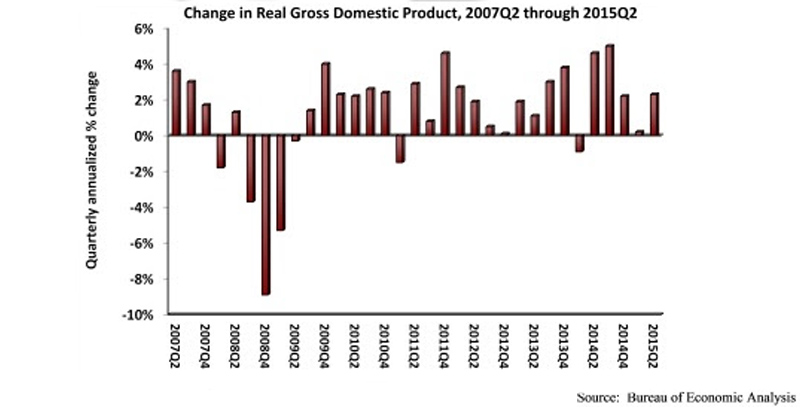
Nonresidential fixed investment fell by 0.6% during the second quarter after expanding by 1.6% during the first quarter, according to the July 30 real gross domestic product (GDP) report by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
For the economy as a whole, real GDP expanded by 2.3% (seasonally adjusted annual rate) during the second quarter following a 0.6% increase during the year's first quarter. Note that the first quarter estimate for nonresidential fixed investment was revised upward from -3.4% annualized growth.
"In the first half of 2015, both the broader economy and nonresidential investment lost the momentum they had coming into the year," said Associated Builders and Contractors Chief Economist Anirban Basu. "Rather than indicating renewed progress in terms of achieving a more robust recovery, today's GDP release indicates that a variety of factors helped to stall investment in nonresidential structures. There are many viable explanations, including a weaker overall U.S. economy, a stronger U.S. dollar, decreased investment in structures related to the nation's energy sector, soft public spending, and uncertainty regarding monetary policy and other abstracts of public policy. While the expectation is that the second half of the year will be better, unfortunately not much momentum is being delivered by the year's initial six months.
"Perhaps the most salient facet of this GDP release was the revisions," said Basu. "The BEA revised the first quarter estimate upward from -0.2% to 0.6% annualized growth. This is not surprising; many economists insisted that the economy did not shrink in the first quarter. However, the BEA also downwardly revised growth figures from the fourth quarter of 2011 to the fourth quarter of 2014. Over that period, GDP increased at an average annual rate of 2.1%, 0.3 percentage points lower than previously thought. These revisions could be a function of the agency's ongoing effort to tackle residual seasonality, a pattern in which seasonal adjustments led to repeated first quarter slowdowns. It will take a few more quarters to understand the full impact of the improved seasonal adjustments."
Performance of key segments during the first quarter:
- Investment in nonresidential structures decreased at a 1.6% rate after decreasing at a 7.4% rate in the first quarter.
- Personal consumption expenditures added 1.99% to GDP after contributing 1.19% in the first quarter.
- Spending on goods grew 1.1% from the first quarter.
- Real final sales of domestically produced output – minus changes in private inventories – increased 2.5% for the second quarter after a 2.5% increase in the first quarter.
- Federal government spending decreased 1.1% in the second quarter after increasing by 1.1% in the first quarter.
- Nondefense spending decreased 0.5% after expanding by 1.2% in the previous quarter.
- National defense spending fell 1.5% after growing 1% in the first quarter.
- State and local government spending grew 2% during the second quarter after a decrease of 0.8% in the first.
To view the previous GDP report, click here.
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
Addition provides new school for pre-K and special-needs kids outside Chicago
Perkins+Will, Chicago, designed the Early Learning Center, a $9 million, 37,000-sf addition to Barrington Middle School in Barrington, Ill., to create an easily accessible and safe learning environment for pre-kindergarten and special-needs students.
| May 18, 2011
Raphael Viñoly’s serpentine-shaped building snakes up San Francisco hillside
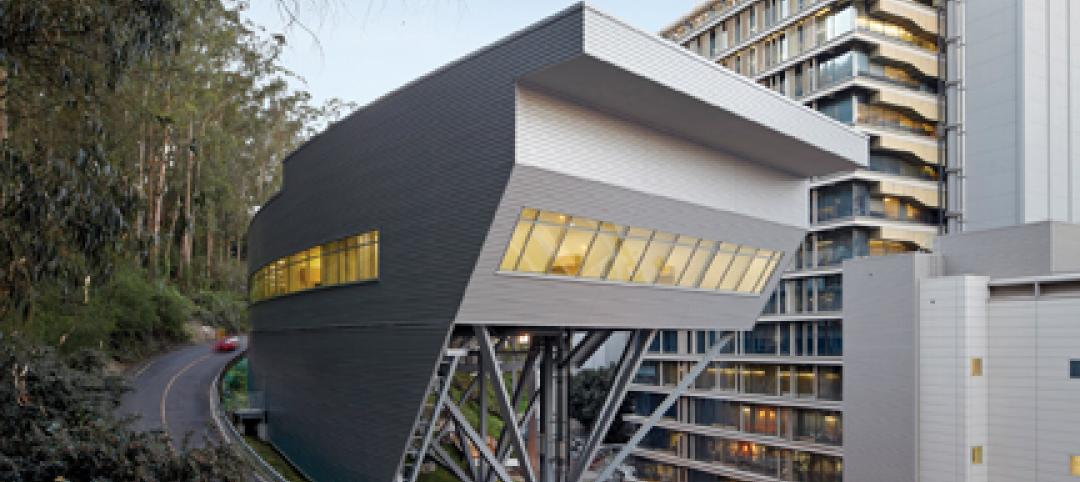
The hillside location for the Ray and Dagmar Dolby Regeneration Medicine building at the University of California, San Francisco, presented a challenge to the Building Team of Raphael Viñoly, SmithGroup, DPR Construction, and Forell/Elsesser Engineers. The 660-foot-long serpentine-shaped building sits on a structural framework 40 to 70 feet off the ground to accommodate the hillside’s steep 60-degree slope.
| May 18, 2011
New center provides home to medical specialties
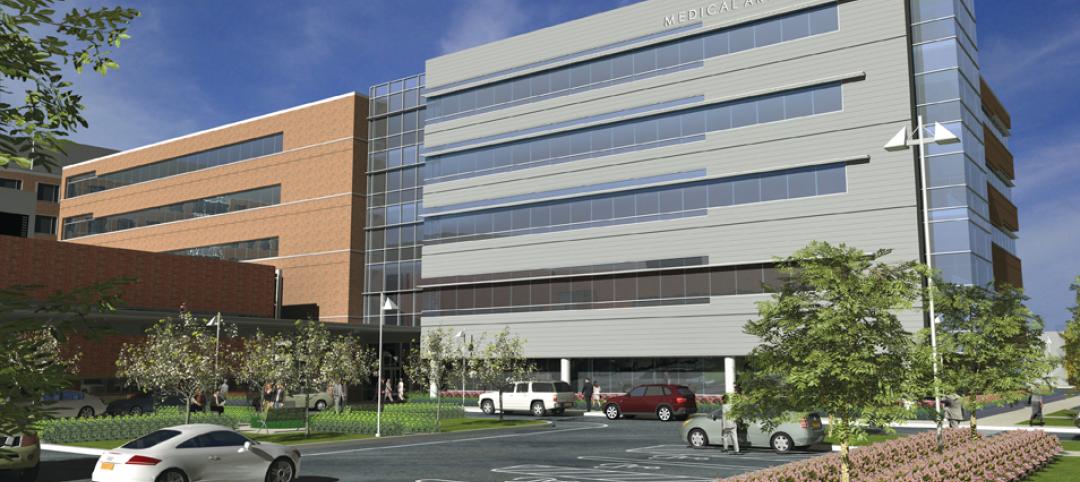
Construction has begun on the 150,000-sf Medical Arts Pavilion at the University Medical Center in Princeton, N.J.
| May 18, 2011
Improvements add to Detroit convention center’s appeal
Interior and exterior renovations and updates will make the Detroit Cobo Center more appealing to conventioneers. A new 40,000-sf ballroom will take advantage of the center’s riverfront location, with views of the river and downtown.
| May 18, 2011
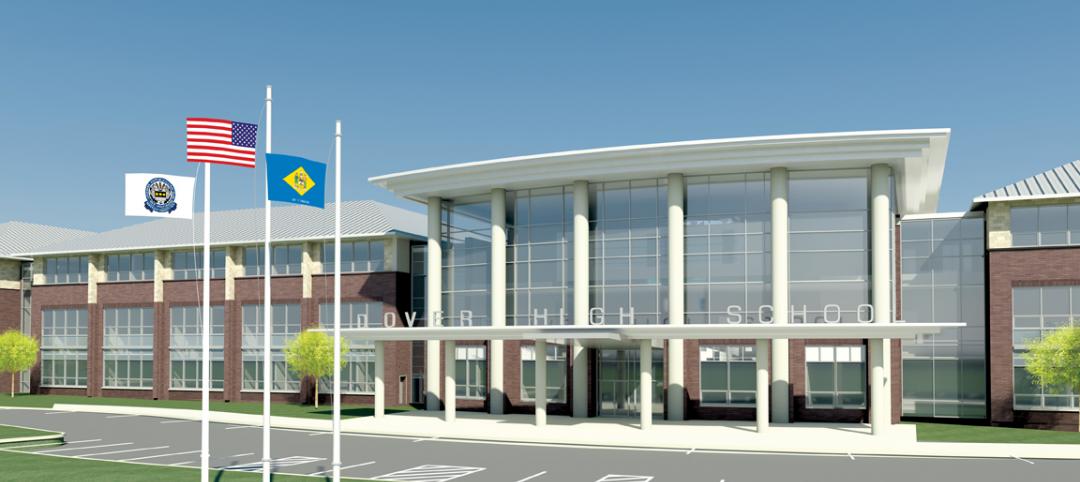
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 18, 2011
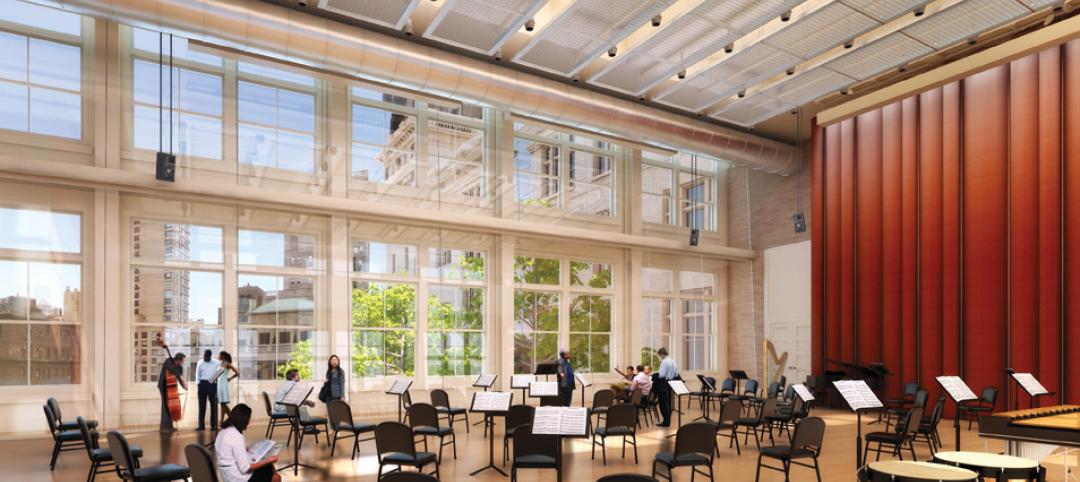
Carnegie Hall vaults into the 21st century with a $200 million renovation
Historic Carnegie Hall in New York City is in the midst of a major $200 million renovation that will bring the building up to contemporary standards, increase educational and backstage space, and target LEED Silver.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 17, 2011
Gilbane partners with Steel Orca on ultra-green data center
Gilbane, along with Crabtree, Rohrbaugh & Associates, has been selected to partner with Steel Orca to design and build a 300,000-sf data center in Bucks County, Pa., that will be powered entirely through renewable energy sources--gas, solar, fuel cells, wind and geo-thermal. Completion is scheduled for 2013.
| May 17, 2011
Should Washington, D.C., allow taller buildings?
Suggestions are being made that Washington revise its restrictions on building heights. Architect Roger Lewis, who raised the topic in the Washington Post a few weeks ago, argues for a modest relaxation of the height limits, and thinks that concerns about ruining the city’s aesthetics are unfounded.