While suspended, lay-in ceilings have long been the norm in commercial design, the open-plenum ceiling has become trendy and economical, particularly in office and retail environments. However, calculating the tradeoffs between cost and performance can be tricky.
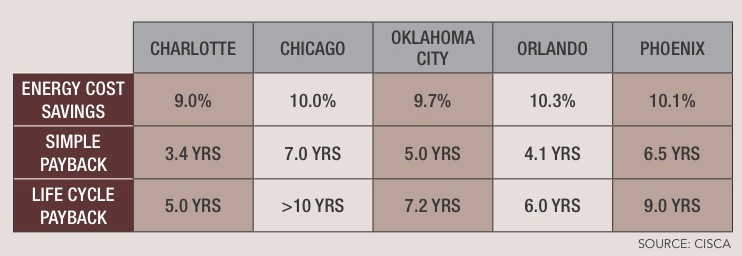
Very little data exists comparing suspended ceilings with open ceilings on the basis of cost and performance. The most recent study came from the Ceilings & Interior Systems Construction Association (www.cisca.org) five years ago. In the study, office and retail spaces were modeled in Chicago, Charlotte, Oklahoma City, Orlando, and Phoenix to reflect the differences in energy costs, climate, and installation costs. Initial construction costs were determined using RSMeans data; annual operating costs for HVAC, lighting, and maintenance were calculated according to Building Owners and Managers Association data.
The study found initial construction costs for suspended ceilings to be 15-22% higher in offices, and 4-11% higher in retail spaces. However, total energy savings for lay-in ceilings vs. open plenums were 9-10.3% in offices and 12.7-17% for retail. A 10.5% energy reduction qualifies buildings for a LEED EA credit, and a 14% reduction is good for two points.
The study attributed the energy performance advantage of suspended ceilings to the use of a return air plenum with low static pressures and fan horsepower vs. ducted air returns with higher static pressures and fan horsepower in open-plenum systems. In addition, return air plenums more efficiently remove heat from lighting systems and reduce the AC load. Suspended ceilings also offer about 20% higher light reflectance, thereby reducing lighting costs.
For more information, see: http://www.cisca.org/files/public/LCS_brochure_rev_9-08_lo-res.pdf.
Related Stories
Cladding and Facade Systems | Jun 5, 2023
27 important questions about façade leakage
Walter P Moore’s Darek Brandt discusses the key questions building owners and property managers should be asking to determine the health of their building's façade.
Retail Centers | Jun 2, 2023
David Adjaye-designed mass timber structure will be a business incubator for D.C.-area entrepreneurs
Construction was recently completed on The Retail Village at Sycamore & Oak, a 22,000-sf building that will serve as a business incubator for entrepreneurs, including emerging black businesses, in Washington, D.C. The facility, designed by Sir David Adjaye, the architect of the National Museum of African American History and Culture, is expected to attract retail and food concepts that originated in the community.
Mixed-Use | Jun 1, 2023
The Moore Building, a 16-story office and retail development, opens in Nashville’s Music Row district
Named after Elvis Presley’s onetime guitarist, The Moore Building, a 16-story office building with ground-floor retail space, has opened in Nashville’s Music Row district. Developed by Portman and Creed Investment Company and designed by Gresham Smith, The Moore Building offers 236,000 sf of office space and 8,500 sf of ground-floor retail.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 1, 2023
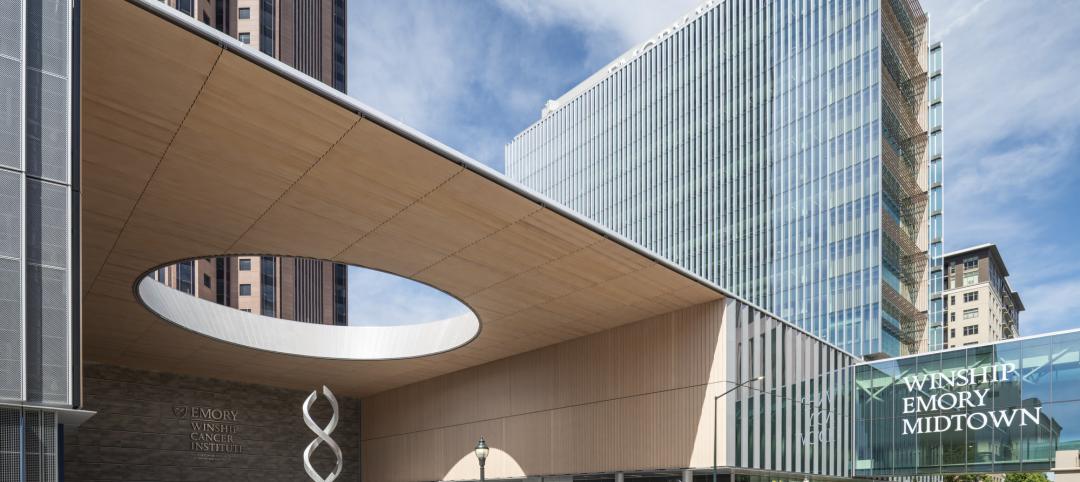
High-rise cancer center delivers new model for oncology care
Atlanta’s 17-story Winship Cancer Institute at Emory Midtown features two-story communities that organize cancer care into one-stop destinations. Designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) and May Architecture, the facility includes comprehensive oncology facilities—including inpatient beds, surgical capacity, infusion treatment, outpatient clinics, diagnostic imaging, linear accelerators, and areas for wellness, rehabilitation, and clinical research.
K-12 Schools | May 30, 2023
K-12 school sector trends for 2023
Budgeting and political pressures aside, the K-12 school building sector continues to evolve. Security remains a primary objective, as does offering students more varied career options.
Multifamily Housing | May 30, 2023
Boston’s new stretch code requires new multifamily structures to meet Passive House building requirements
Phius certifications are expected to become more common as states and cities boost green building standards. The City of Boston recently adopted Massachusetts’s so-called opt-in building code, a set of sustainability standards that goes beyond the standard state code.
Contractors | May 24, 2023
The average U.S. contractor has 8.9 months worth of construction work in the pipeline, as of April 2023
Contractor backlogs climbed slightly in April, from a seven-month low the previous month, according to Associated Builders and Contractors.
Mass Timber | May 23, 2023
Luxury farm resort uses CLT framing and geothermal system to boost sustainability
Construction was recently completed on a 325-acre luxury farm resort in Franklin, Tenn., that is dedicated to agricultural innovation and sustainable, productive land use. With sustainability a key goal, The Inn and Spa at Southall was built with cross-laminated and heavy timber, and a geothermal variant refrigerant flow (VRF) heating and cooling system.
Multifamily Housing | May 23, 2023
One out of three office buildings in largest U.S. cities are suitable for residential conversion
Roughly one in three office buildings in the largest U.S. cities are well suited to be converted to multifamily residential properties, according to a study by global real estate firm Avison Young. Some 6,206 buildings across 10 U.S. cities present viable opportunities for conversion to residential use.
K-12 Schools | May 22, 2023
The revival of single-building K-12 schools
Schools that combine grades PK through 12 are suddenly not so uncommon. Education sector experts explain why.