Most AEC executives would probably agree with Greg Peele, Skanska’s Executive Vice President for operations in North Carolina and Virginia, who states that 2020 was a year “of remarkable growth and transformation” for the science and technology (S+T) sector.
The coronavirus pandemic triggered a private- and public-sector recommitment to bringing drug production back to the U.S. Firms like SmithGroup and Payette helped clients convert vacant or underutilized offices into life science spaces. The pandemic heightened the urgency for speed to market, especially among midstream pharma and personalized medicine/gene therapy focused clients, says Ed Cordes, Perkins and Will’s Global S+T Practice Leader. Cordes also points to a “doubling down” on research labs in clinical facilities.
The pandemic made virtual project design, coordination, and approvals more expedient and acceptable, say Vanderweil Engineers’ Managing Principals John Saad, LEED AP, and Chad Wisler, PE, LEED AP BD+C. But the health emergency also created delays in the overseas shipments of equipment and materials that can still impact the commissioning and validation processes. “It’s important to identify these critical items early in project procurement, evaluate alternative manufacturers where possible, and create flexibility with the schedule,” warns Brian Garbecki, Vice President with Gilbane Building Company.
RENOVATION, ADAPTIVE REUSE ASCENDING IN SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY BUILDING SECTOR
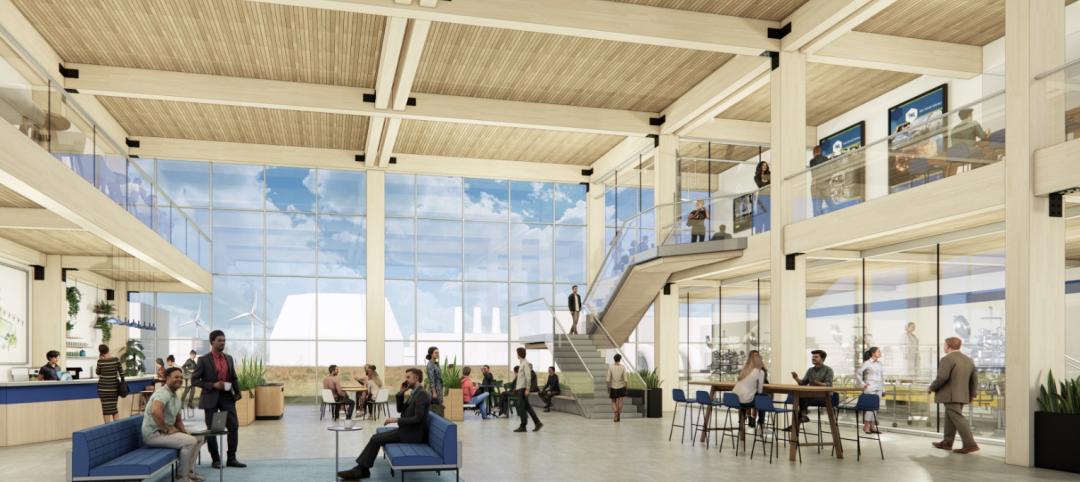
New construction still accounts for the bulk of S+T projects for AEC firms like Vanderweil, McCownGordon Construction, Jacobs, SmithGroup, and Payette.
However, Ellen Sisle, AIA, LEED AP BD+C, Jacobs’ Principal and Global Director of Science and Research, acknowledges that her firm’s ratio of new builds to renovations or adaptive reuse projects varies by location, with adaptive reuse being more prevalent in urban areas with a concentration of biotech, like Cambridge, Mass.
Joe Grosshart, President of Good & Roberts, a design-build affiliate of C.W. Driver Companies, notes that in Southern California, one of the country’s S+T hotbeds, 52% of life-science clients are choosing to repurpose existing buildings rather than build from the ground up. Good & Roberts recently completed a $4 million renovation project in San Diego for the medical device supplier NuVasive that converted a three-story building into a showroom and surgery suite; and a $2 million renovation of an existing 15,000-sf building for Cell Applications, which distributes cell cultures for medical research.
Developer and property manager The RMR Group (https://www.rmrgroup.com/Home/) redeveloped what had been the north campus of Scripps Research Institute for two decades into Muse, a 186,000-sf life sciences space whose three-building campus is owned by Diversified Healthcare Trust. The RMR Group manages this property and expected tenants to start occupying the building by mid-summer of this year.
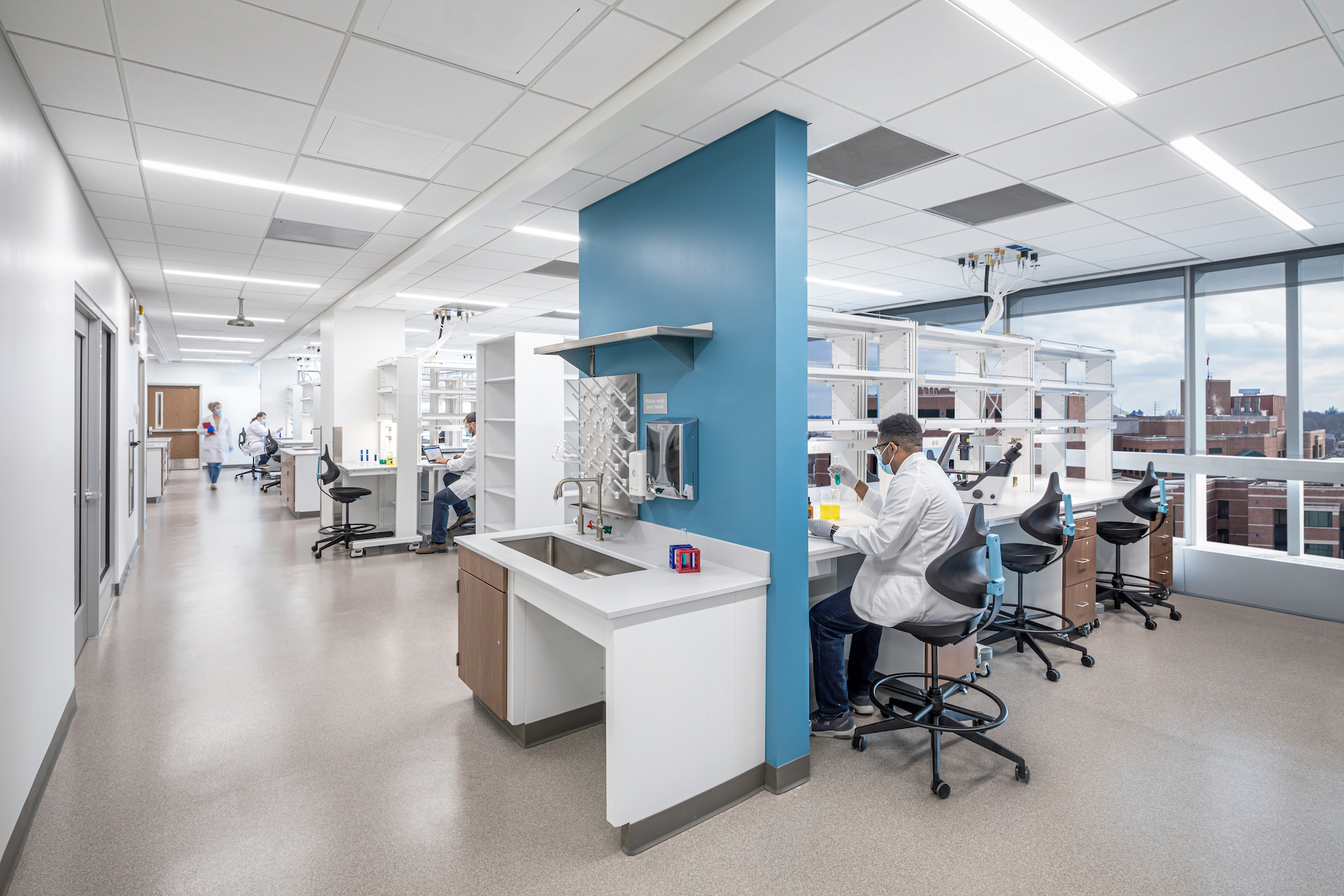

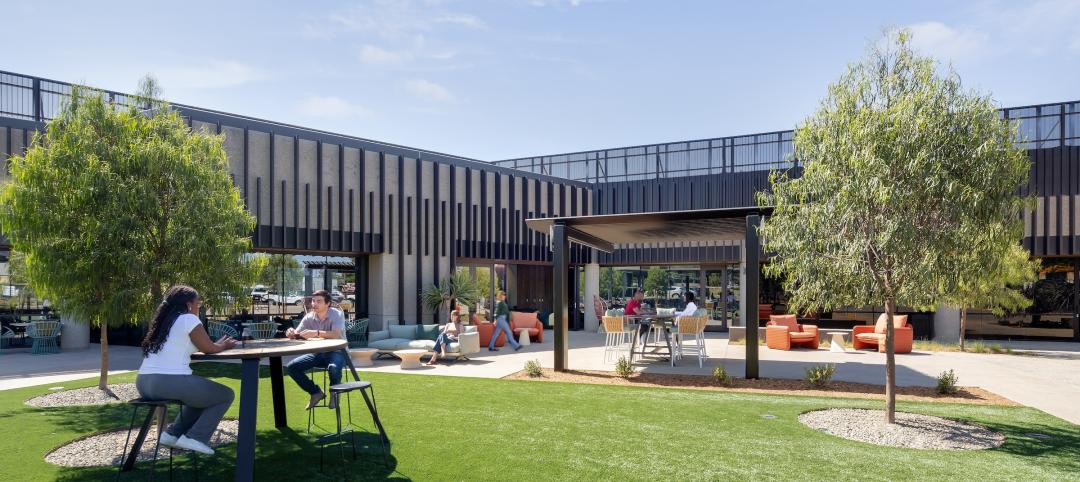
“Functionality is most in demand for life science buildings that need to serve both R&D and business purposes, so providing a mix of modern lab facilities and flexible office space is crucial,” says Chris Bilotto, RMR’s Senior Vice President. Other in-demand features include connection to the outdoors, and food amenities.
Skanska anticipates an uptick in adaptive reuse for S+T projects, too, but this will vary by region and mostly depend on the relative availability of land. When it comes to design changes, Skanska has seen the greatest shifts among its higher ed clients. It recently completed labs for North Carolina State University, Duke University, and a private company in Durham, N.C. “Three different clients with three different designers, and in all three, we saw an increase in the size of the lab benches and the addition of cubicle dividers on the bench offices to support social distancing,” says Peele.
During renovations, it’s not uncommon for tenants’ employees to continue working in the building. AEC firms say they regularly confer with those workers about logistics. The firms also proactively seek occupant input about their projects’ parameters.
Communicating with people who will be using the building “is the heart and soul of our programming and planning,” says Jeffery Talka, AIA, LEED AP, Science + Technology Practice Leader for SLAM. He explains that end users establish area requirements, quality of space, engineering controls, equipment needs, cultural relationships, and safety measures.
“Good science is not just about coordinating utilities and meeting technical demands,” says P&W’s Cordes. “The right environments can attract and retain top talent, support collaboration and innovation, and help improve speed to market.”
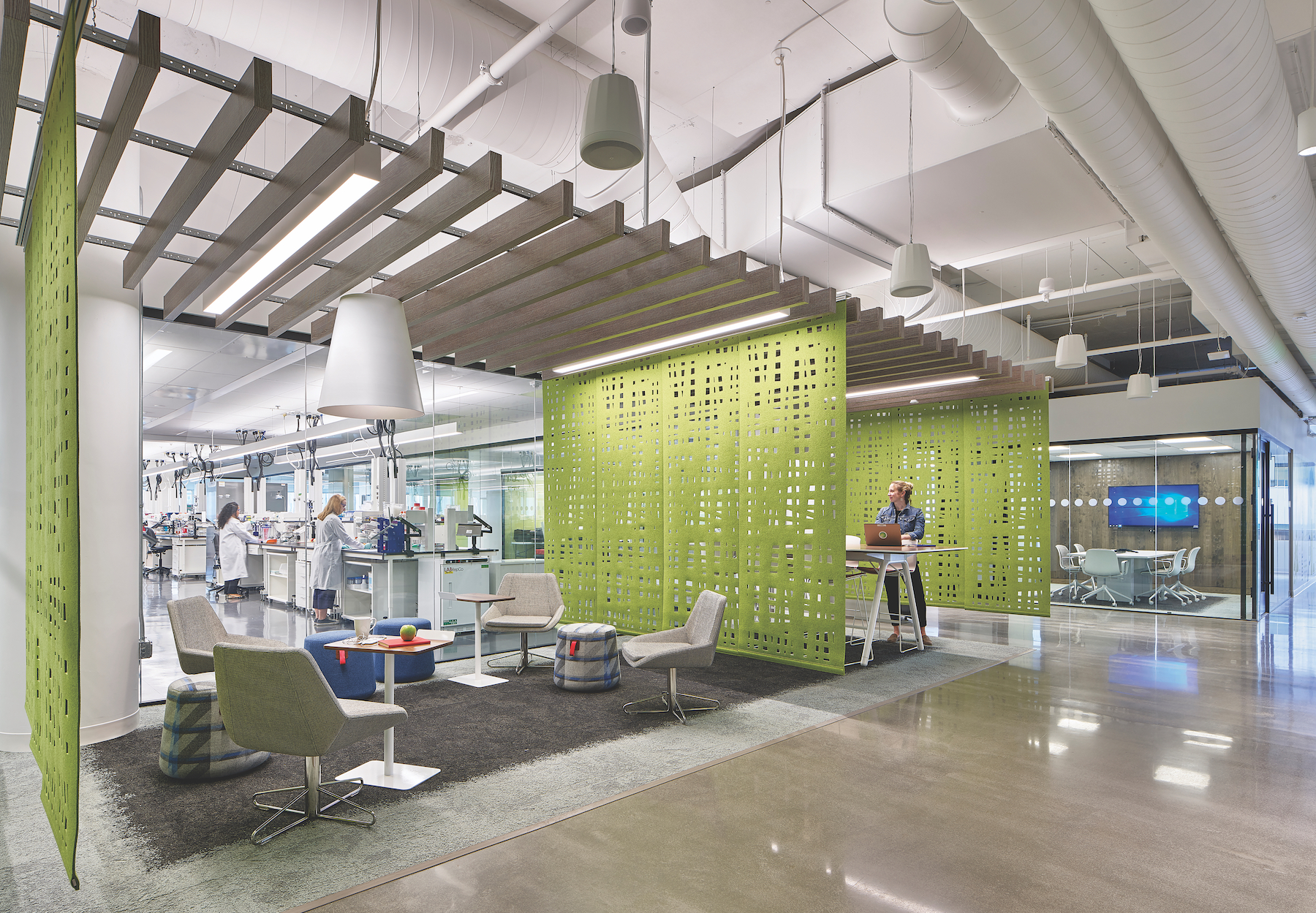
The input from end users might be what’s spurred the interest among developers and AEC teams in computational fluid dynamics that optimizes a building’s airflow and personnel comfort. It also goes without saying the conversations with occupants have led to the emphasis on visibility for the interior design of S+T projects.
“Space is a social system,” says Tom Simister, AIA, LEED AP, Payette’s Director of Space Strategies. “The whole point of investing in a science or technology building is to bring people together with specific resources to solve problems. Visibility makes that interaction intuitive and effortless, and enables buildings to showcase innovation and inspire a new generation of scientists.”
Visibility has included minimizing storage above workbenches. Daniel Lacy, Vice President of McCownGordon’s Healthcare and S+T Business Unit, says visibility is also manifested in clients’ requests for “critical” natural light, and for providing the public with opportunities to view a facility’s inner workings. Vanderweil Engineers has been incorporating visual mechanical rooms and interactive control/sustainability data boards into its S+T projects.
Several sources contacted for this article have seen S+T owners move toward digital technologies like artificial intelligence (AI). Skanska’s Peele says AI is improving the operation of clinical trials and enabling remote participation. “Our pharmaceutical clients are also using AI to find sequences and patterns that took much longer to run before.”
P&W’s Cordes observes that as production related to cell and gene therapies becomes more modular and accelerated, AI and automated processes are prevalent. “Some clients have set goals of 100% automation by the end of 2025.”
Related Stories
Laboratories | Oct 23, 2024
From sterile to stimulating: The rise of community-centric life sciences campuses
To distinguish their life sciences campuses, developers are partnering with architectural and design firms to reimagine life sciences facilities as vibrant, welcoming destinations. By emphasizing four key elements—wellness, collaboration, biophilic design, and community integration—they are setting their properties apart.
Laboratories | Oct 2, 2024
Trends in scientific research environments: Q&A with Flad's Matt McCord
As part of an ongoing series, Matt McCord, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP BD+C, Associate Principal with Flad Architects, discusses the future of the scientific workplace.
Laboratories | Sep 27, 2024
Traditional lab design doesn't address neurodiverse needs, study finds
A study conducted by ARC, HOK, and the University of the West of Scotland, has revealed that half (48.1%) of all survey respondents who work in laboratory settings identify as neurodivergent.
Laboratories | Sep 26, 2024
BSL conversions: A cost-efficient method to support high-containment research
Some institutions are creating flexible lab spaces that can operate at a BSL-2 and modulate up to a BSL-3 when the need arises. Here are key aspects to consider when accommodating a rapid modulation between BSL-2 and BSL-3 space.
Higher Education | Sep 18, 2024
Modernizing dental schools: The intersection of design and education
Page's John Smith and Jennifer Amster share the how firm's approach to dental education facilities builds on the success of evidence-based design techniques pioneered in the healthcare built environment.
Great Solutions | Jul 23, 2024
41 Great Solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
AI ChatBots, ambient computing, floating MRIs, low-carbon cement, sunshine on demand, next-generation top-down construction. These and 35 other innovations make up our 2024 Great Solutions Report, which highlights fresh ideas and innovations from leading architecture, engineering, and construction firms.
Laboratories | Jul 3, 2024
New science, old buildings: Renovating for efficiency, flexibility, and connection
What does the research space of the future look like? And can it be housed in older buildings—or does it require new construction?
Mass Timber | Jun 26, 2024
Oregon State University builds a first-of-its-kind mass timber research lab
In Corvallis, Oreg., the Jen-Hsun Huang and Lori Mills Huang Collaborative Innovation Complex at Oregon State University aims to achieve a distinction among the world’s experimental research labs: It will be the first all-mass-timber lab meeting rigorous vibration criteria (2000 micro-inches per second, or MIPS).
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 18, 2024
A healthcare simulation technology consultant can save time, money, and headaches
As the demand for skilled healthcare professionals continues to rise, healthcare simulation is playing an increasingly vital role in the skill development, compliance, and continuing education of the clinical workforce.
Laboratories | May 24, 2024
The Department of Energy breaks ground on the Princeton Plasma Innovation Center
In Princeton, N.J., the U.S. Department of Energy’s Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) has broken ground on the Princeton Plasma Innovation Center (PPIC), a state-of-the-art office and laboratory building. Designed and constructed by SmithGroup, the $109.7 million facility will provide space for research supporting PPPL’s expanded mission into microelectronics, quantum sensors and devices, and sustainability sciences.