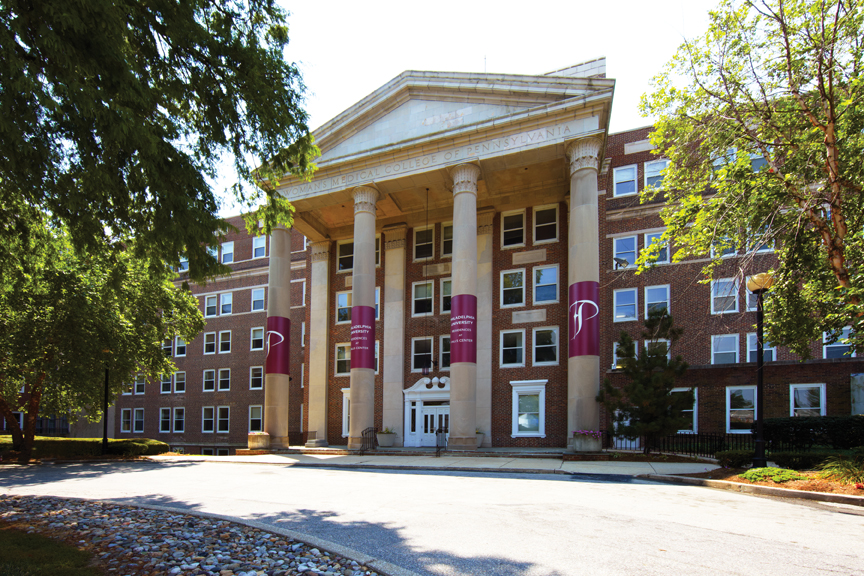
The Falls Center redevelopment gave new life to the historic former Women’s Medical College of Pennsylvania, the country’s first medical school for women. The complex’s original hospital facility, the Heritage Building, was designed by Philadelphia-based architecture firm Ritter and Shay and built in 1929.
In a bind, six years ago the building owners approached development and investment firm Iron Stone Real Estate Group with an offer to buy the property.
“We liked the layout, parking, and hospital-grade infrastructure of the building,” says Jason Friedland, director of operations and investment at Iron Stone. “We believed that at our entry basis we could withstand a long lease-up and offer a better-priced finished product for medical and educational tenants than our competitors.”
Within two weeks, Iron Stone acquired the former Women’s Medical College campus for $10 million. Along with Building Team members Wulff Architects, Axis Construction, Morrissey Design, Digenova Sam Inc., Direct Air Design and Build, Mirarchi Brothers, and Bofinger Plumbing Contractors, Iron Stone recasted the Heritage Building into a modern structure.
Finding the funding
IIn 2007, Iron Stone was granted zoning approval to revamp the 700,000-sf historic site into a mixed-use development. Phase one was the commercial development of medical offices, light manufacturing, and retail; phase two incorporated 132 residential units.
Before phase two got off the ground, the 2008 economic slump put the entire project at a standstill. As a partially completed commercial real estate development with an expiring bridge construction loan, the project was in jeopardy.
“Even though we had strong demand and several signed leases from institutional not-for-profit and educational tenants, at times we were unable to procure construction financing,” recalls Friedland. In the absence of conventional financing, Iron Stone used the cash infusion from its historic tax credit investors to bridge construction financing gaps for tenant improvements.
Iron Stone brought in Chevron Corp. as an equity investor in the historic tax credits as well as additional private investors, and put a condominium regime in place. This tactic allowed for individual construction loans and mortgages for each building as opposed to a single loan for the whole campus. This financing structure allowed residential-phase development to commence again.
Financing markets were still tight, however, and the possibility of a speculative market development was ruled out. At the same time, Philadelphia University, whose main campus is a mile down the road from the Heritage Building, was experiencing a boom. Because of the influx the university was housing students at scattered sites that weren’t up to par. The proximity of the Heritage Building, the already-developed apartment unit plans, and the site’s history made it a perfect place for a dormitory. Philadelphia University signed a lease in July 2010.
PROJECT SUMMARY
Falls Center, Heritage Building, Philadelphia
Building Team
Owner/Developer: Iron Stone Real Estate Group
Architect: Wulff Architects Inc.
Interior Architect: Morrissey Design LLC
Structural Engineer: Digenova Sam Inc.
Mechanical Engineer: Direct Air-Design and Build
Electrical Engineer: Mirarchi Brothers Inc.-Design and Build
Plumbing Enginner: Bofinger Plumbing Contractors LLC
General Contractor: Axis Construction Management LLCGeneral Information
Size: 160,000 sf
Construction Cost: $14.7 million
Construction Period: September 2010 to July 2011
Delivery Method: Stipulated Sum
Because the school was on a set schedule, the Building Team had only 10 months to finish the apartments. If not, Iron Stone would have to foot the bill for 300 students to stay in hotels.
Plowing through eight decades of history
When Iron Stone acquired the property, it had to organize the immense number of construction documents and blueprints housed in a storage closet. The original Heritage Building contained laboratories, exam rooms, human and animal morgues, administrative offices, nursing facilities, classrooms, and an auditorium. Moreover, previous hospital administrations had made several renovations. The Building Team sought to reuse as much of the existing infrastructure as possible; ultimately, 78% of the material removed from the site was salvaged or recycled.
Preconstruction and initial demolition started before the lease with the university was signed, which turned out to be a blessing in disguise. There was more asbestos in the building than anticipated, and it had to be remediated before demolition could begin. Original flooring, doors, and HVAC systems also had to be removed before this step, all the while carefully saving the interior walls for historic preservation purposes.
Exterior work included a complete roof replacement, partial repointing of the brick façade, and replacement of the windows, which were aluminum or wood. In order to keep the windows in compliance with the National Parks Service standards, the Building Team surveyed nearly 600 units to catalogue their configurations. For each of the four window types found in the building, a modern replica replacement was found.
Fortunately, when the commercial phase of the Heritage Building was developed two years prior, a new water-source loop air-conditioning system had already been installed and was easily expanded to the residential portion of the development. The electrical infrastructure was built from scratch and a new network of copper water supply lines was installed, but the existing sprinkler system and elevators only needed minor improvements. The Building Team also chose a spray insulation made from soybeans, which naturally provides a vapor barrier, to replace the mineral wool batts.
A contemporary loft aesthetic was chosen for the units, with neutral colors, exposed original brick walls, high ceilings, and large windows. A few of the units were lined with windows, originally to provide sunlight to tuberculosis sufferers. Slate windowsills and thirty-degree ceiling angles, which were characteristic of hospital design in 1929, were also preserved. Many of the original eight-foot corridors were saved, as were the original wood railings and soapstone treads in the stairways.
“Convincing the design professionals that several of the existing systems could be tweaked and reused instead of tearing everything out and starting from scratch was a challenge,” says Friedland. “But this savings was significant and helped us to attract price-sensitive tenants during the financial crisis.”
The lobby was the last piece of the puzzle for the Building Team to put into place. To restore it to its original condition, the team used marble to replace the 12-inch ceramic floor tiles, the aluminum revolving door was removed, original paint colors were matched, and a bas-relief in the entrance was preserved.
The demolition of the lobby also led to an unexpected discovery—a time capsule that had been buried in June 1930, The contents were donated to The Legacy Center: Archives & Spelcial Collections at Drexel University College of Medicine and act as a poignant reminder of the building’s place in local history.
Construction on the new Heritage Building was completed ahead of schedule and under budget. The building now has a new purpose, but continues to educate Philadelphia students. +
Related Stories
| May 25, 2011
Developers push Manhattan office construction
Manhattan developers are planning the city's biggest decade of office construction since the 1980s, betting on rising demand for modern space even with tenants unsigned and the availability of financing more limited. More than 25 million sf of projects are under construction or may be built in the next nine years.
| May 25, 2011
Olympic site spurs green building movement in UK
London's environmentally friendly 2012 Olympic venues are fuelling a green building movement in Britain.
| May 25, 2011
TOTO tests universal design at the AIA conference
If you could be 80 years old for 30 minutes—and have to readjust everything you think you know about your own mobility—would you do it?
| May 20, 2011
Hotels taking bath out of the bathroom
Bathtubs are disappearing from many hotels across the country as chains use the freed-up space to install ever more luxurious showers, according to a recent USAToday report. Of course, we reported on this move--and 6 other hospitality trends--back in 2006 in our special report "The Inn Things: Seven Radical New Trends in Hotel Design."
| May 19, 2011
BD+C’s "40 Under 40" winners for 2011
The 40 individuals profiled here are some of the brightest stars in the AEC universe—and they’re under the age of 40. These young architects, engineers, contractors, designers, and developers stood out among a group of 164 outstanding entrants in our sixth annual “40 Under 40” competition.
| May 18, 2011
Sanford E. Garner on the profitability of being diverse
Sanford E. Garner, AIA, NOMA, LEED AP ND, NCARB, founding partner and president of A2SO4 Architecture, LLC, Indianapolis, on gentrification, the profitability of being diverse, and his goals as NOMA president.
| May 18, 2011
8 Tips for Designing Wood Trusses
Successful metal-plate-connected wood truss projects require careful attention to detail from Building Team members.
| May 18, 2011
Major Trends in University Residence Halls
They’re not ‘dorms’ anymore. Today’s collegiate housing facilities are lively, state-of-the-art, and green—and a growing sector for Building Teams to explore.
| May 18, 2011
Former Bronx railyard redeveloped as shared education campus
Four schools find strength in numbers at the new 2,310-student Mott Haven Campus in New York City. The schools—three high schools and a K-4 elementary school—coexist on the 6.5-acre South Bronx campus, which was once a railyard.