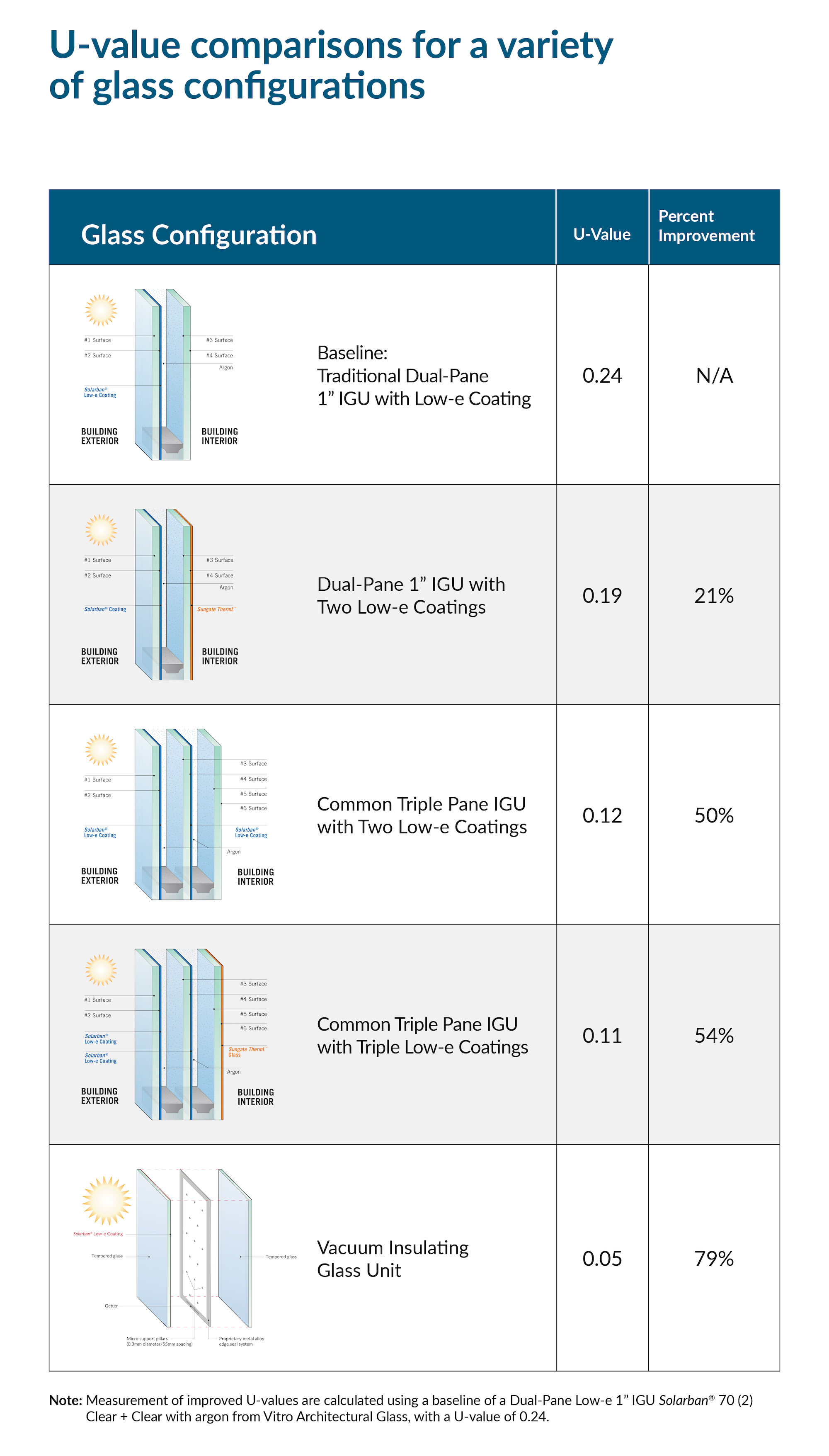
Building on the improvements that dual- and triple-pane IGUs have offered for decades, advancements in energy-efficient technologies, such as fourth-surface low-e coatings and VIG, represent the next generation of thermal glazings. These new high-performance IGUs significantly improve thermal insulation capabilities, energy savings and the overall sustainability of the building.
As building code standards demand more energy-efficient products in the future, U-value-optimized IGUs will play a major role in new construction or renovations as they ensure compliance with building energy codes, exceed sustainable design goals and leave a positive environmental impact.
About the Author
Emily Losego is the Director of Commercial Segment Innovation for Vitro Architectural Glass. She works with Vitro’s Marketing & Innovation Team to bring new glass product ideas from the drawing board to the production line. A former practicing architect, national architectural manager and magnetron sputter vacuum deposition (MSVD) product manager for Vitro, Losego is responsible for defining the vision for the architectural commercial market.
Related Stories
Industry Research | Jan 31, 2024
ASID identifies 11 design trends coming in 2024
The Trends Outlook Report by the American Society of Interior Designers (ASID) is the first of a three-part outlook series on interior design. This design trends report demonstrates the importance of connection and authenticity.
Products and Materials | Jan 31, 2024
Top building products for January 2024
BD+C Editors break down January's top 15 building products, from SloanStone Quartz Molded Sinks to InvisiWrap SA housewrap.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Jan 17, 2024
Waterproofing deep foundations for new construction
This continuing education course, by Walter P Moore's Amos Chan, P.E., BECxP, CxA+BE, covers design considerations for below-grade waterproofing for new construction, the types of below-grade systems available, and specific concerns associated with waterproofing deep foundations.
Sponsored | Performing Arts Centers | Jan 17, 2024
Performance-based facilities for performing arts boost the bottom line
A look at design trends for “budget-wise” performing arts facilities reveals ways in which well-planned and well-built facilities help performers and audiences get the most out of the arts. This continuing education course is worth 1.0 AIA learning unit.
Concrete | Jan 12, 2024
Sustainable concrete reduces carbon emissions by at least 30%
Designed by Holcim, a building materials supplier, ECOPact offers a sustainable concrete alternative that not only meets, but exceeds the properties of standard concrete.
Mass Timber | Jan 2, 2024
5 ways mass timber will reshape the design of life sciences facilities
Here are five reasons why it has become increasingly evident that mass timber is ready to shape the future of laboratory spaces.
75 Top Building Products | Dec 13, 2023
75 top building products for 2023
From a bladeless rooftop wind energy system, to a troffer light fixture with built-in continuous visible light disinfection, innovation is plentiful in Building Design+Construction's annual 75 Top Products report.
Products and Materials | Oct 31, 2023
Top building products for October 2023
BD+C Editors break down 15 of the top building products this month, from structural round timber to air handling units.
Building Materials | Oct 19, 2023
New white papers offer best choices in drywall, flooring, and insulation for embodied carbon and health impacts
“Embodied Carbon and Material Health in Insulation” and “Embodied Carbon and Material Health in Gypsum Drywall and Flooring,” by architecture and design firm Perkins&Will in partnership with the Healthy Building Network, advise on how to select the best low-carbon products with the least impact on human health.
Engineers | Oct 12, 2023
Building science: Considering steel sheet piles for semi-permanent or permanent subsurface water control for below-grade building spaces
For projects that do not include moisture-sensitive below-grade spaces, project teams sometimes rely on sheet piles alone for reduction of subsurface water. Experts from Simpson Gumpertz & Heger explore this sheet pile “water management wall” approach.