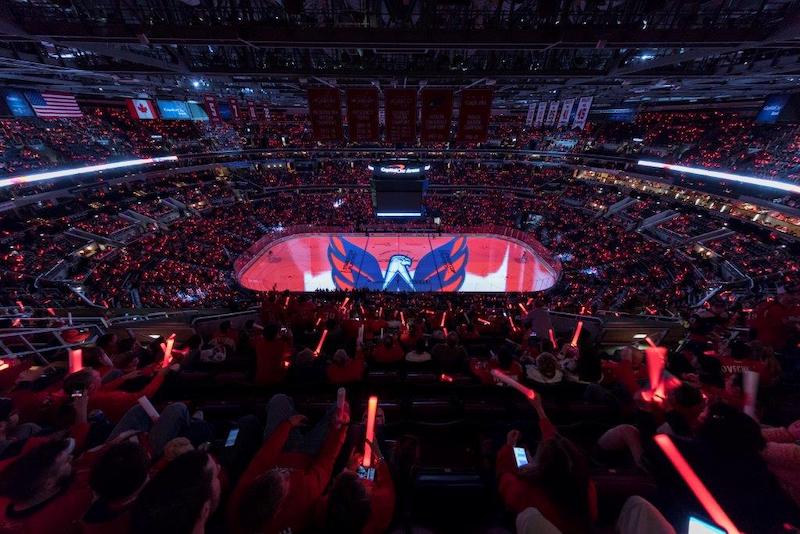
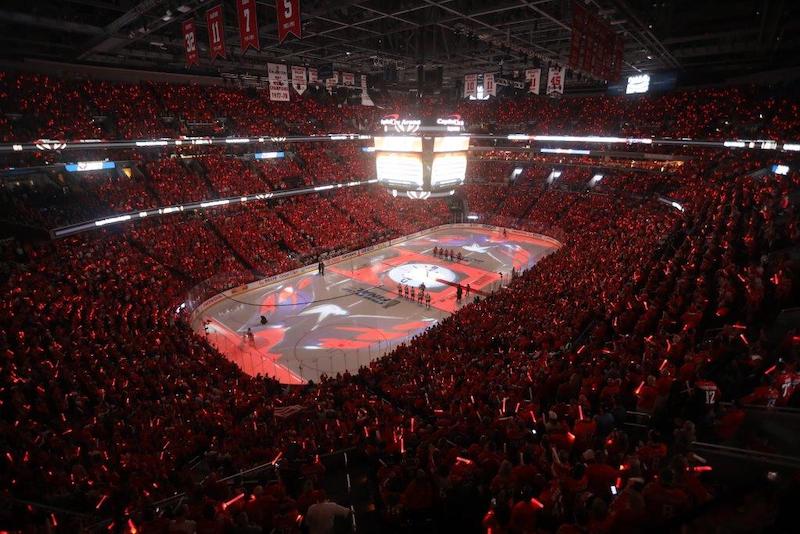
Last winter, basketball fans at Oracle Arena, then-home to the Golden State Warriors, were introduced to the PlayStation game God of War. In an elaborate, multimedia promotion, animated content took over the arena’s massive, overhanging score board and ribbon displays. It then transitioned to the basketball court itself, which turned into a snowy dystopia of projected light as the game’s characters battled in front of the sold-out crowd and countless viewers watching online and on TV.
As amazing as it was at the time, this type of projection show — using audiovisual (AV) and digital technologies to transform sports venues into new experiences — has become much more prominent. Venues are effectively using applied video as a design element. For many years, arenas have staged such shows on a temporary basis, but now more are designing the technological capability into their facilities on a permanent basis. What’s known in the AV and production industries as “projection mapping” is becoming as integral to sports venue design as digital signage and public address systems. The video content can be as varied as player profiles and promotion or sponsor marketing and engagement.
“When we do hockey ice or basketball court projection, we try to create fan engagement,” explains Mark Ouwerkerk, Director of Events and Staging for Christie Digital Systems, which makes many of the projectors and supporting technologies used in arenas. “We’re trying to get people more involved in what we’re presenting, because we believe the visual images are what they remember.”

How Projection Mapping Works
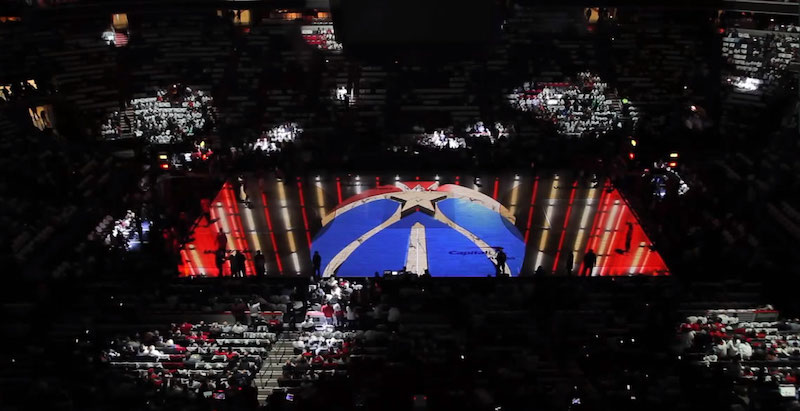
Projection mapping is the process of presenting visual content on non-traditional surfaces, such as three-dimensional objects, the outside of buildings, or on basketball courts. At the 2018 Major League Baseball All-Star Game at Nationals Park in Washington, D.C., technologists even projection-mapped the stadium’s infield. At one point, the U.S. Capitol appeared to rise from home plate.
Projection mapping combines powerful projectors, media servers, computer software, and video content to create a unique, immersive show. It’s considered mapping because the specialized software takes the visual content — usually from multiple projectors — and shapes it to fit the target surface, precisely placing (mapping) the video pixels and creating the illusion that the content has been painted virtually onto the court, ice, or infield. The system intelligently combines video streams, and often blends, warps, or otherwise manipulates the video into a uniform, digital canvas. For example, in the case of projection mapping onto an ice rink, the video perfectly fits the surface’s rounded corners and light does not spill into the seats.
“The more complex,” says Ouwerkerk, “the more technology required.” In existing arenas, he says, the positioning of elements like scoreboards and other permanent fixtures can determine where projectors must be placed and how much processing will be applied to the content to compensate for odd angles and ensure the video looks perfect.
Design Considerations
Quince Imaging, projection-mapping specialists based in Sterling, Virginia, executed the Oracle Arena and Nationals Park productions and have worked in professional and college sports venues throughout the United States. Scott Williams, Quince Imaging’s co-founder and chief operating officer says that by now, virtually every major arena has staged a projection-mapping production, but less than one-quarter have built the capability into the venue’s infrastructure as a permanent feature. Doing so takes planning and coordination among design, construction, and technology teams.
“For existing arenas, we do an engineering analysis and study and get our technical plan approved to ensure the structure can hold the system the way we intend to install it,” Williams says. “More recently, for new venues, we’ve been working with construction firms like Samet Corp. and Turner Construction at the very beginning, when it’s still in the design phase, to integrate the desired projection-mapping system in the early stages. That way we can plan for power, signal, structure, weight, and methodology, and it works very smoothly.”
Installed projection-mapping systems are usually purpose-built — specified and installed to support the intended content and experience, but not usually repurposed or reconfigured for other uses. When incorporated into a venue’s design, today’s projection-mapping systems are often treated as lighting. The same way a lighting designer creates a plot to evenly illuminate the venue, AV integrators ensure a sufficient number of projectors, installed in the right locations, will bathe the target surface in video light.

Systems Vary in Size
In sports arenas, a typical projection-mapping installation can include eight to 12 large projectors and cost $750,000 to $1 million or more, which more teams and venues see as a sound investment toward creating an exceptional live experience. Quince Imaging recently installed 18 projectors at PNC Arena in Raleigh, North Carolina, home to the NHL’s Carolina Hurricanes and college’s N.C. State Wolfpack. “They wanted the best system, designed to be the brightest, highest-resolution system in sports,” Williams says. “And it is.”
The size and scope of a projection-mapping system depends on the content the venue intends to project and characteristics of the venue itself. For example, professional sports arenas often require more projectors than college sports arenas because they must overcome ambient light from other digital signage, which teams may be contractually required to keep illuminated even when a projection show is taking place. And because ice rinks are larger than basketball courts, they typically require more projection.
Quince Imaging worked with Monumental Sports & Entertainment on Capital One Arena, which supports Washington, D.C. hockey and basketball teams. The turnkey system, which consisted of 12 high-brightness 4K-resolution projectors, maps 2D and 3D content onto the ice for the Capitals and onto the court for the Wizards, adjusting to the different size of each surface.
Mapping Exterior Surfaces
And that’s just the inside of sports venues. The next frontier will be projection mapping on the exterior of arenas and stadia. For example, Little Caesars Arena in Detroit was designed with a curved, metal-canvas “skin” on 600 feet of its outer wall. Venue operators use 12 projectors to “paint” it with digital branding, advertising, and feeds from events inside the arena. In London, AV technologists turned the roof of the O2 Arena into an enormous projection surface (16,000 square meters) with a staggering 68 projectors putting out 1.4 million lumens of light.
“Projecting on arena facades takes an installed system, too, and can be thought of like lighting or digital signage,” says Quince Imaging’s Williams. “When the venue is hosting 200 different events a year it creates an engaging experience for visitors.”
As AV technology evolves, designers can expect projection mapping solutions to be more colorful, vibrant, lifelike, and interactive. Eventually, with tracking technology, fans will be able to play games on the ice or court. “Real-time fan engagement is the next great trend in this industry,” says Williams. “We’re in territory now where we’ve never been before.”
Related Stories
| May 16, 2013
Chicago unveils $1.1 billion plan for DePaul arena, Navy Pier upgrades
Hoping to send a loud message that Chicago is serious about luring tourism and entertainment spending, Mayor Rahm Emanuel has released details of two initiatives that have been developing for more than a year and that it says will mean $1.1 billion in investment in the McCormick Place and Navy Pier areas.
| May 7, 2013
First look: Golden State Warriors stadium by Snøhetta, AECOM
Architects Snøhetta and AECOM have revealed their latest renderings of a new stadium for NBA basketball team the Golden State Warriors on the waterfront in San Francisco.
| May 2, 2013
Holl-designed Campbell Sports Center completed at Columbia
Steven Holl Architects celebrates the completion of the Campbell Sports Center, Columbia University’s new training and teaching facility.
| Apr 30, 2013
Tips for designing with fire rated glass - AIA/CES course
Kate Steel of Steel Consulting Services offers tips and advice for choosing the correct code-compliant glazing product for every fire-rated application. This BD+C University class is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.
| Apr 26, 2013
BIG tapped to design Europa City in suburban Paris
Danish architecture firm, BIG - led by Bjarke Ingels – has been announced as the winner of an international invited competition for the design of Europa City, a 800,000 square meter cultural, recreational and retail development in Triangle de Gonesse, France.
| Apr 24, 2013
Los Angeles may add cool roofs to its building code
Los Angeles Mayor Antonio Villaraigosa wants cool roofs added to the city’s building code. He is also asking the Department of Water and Power (LADWP) to create incentives that make it financially attractive for homeowners to install cool roofs.
| Apr 12, 2013
Chicago rail conversion puts local twist on High Line strategy
Plans are moving forward to convert an unused, century-old Chicago rail artery to a 2.7 mile, 13 acre recreational facility and transit corridor.
Building Enclosure Systems | Mar 13, 2013
5 novel architectural applications for metal mesh screen systems
From folding façades to colorful LED displays, these fantastical projects show off the architectural possibilities of wire mesh and perforated metal panel technology.
| Mar 5, 2013
Recycled recreation: Waste-to-energy plant combines with ski resort
A new project near Copenhagen pushes the boundaries of the term "mixed use," combining a waste-to-energy plant with a ski resort.