Purdue University civil engineers have developed innovative materials that can dissipate energy caused by bending, compression, torque, and tensile stresses without sustaining permanent damage. These intelligent architected materials may also possess shape memory properties, making them reusable while enhancing safety and durability.
The research, led by Professor Pablo Zavattieri, believe the new class of adaptable materials offer potential uses in multiple industries, such as earthquake engineering, impact-resistant structures, biomedical devices, sporting goods, building construction, and automotive components. The technology is currently being tested for 3D-printed panels for aircraft runway mats and nonpneumatic tires for military vehicles, providing resistance to punctures and leaks while maintaining performance in various terrains.
Purdue develops intelligent architected materials

“These materials are designed for fully recoverable, energy-dissipating structures, akin to what is referred to as architected shape memory materials, or phase transforming cellular materials, known as PXCM,” Zavattieri said. “They can also exhibit intelligent responses to external forces, changes in temperature, and other external stimuli.”
These materials can be created from various substances, such as polymers, rubber, and concrete, as long as they remain within the elastic range. They are designed to deform in controlled and programmable ways, providing enhanced energy absorption and adaptability. For the aircraft runway mats, Zavattieri sees the material aiding in self-healing properties, resulting in a longer life span than a runway made with AM-2 matting. "Another benefit is that debris on the runway will not hamper the runway’s performance with our technology," he says.
The Purdue researchers have demonstrated scalability from macro to micro applications and an improvement over traditional lightweight cellular materials.
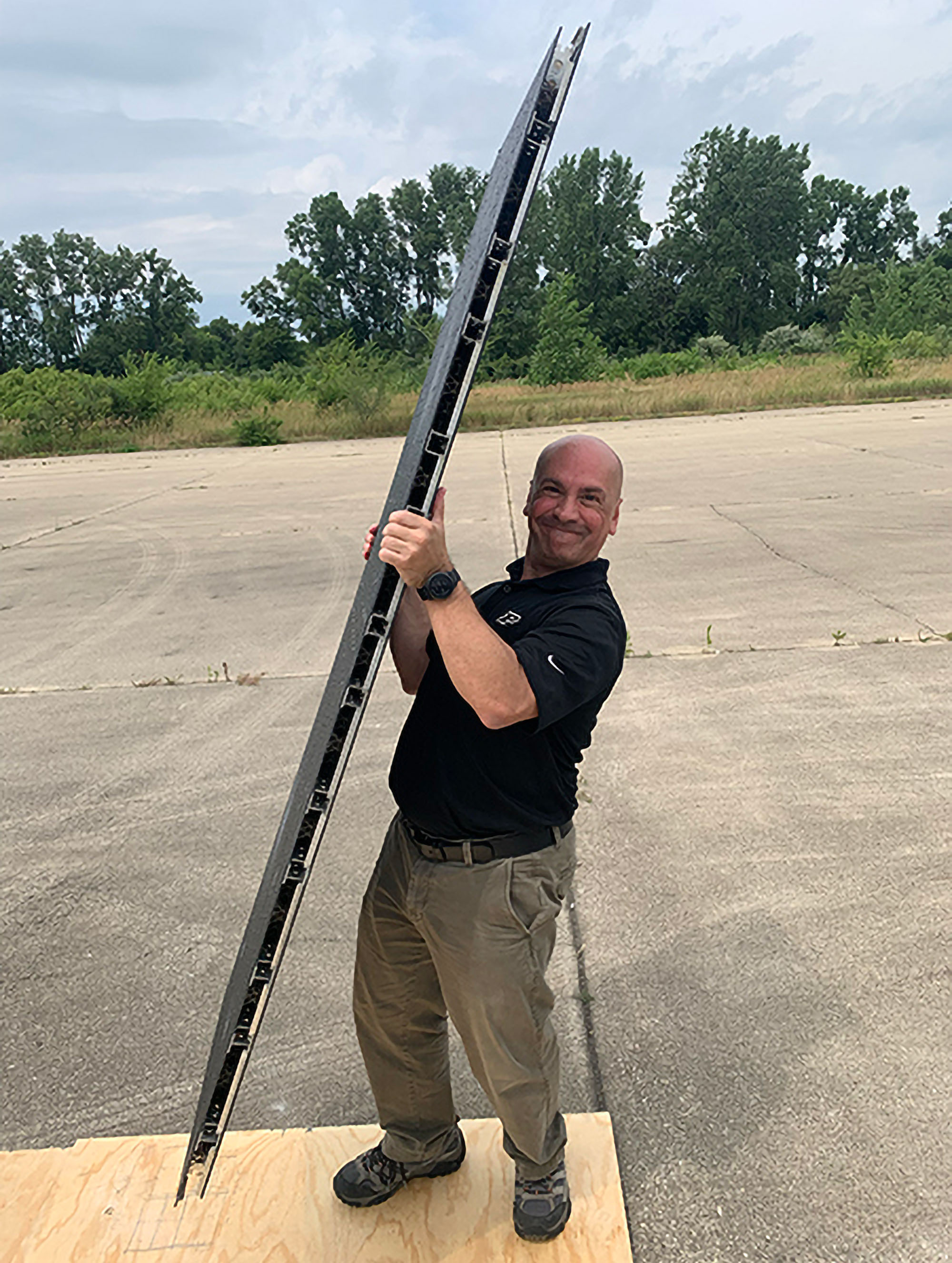

“We have produced intelligent architected materials as large as 12 inches, which are ideal for applications like building and bridge construction to absorb and harness energy,” Zavattieri said. “Conversely, we have created materials with unit cells smaller than the thickness of a human hair. This scalability opens up a world of possibilities from macro to micro applications.”
The research has received funding from organizations like General Motors, ITAMCO (Indiana Technology and Manufacturing Companies), the National Science Foundation, and the U.S. Air Force. Additionally, patents have been filed to protect the intellectual property, and industry partners interested in commercializing the materials for the marketplace should contact Dipak Narula, Assistant Director of Business Development and Licensing in Physical Sciences, at dnarula@prf.org about 2018-ZAVA-68252, 2019-ZAVA-68691, 2020-ZAVA-69072 and 2022-ZAVA-69900.
Related Stories
| Oct 14, 2014
Proven 6-step approach to treating historic windows
This course provides step-by-step prescriptive advice to architects, engineers, and contractors on when it makes sense to repair or rehabilitate existing windows, and when they should advise their building owner clients to consider replacement.
| Sep 25, 2014
Arup's Solarleaf façade system wins Zumtobel innovation award
The system uses the bio-chemical process of photosynthesis to absorb CO2 emissions, while cultivating microalgae to generate biomass and heat as renewable energy resources.
Sponsored | | Sep 15, 2014
Fire resistance of metal cladding is an asset in wildfire-prone areas
Construction projects in fire-prone areas need to take wildfire danger into account, and metal panels provide some fire-resistant qualities.
| Sep 5, 2014
Tyco SimplexGrinnell receives Internet of Things Innovator of the Year Award
The award recognizes the company for excellence in leveraging advanced Internet-connected technology to deliver smart eService fire alarm solutions that improve service delivery and provide significant value to customers.
| Aug 21, 2014
Firestone Building Products' Bristol facility chosen as Northeast business leader for energy efficiency
Firestone Building Products Company, LLC announced that its Bristol, Conn. manufacturing facility was recognized by the Northeast Energy Efficiency Partnerships (NEEP) as a 2014 Northeast Business Leader for Energy Efficiency.
| Aug 5, 2014
New bomb-proof concrete mixture used in One World Trade Center
The new concrete mix deforms instead of breaking, removing the threat of flying debris in an explosive attack.
| Aug 1, 2014
Johns Manville realigning Engineered Products into global business unit
New structure of Johns Manville Engineered Products unit expected to enhance customer experiences while strengthening innovation, agility, and manufacturing capabilities.
| Jul 17, 2014
A harmful trade-off many U.S. green buildings make
The Urban Green Council addresses a concern that many "green" buildings in the U.S. have: poor insulation.
| Jul 15, 2014
Trade groups form task force to further transparency and optimization of building product ingredients
The Harmonization Task Group will offer marketplace benefits including consistent messaging, simplification, elimination of redundancies, and creation of more accurate, faster and less costly assessments.
| Jul 10, 2014
Vetrotech Saint-Gobain first fire-rated glass ceramic fabricator to assess products' environmental footprint
Vetrotech is the first fire-rated glass company in the world to have made a comprehensive life cycle assessment of fire-rated glazing products.