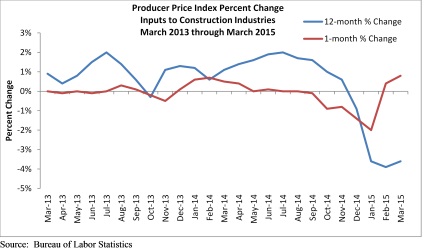
Results from the Bureau of Labor Statistics showed that prices for construction materials rose 0.8% in March. According to Associated Builders and Contractors, Inc., it was the largest monthly increase in more than two years.
Prices for construction materials have risen for two straight months after falling for the previous six.
Although prices are up on a monthly basis, statistics showed that input prices are down 3.6% on a year-over-year basis, the fourth consecutive month this has occurred. The steady decline in input prices is the longest streak since 2009 as crude petroleum prices fell 4% in March and are down eight of the last nine months.
"Though U.S. nonresidential and residential segments continue to expand, global construction volumes remain suppressed by widespread weakness in Asia, Europe, and Latin America," said ABC Chief Economist Anirban Basu. "With the U.S. dollar likely to get stronger over the next few months as domestic interest rates begin to rise, there is little likelihood of significant increases in construction input prices over the next six to nine months. Overall producer prices managed to increase 0.5% on a monthly basis, the first increase since June 2014. This reading serves to increase the likelihood that the Federal Reserve will begin to increase short-term interest rates later this year."
There were only two key material categories that saw an increase in construction prices in March: fabricated strucutal metal produce prices (0.4%) and natural gas prices (1.5%).
While these two inputs rose, others fell:
- Prices for plumbing fixtures dropped 0.3% in March but remain up 2.5% year-over-year.
- The price of prepared asphalt, tar roofing, and siding dipped 0.4% in March.
- Iron and steel prices dropped 2.5% in March and are down 11.5% year-over-year.
- Prices for steel mill products slipped 1.9% in March and are down 4.8% on a yearly basis.
- Concrete products prices were flat but up 4.1% year-over-year.
- Crudge petroleum prices dropped 4% in March and are down 55% from the same time last year.
- Crude energy material costs decreased 1.4% in March and are down 43.7% from the previous year.
- Softwood lumed prices fell 4.1% and are down 7.4% year-over-year.
- Prices for nonferrous wire and cable were flat in March and rose 2.5% on a yearly basis.
To read the entire report, click here.
Related Stories
| Mar 21, 2014
Forget wood skyscrapers - Check out these stunning bamboo high-rise concepts [slideshow]
The Singapore Bamboo Skyscraper competition invited design teams to explore the possibilities of using bamboo as the dominant material in a high-rise project for the Singapore skyline.
| Mar 20, 2014
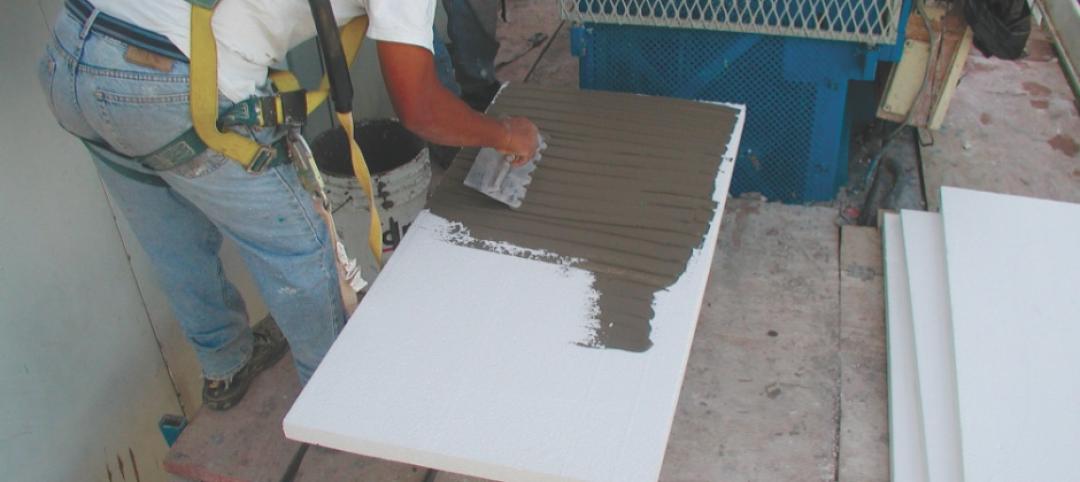
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 20, 2014
13 dazzling wood building designs [slideshow]
From bold structural glulam designs to striking textured wall and ceiling schemes, these award-winning building projects showcase the design possibilities using wood.
| Mar 19, 2014
Federal agency gives thumbs up to tall wood buildings
USDA's support for wood projects includes training for AEC professionals and a wood high-rise design competition, to launch later this year.
| Mar 17, 2014
Rem Koolhaas explains China's plans for its 'ghost cities'
China's goal, according to Koolhaas, is to de-incentivize migration into already overcrowded cities.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 10, 2014
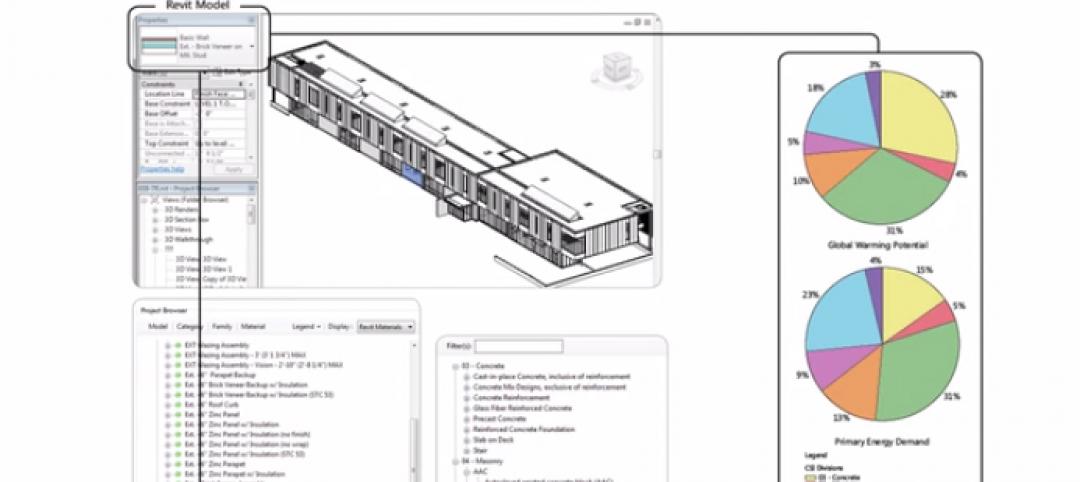
Meet Tally – the Revit app that calculates the environmental impact of building materials
Tally provides AEC professionals with insight into how materials-related decisions made during design influence a building’s overall ecological footprint.
| Mar 5, 2014
5 tile design trends for 2014
Beveled, geometric, and high-tech patterns are among the hot ceramic tile trends, say tile design experts.
| Mar 4, 2014
How EIFS came to America
Design experts from Hoffmann Architects offer a brief history of exterior insulation and finish systems in the U.S.
| Feb 27, 2014
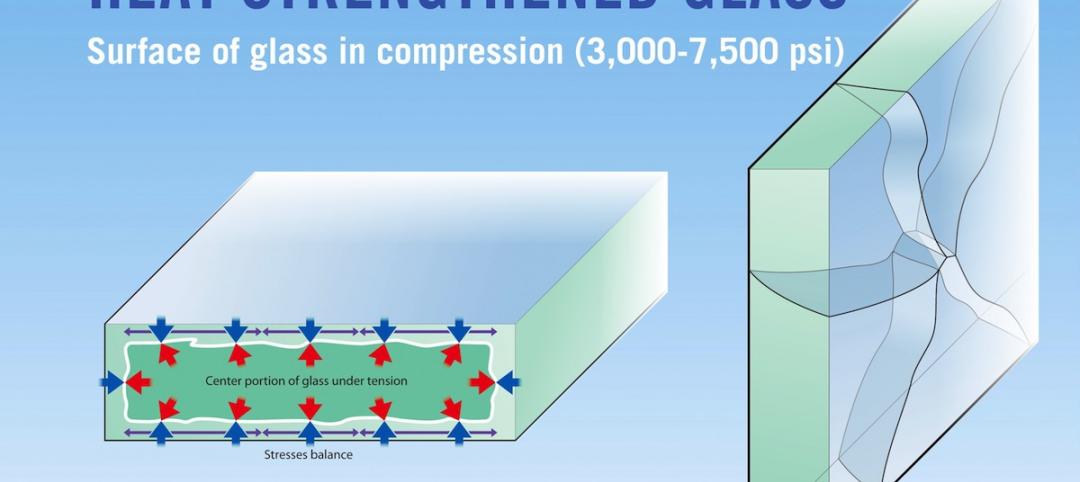
12 facts about heat-treated glass: Why stronger isn’t always better
Glass is heat-treated for two reasons: the first is to increase its strength to resist external stresses such as wind and snow loads, or thermal loads caused by the sun’s energy. The second is to temper glass so that it meets safety glazing requirements defined by applicable codes or federal standards.