While suspended, lay-in ceilings have long been the norm in commercial design, the open-plenum ceiling has become trendy and economical, particularly in office and retail environments. However, calculating the tradeoffs between cost and performance can be tricky.
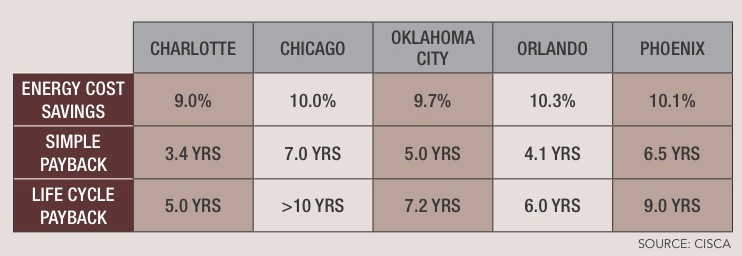
Very little data exists comparing suspended ceilings with open ceilings on the basis of cost and performance. The most recent study came from the Ceilings & Interior Systems Construction Association (www.cisca.org) five years ago. In the study, office and retail spaces were modeled in Chicago, Charlotte, Oklahoma City, Orlando, and Phoenix to reflect the differences in energy costs, climate, and installation costs. Initial construction costs were determined using RSMeans data; annual operating costs for HVAC, lighting, and maintenance were calculated according to Building Owners and Managers Association data.
The study found initial construction costs for suspended ceilings to be 15-22% higher in offices, and 4-11% higher in retail spaces. However, total energy savings for lay-in ceilings vs. open plenums were 9-10.3% in offices and 12.7-17% for retail. A 10.5% energy reduction qualifies buildings for a LEED EA credit, and a 14% reduction is good for two points.
The study attributed the energy performance advantage of suspended ceilings to the use of a return air plenum with low static pressures and fan horsepower vs. ducted air returns with higher static pressures and fan horsepower in open-plenum systems. In addition, return air plenums more efficiently remove heat from lighting systems and reduce the AC load. Suspended ceilings also offer about 20% higher light reflectance, thereby reducing lighting costs.
For more information, see: http://www.cisca.org/files/public/LCS_brochure_rev_9-08_lo-res.pdf.
Related Stories
| Apr 6, 2012
Batson-Cook breaks ground on hotel adjacent to Infantry Museum & Fort Benning
The four-story, 65,000-ft property will feature 102 hotel rooms, including 14 studio suites.
| Apr 6, 2012
Perkins Eastman unveils Qatar mixed-use sports complex
Home stadium for Lekhwiya Club a vibrant addition to Doha’s architectural identity.
| Apr 5, 2012
5 tips for a successful door and window retrofit
An exclusive tip sheet to help the Building Team manage door and window retrofits successfully.
| Apr 4, 2012
Educational facilities see long-term benefits of fiber cement cladding
Illumination panels made for a trouble-free, quick installation at a cost-effective price.
| Apr 4, 2012
HDS designs Mount Auburn Hospital’s new healthcare center in Waltham, Mass.
HDS Architecture provided design services for all the Mount Auburn Healthcare suites including coordination of HVAC and FP engineering.
| Apr 4, 2012
Bald joins the Harmon glazing team
Bald has 13 years of experience in the glazing industry, coming to Harmon from Trainor where he was the regional manager of the Mid-Atlantic region.
| Apr 4, 2012
JCJ Architecture designs New York City's first casino
Aqueduct Racetrack complex transformed into modern entertainment destination.
| Apr 4, 2012
San Antonio animal hospital earns LEED Platinum certification
Middleman Construction Company builds the city?s first commercial building to earn certification.
| Apr 4, 2012
Hason joins RNL’s as MENA regional director
Hason specializes in planning and urban design, hospitality, office, corporate headquarters and transportation structures, as well as, higher education and museum facilities.
| Apr 3, 2012
Product Solutions
Two new PV systems; a lighter shelf; and fire alarm/emergency communication system.