In late January, CARsgen Therapeutics, a biopharmaceutical company with operations in China and the U.S., started moving employees into a biomanufacturing facility in Durham, N.C., the company’s first such operations in North America.
CARsgen has clinical offices in Houston, and its holding company was founded in Shanghai in 2014. It is investing $157 million for the North Carolina campus, which is expected to eventually house 200 workers by 2026. That campus is being developed in two phases: the first (which opened officially on February 21) is a 37,000-sf research and development lab for early-stage manufacturing of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies that battle cancers. Upon FDA approval of those therapies, CARsgen will start construction on a 100,000-sf cGMP commercial manufacturing plant.
Jie Jia, PhD, CARsgen’s Vice President of Strategic Alliances and Operations, is hopeful that the factory can be started by late 2022.
This project is but the latest example of demand-driven construction of lab space. The Raleigh-Durham market is a hot bed for companies developing CAR-T therapies that use patient-derived T cells that are customized in the manufacturing process for each patient.
Jie tells BD+C that his company selected North Carolina’s Research Triangle for its campus because of its “local ecosystem” that, according to the North Carolina Biotechnology Center’s website, includes three comprehensive cancer centers—UNC Lineberger, Duke Cancer Institute, and Wake Forest Baptist Health—as well as the NC Rare Disease Network and the North Carolina Precision Health Collaborative.
CARsgen reportedly considered locating its facility in Maryland, which offered $35 million in incentives, but ultimately chose North Carolina, which offered a $2.2 million grant and tax reimbursement package over 12 years, according to the state’s Economic Development Partnership, which with NCBioTech and North Carolina’s Department of Commerce recruited the company.
Helping CARsgen with site selection was CRB, an AEC and consulting firm that specializes in life sciences projects. It has been working with CARsgen since late 2020 to develop the entire program in North Carolina. CRB is providing engineering, design, and construction services as part of a building team that includes EAS (prefabrication), Star Electric (electrical), Edwards Inc. (structural, demolition, and concrete), and Dagard (which provided the lab’s cleanroom wall and ceiling panel systems).
LAB FACILITY IS LIKE BUILDING AN OREO COOKIE IN REVERSE
The R&D facility is an adaptive reuse of what had been an office and warehouse built in the early 1990s. CARsgen singled out this building over several others it and CRB looked at, explains Jie, because “it could be transformed quickly.” But that didn’t necessarily mean easily.
The first building took 13 months from conception to occupancy, and construction started in July 2021, says Ryan Lowder, DBIA, Project Director for CRB. The design team considered 15 different floor plans, as CARsgen at first preferred a smaller facility. “It realized that its plans needed to expand to accommodate the number of patients it would be creating drugs for,” Lowder explains.
The project’s biggest challenge, says A.L. Nesbitt, CRB’s Project Management Group Lead, was getting the floors to the height needed for HVAC systems the cleanroom required. This single-story building had an interior ceiling height of 18 feet, “which wasn’t optimal,” laments Lowder. The headroom space for the lab’s cleanroom is a tight nine feet, six inches, says Nesbitt.
In addition, the building team had to refortify the building’s floor slab—which over the years had been cut up into pieces for multiple tenants—to support new equipment plus dead loads like ductwork.
In adapting the building, CRB deployed its ONEsolution integrated project delivery (IPD) approach. Lowder elaborates that the building used a “self-supporting” modular cleanroom system, so that everything else in the lab could be installed first to meet timelines and the space available. “It was like building an Oreo cookie in reverse,” he quips. Abetting this approach was offsite manufacturing, by EAS, of ductwork, pipe racks, and other components that were assembled into five large sections and then transported to the jobsite for installation.
Nesbitt observes that developers of offices and labs are scrambling to get into cleanroom construction. CRB, which already had the expertise, was “lucky” to be working with CARsgen, “that was willing to be innovative,” she says. Jie adds that his company is receptive to adaptive reuse for future expansion. But supply chain snags for materials pose dilemmas. “So we have to get into projects earlier,” he says. That’s especially true for a biopharm company whose business model success hinges on speed to market.
Related Stories
Daylighting | Aug 18, 2022
Lisa Heschong on 'Thermal and Visual Delight in Architecture'
Lisa Heschong, FIES, discusses her books, "Thermal Delight in Architecture" and "Visual Delight in Architecture," with BD+C's Rob Cassidy.
| Aug 16, 2022
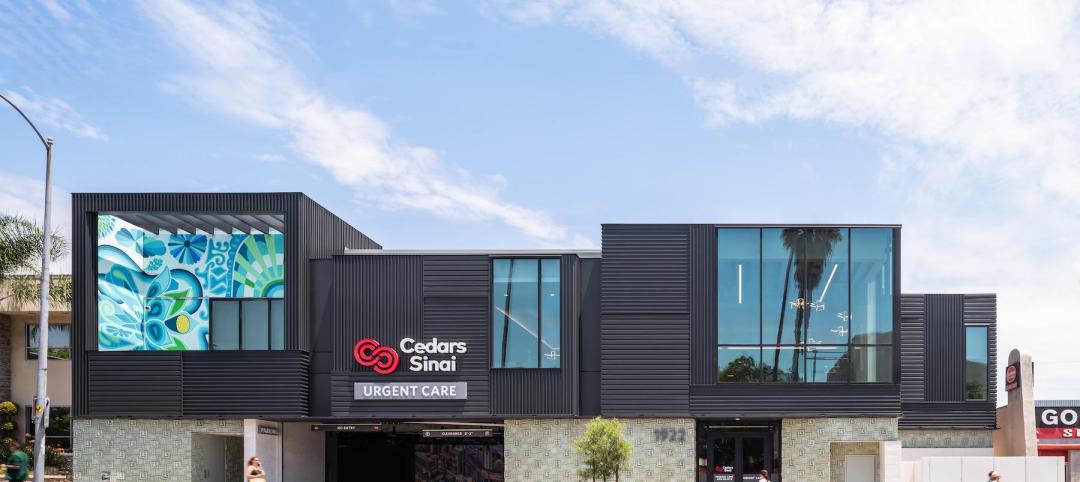
Cedars-Sinai Urgent Care Clinic’s high design for urgent care
The new Cedars-Sinai Los Feliz Urgent Care Clinic in Los Angeles plays against type, offering a stylized design to what are typically mundane, utilitarian buildings.
| Aug 15, 2022
IF you build it, will they come? The problem of staff respite in healthcare facilities
Architects and designers have long argued for the value of respite spaces in healthcare facilities.
AEC Tech | Aug 8, 2022
The technology balancing act
As our world reopens from COVID isolation, we are entering back into undefined territory – a form of hybrid existence.
| Aug 3, 2022
Designing learning environments to support the future of equitable health care
While the shortage of rural health care practitioners was a concern before the COVID-19 pandemic, the public health crisis has highlighted the importance of health equity in the United States and the desperate need for practitioners help meet the needs of patients in vulnerable rural communities.
Healthcare Facilities | Aug 1, 2022
New Phoenix VA outpatient clinic is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
The new Phoenix 32nd Street VA Clinic, spanning roughly 275,000 sf over 15 acres, is one of the largest veteran care facilities in the U.S.
Building Team | Jul 12, 2022
10 resource reduction measures for more efficient and sustainable biopharma facilities
Resource reduction measures are solutions that can lead to lifecycle energy and cost savings for a favorable return on investment while simultaneously improving resiliency and promoting health and wellness in your facility.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 22, 2022
Arizona State University’s Health Futures Center: A new home for medical tech innovation
In Phoenix, the Arizona State University (ASU) has constructed its Health Futures Center—expanding the school’s impact as a research institution emphasizing medical technology acceleration and innovation, entrepreneurship, and healthcare education.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 20, 2022
Is telehealth finally mainstream?
After more than a century of development, telehealth has become a standard alternative for many types of care.
Codes and Standards | Jun 14, 2022
Hospitals’ fossil fuel use trending downward, but electricity use isn’t declining as much
The 2021 Hospital Energy and Water Benchmarking Survey by Grumman|Butkus Associates found that U.S. hospitals’ use of fossil fuels is declining since the inception of the annual survey 25 years ago, but electricity use is dipping more slowly.