While suspended, lay-in ceilings have long been the norm in commercial design, the open-plenum ceiling has become trendy and economical, particularly in office and retail environments. However, calculating the tradeoffs between cost and performance can be tricky.
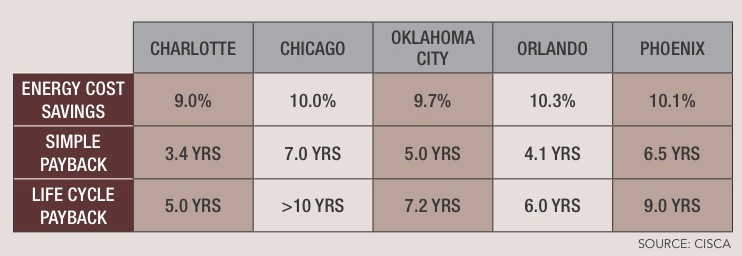
Very little data exists comparing suspended ceilings with open ceilings on the basis of cost and performance. The most recent study came from the Ceilings & Interior Systems Construction Association (www.cisca.org) five years ago. In the study, office and retail spaces were modeled in Chicago, Charlotte, Oklahoma City, Orlando, and Phoenix to reflect the differences in energy costs, climate, and installation costs. Initial construction costs were determined using RSMeans data; annual operating costs for HVAC, lighting, and maintenance were calculated according to Building Owners and Managers Association data.
The study found initial construction costs for suspended ceilings to be 15-22% higher in offices, and 4-11% higher in retail spaces. However, total energy savings for lay-in ceilings vs. open plenums were 9-10.3% in offices and 12.7-17% for retail. A 10.5% energy reduction qualifies buildings for a LEED EA credit, and a 14% reduction is good for two points.
The study attributed the energy performance advantage of suspended ceilings to the use of a return air plenum with low static pressures and fan horsepower vs. ducted air returns with higher static pressures and fan horsepower in open-plenum systems. In addition, return air plenums more efficiently remove heat from lighting systems and reduce the AC load. Suspended ceilings also offer about 20% higher light reflectance, thereby reducing lighting costs.
For more information, see: http://www.cisca.org/files/public/LCS_brochure_rev_9-08_lo-res.pdf.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Three Opus Corporation companies file for bankruptcy
Opus Corporation, a developer headquartered in Minnetonka, Minn., filed for bankruptcy in three of its five regional operating companies: Opus East, Opus South, and Opus West. CEO Mark Rauenhorst said sharp declines in commercial real estate values and tight credit markets caused difficulties in refinancing assets and restructuring lending agreements.
| Aug 11, 2010
ZweigWhite names its fastest-growing architecture, engineering, and environmental firms
Management consulting and research firm ZweigWhite has identified the 200 fastest-growing architecture, engineering, and environmental consulting firms in the U.S. and Canada for its annual ranking, The Zweig Letter Hot Firm List. This annual list features the design and environmental firms that have outperformed the economy and competitors to become industry leaders.
| Aug 11, 2010
SSOE, Fluor among nation's largest industrial building design firms
A ranking of the Top 75 Industrial Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants
| Aug 11, 2010
Best AEC Firms of 2011/12
Later this year, we will launch Best AEC Firms 2012. We’re looking for firms that create truly positive workplaces for their AEC professionals and support staff. Keep an eye on this page for entry information. +
| Aug 11, 2010
Report: Building codes and regulations impede progress toward uber-green buildings
The enthusiasm for super green Living Buildings continues unabated, but a key stumbling block to the growth of this highest level of green building performance is an existing set of codes and regulations. A new report by the Cascadia Region Green Building Council entitled "Code, Regulatory and Systemic Barriers Affecting Living Building Projects" presents a case for fundamental reassessment of building codes.
| Aug 11, 2010
Portland Cement Association offers blast resistant design guide for reinforced concrete structures
Developed for designers and engineers, "Blast Resistant Design Guide for Reinforced Concrete Structures" provides a practical treatment of the design of cast-in-place reinforced concrete structures to resist the effects of blast loads. It explains the principles of blast-resistant design, and how to determine the kind and degree of resistance a structure needs as well as how to specify the required materials and details.