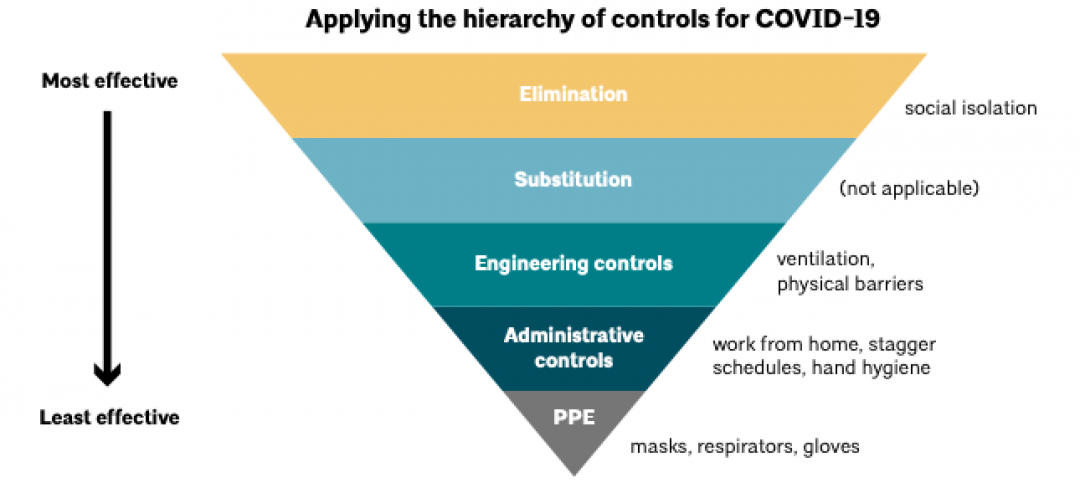
“Never let a good crisis go to waste” – Rahm Emanuel
It’s hard to imagine anyone who hasn’t had some significant loss during the current crisis. Perhaps you’ve had the virus; worse still, it might have killed someone among your family or friends. Almost all of us have lost, for some period yet unknown, significant parts of our life savings, and some have lost businesses they may have just started or have invested considerable resources in establishing.
What have we learned so far from the coronavirus pandemic? It will soon end, soon be in the rear-view mirror, but we can still take lessons learned as directions for going forward. Even in the most fire-ravaged forest, new seeds begin sprouting almost immediately after the first rain.
First, as individuals, we’ve already learned that can get by with much less than we are used to. Maybe this crisis might be a wake-up call to simplify our lives, to focus on what really matters, which will strengthen our ability to respond in the future.
Second, few of us are really prepared for the intellectual, emotional and spiritual challenges of dealing with ramifications of the Covid-19 virus and its impact on our lives. The social and economic crisis we are living through may lead us to think more deeply about how well we are living our values and how we might explore more inner-directed practices such as meditation and mindfulness for a more satisfying life.
Third, despite shortages of essential items and long lines at stores, we are far more resilient as a society than we might have expected. Resiliency is a primary response that we will need for dealing with accelerating climate change in the decade ahead, so we can take some comfort from how we all have responded.
That’s the good news for us as a society, but what lessons can we, as design, construction and operations professionals, take into our work?
By 2030, experts are almost certain that climate change’s effects will begin to resemble a continuous pandemic, threatening daily life in our cities and suburbs and on our farms – droughts, floods, fires, heat waves, tropical diseases spreading north, etc.
To avoid the worst effect of climate change, UN experts have sketched out a “carbon emissions budget” that we shouldn’t exceed over the next decade to have a chance to keep global warming below 1.5C and 2.0C.
Based on current trajectories, including a massive expansion of coal power in China and most of Asia, it’s difficult to see how we can avoid using up the world’s entire “carbon emissions budget” long before the end of the decade. Just as “what happens in Vegas stays in Vegas,” what we put into the atmosphere stays there for a LONG time, hundreds of years into the future.
But experts such as architect Edward Mazria have shown us how to change this trajectory, with building design and construction playing a key role.
Three things we can learn from the Coronavirus pandemic that we must put into practice immediately:
1. No more excuses! Time is short; we're beginning to learn that we may have radically underestimated the speed of climate change. Designing and renovating buildings for zero net energy use needs to be "Job 1" for all projects. We should get not award "green" seals of quality and “attaboy” awards for any project that doesn't at least do this much.
2. More importantly, materials choices matter even more than the energy-use profile, especially in the next decade; zero embodied carbon will be the next design standard. The good news: we have the information systems in place to make this goal attainable in practice.
3. Fully healthy commercial and public buildings, schools and colleges, retail, and hospitals will emerge as the new owner's requirement. Zero net energy is easy; zero net carbon is harder, but we can do it; healthy buildings have yet to be built (and operated) on a mass scale.
The task of renovating buildings to be simultaneously zero net carbon AND healthy will challenge the design and construction industry as never before.
The good news is that all the effort we've expended over the past twenty years, learning how to do (1) - (3), is now available for immediate implementation. Isn't it time for architects and engineers, builders and owners to abandon a strictly economics-based, "values neutral" professionalism and embrace the task that we really need to do (and for the most part, want to do): play our part in making sustainability in practice into our daily work?
If there's anything we as building industry professionals can learn from this close brush with our own mortality and with the country's economic death (and of course it's not over yet), it's that "tomorrow we'll get it right" has to be replaced with "today we did it right."
Jerry Yudelson is a LEED Fellow (Emeritus) and the author of 14 green building books. His next book, The Godfather of Green: An Eco-Spiritual Memoir, will be published on Earth Day 2020.
Related Stories
Glass and Glazing | May 8, 2020
Vitro Architectural Glass releases guide on decontaminating glass surfaces
The five-page technical document offers methods for cleaning and sanitizing glass surfaces.
Coronavirus | May 7, 2020
White paper clarifies steps, roles for use of metal composite material
Responsibilities of manufacturers, distributors, and fabricators outlined.
Coronavirus | May 7, 2020
Architects release new resource for safer re-occupancy of buildings
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is releasing a new Re-occupancy Assessment Tool today that provides strategies for limiting exposure to COVID-19 in buildings.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
Reopening Main Street post-COVID-19 quarantine
Cities and communities will need to adjust public space to allow customers back in with distancing in mind.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
Making jobsites safer in the COVID-19 world
A leading construction manager and installer certification alliance share their insights.
Coronavirus | May 6, 2020
National Construction Association and Procore to release new data showing the impacts of the coronavirus on the constructionindustry
Data will be released on Friday, may 8 at 12 pm EDT.
Healthcare Facilities | May 5, 2020
Holt Construction, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers complete temporary hospital in two weeks
The project is located in Paramus, N.J.
Coronavirus | May 5, 2020
How will COVID-19 change the procurement of professional design services?
We can use this moment as a test-case to build greater flexibility into how we pursue, win and deliver capital projects, better preparing the industry to meet the next disruption.
Coronavirus | May 4, 2020
Design steps for reopening embattled hotels
TPG Architecture recommends post-coronavirus changes in three stages.
Coronavirus | Apr 30, 2020
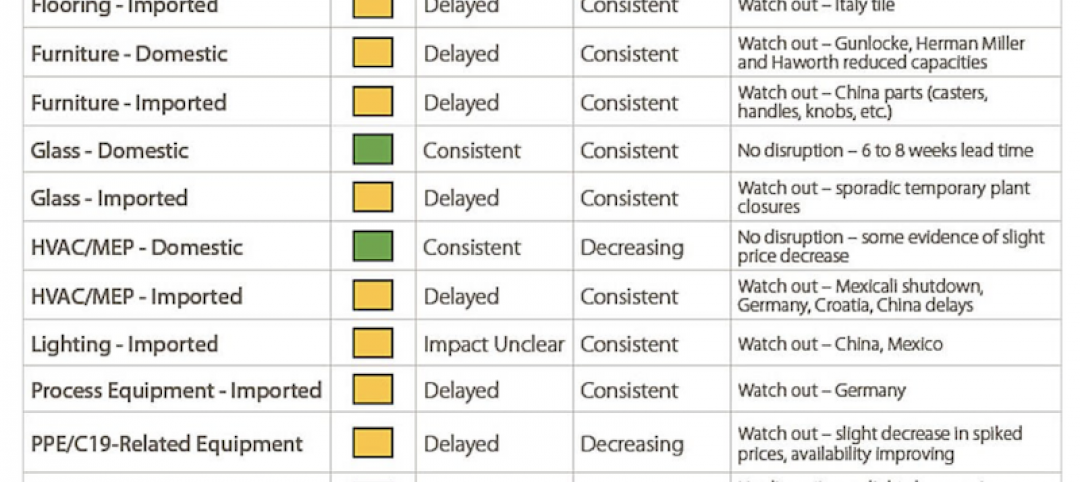
Gilbane shares supply-chain status of products affected by coronavirus
Imported products seem more susceptible to delays