|
|
The newly renovated Fox Oakland Theater is the centerpiece of a plan to revitalize the Uptown district and bring people back to downtoan Oakland. The theater had been boarded up since 1966. |
The story of the Fox Oakland Theater is like that of so many movie palaces of the early 20th century. Built in 1928 based on a Middle Eastern-influenced design by architect Charles Peter Weeks and engineer William Peyton Day, the 3,400-seat cinema flourished until the mid-1960s, when the trend toward smaller multiplex theaters took its toll on the Fox Oakland.
The theater closed in 1966 and dodged demolition several times before making the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. It would remain vacant and in shambles for nearly two decades.
In 1996, then-Mayor Jerry Brown—at the urging of a citizens group called the Friends of the Fox—designated the Fox Oakland Theater the centerpiece of a plan to revitalize the Uptown district and bring people back to the city's core. The city purchased the building and, following several restoration projects between 1999 and 2001 to repair the roof and marquee, embarked on an all-out effort to modernize and transform the theater into world-class performing arts venue and dance school for the Oakland School for the Arts.
 |
|
The Building Team used a series of braces, shear walls, reinforced slabs, and buttresses to stabilize both the new and existing structures without adversely impacting the visual grandeur of the theater. |
Key to the mayor's plan was a public-private funding approach proposed by local developer Phil Tagami that would help cover the $87 million price tag for the project, which included a complete restoration and seismic retrofit of the theater and construction of twin three-story wings for the dance school.
Tagami established both nonprofit and for-profit entities that could contribute funds to the project and benefit from available tax credits and grants. He also worked with city officials and the project's construction manager, Turner Construction, to involve as many local firms and minority- women-owned business enterprises as possible.
“I like how they involved so much of the local workforce,” said Reconstruction Awards judge Matthew H. Johnson, PE, associate principal with Simpson Gumpertz & Heger, Waltham, Mass. “The team split the sub packages into small pieces so that virtually any local firm could work one of the projects.”
To make this delivery approach feasible, the team had to obtain city council approval for a special contracting approach that permitted engaging multiple entities under a management structure. Such an approach is unusual in city projects, which normally are bid in a public, low-bid process that also involves a claims and dispute component. In all, the project created 394 construction jobs, roughly half of which were performed by local workers.
The project scope encompassed 17 major components, including restoring the theater, stage, fly-loft, and supporting infrastructure; stabilizing the 60-foot-tall dome structure over the entrance; reconfiguring the theater floors, stage, orchestra pit, rigging, proscenium, and theater controls; adding theater power, lighting, sound, and air-conditioning systems; and constructing the twin 20,000-sf additions.
But it was the seismic retrofit efforts led by Oakland-based KPA Group that received the most praise from the Reconstruction Awards judges. They were particularly impressed with the Building Team's ability to stabilize both the new and existing structures without adversely impacting the visual grandeur of the theater. The effort involved devising multiple solutions (see diagram), including:
-
Reducing the seismic demands on the main roof diaphragm by inserting new buttresses on each side of the roof mid-span of the diaphragm. These buttresses were also utilized to stabilize the farthest end of the cantilevered balcony structure, eliminating torsion and reducing the demand on the back of theater wall.
-
Reinforcing the proscenium wall and the back-of-theater wall with shotcrete walls and steel framing. The new walls were placed behind existing heavily ornamented walls and are hidden from view.
-
Stabilizing the dome structure with twin U-shaped walls constructed immediately to the north and south of the entrance structure and doweled into the existing walls. The new walls were then interconnected to each other and to the sides of the entrance structure at several levels, thereby boxing the entire dome and entrance building inside new well-reinforced walls designed for the entire lateral load of the dome and entrance structure under the dome.
-
Stabilizing existing brick walls by connecting the brick to a series of structural tubes epoxy bolted into the back of the walls. New steel channels were added to brick pilasters that, in turn, were integrated as part of the street-level façade of the new school buildings.
-
Incorporating a series of horizontal steel tubes, shear walls, a horizontal steel diaphragm structure, and a reinforced slab on grade to stabilize the wraparound buildings.
“It was a good, clean job,” said SGH's Johnson of. “I think they did the seismic retrofit intelligently.”
Related Stories
| May 13, 2014
Libeskind wins competition to design Canadian National Holocaust Monument
A design team featuring Daniel Libeskind and Gail Dexter-Lord has won a competition with its design for the Canadian National Holocaust Monument in Toronto. The monument is set to open in the autumn of 2015.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| May 9, 2014
New York Public Library scraps drastic renovation plans
The New York Public Library's controversial renovation, involving the removal of stacks from the Schwarzman building and the closing of the mid-Manhattan branch, has been dropped in favor of a less dramatic plan.
| May 2, 2014
World's largest outdoor chandelier tops reworked streetscape for Cleveland's PlayhouseSquare
Streetscape project includes monumental gateway portals, LED signage, and a new plaza, fire pit, sidewalk café, and alfresco dining area.
| May 2, 2014
Must see: French pavilion to take food from roof to table
France has presented its design for Expo Milano 2015 in Milan—its representative building will be covered in gardens on the outside, from which food will be harvested and served inside.
| Apr 30, 2014
Visiting Beijing's massive Chaoyang Park Plaza will be like 'moving through a urban forest'
Construction work has begun on the 120,000-sm mixed-use development, which was envisioned by MAD architects as a modern, urban forest.
| Apr 29, 2014
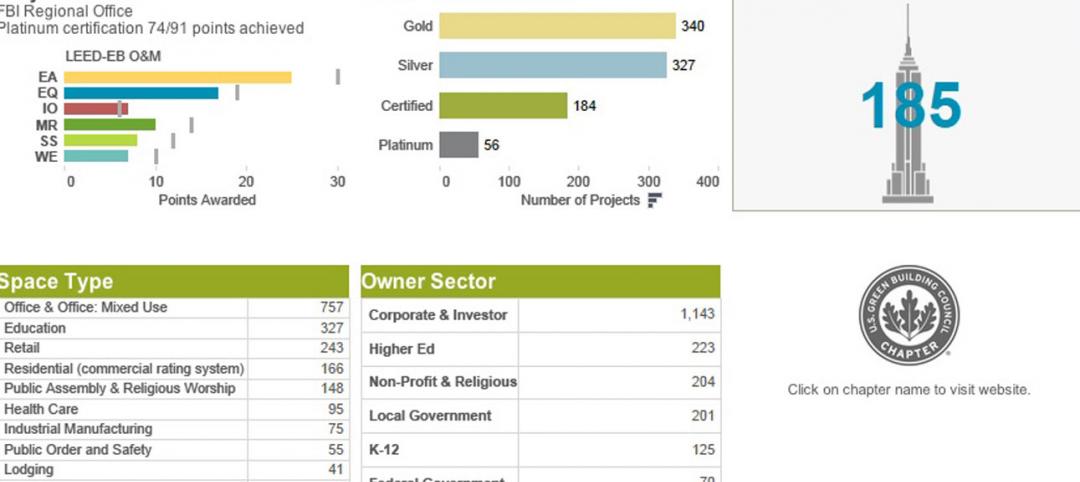
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
Smart Buildings | Apr 28, 2014
Cities Alive: Arup report examines latest trends in urban green spaces
From vertical farming to glowing trees (yes, glowing trees), Arup engineers imagine the future of green infrastructure in cities across the world.
| Apr 24, 2014
Unbuilt and Famous: LEGO releases box set of Bjarke Ingels' LEGO museum
LEGO Architecture has created a box set that customers can use to build replicas of the LEGO Museum, which is not yet built in real life. The museum, designed by the Bjarke Ingels Group, will commemorate the history of LEGO.
| Apr 24, 2014
Gothic-style dance center breaks ground at University of Southern California
The program for the three-story building will include a dance/performance studio, five dance studios, instructional classrooms, performer support spaces, costume storage, and faculty and administrative offices.