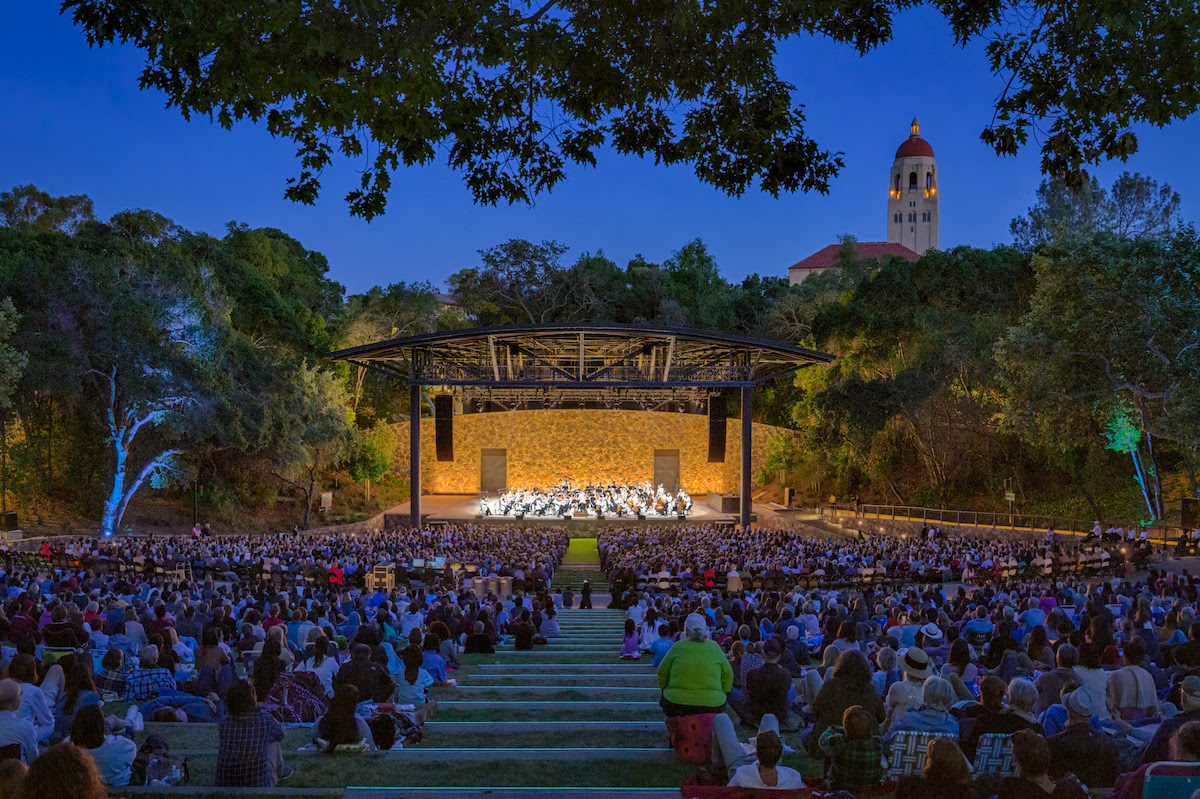
The Laurence Frost Amphitheater redesign has completed at Stanford University.
The amphitheater was originally built in 1937 to host university functions and events. The space quickly evolved to host community events, musical acts, and classical concerts before falling into disuse over the past few decades due to lack of accessibility and production infrastructure.

The goal of the Frost Amphitheater's recent redesign was to create greater accessibility for larger acts to play and the ability to house student shows and various university events. Additionally, CAW’s design mission was to create a more modern experience while preserving the beauty and serenity of the historic site. The modernization was achieved by the creation of curved tunnels for wayfinding and crowd management and a curved wall that serves as a shield to the stage building beyond.

New entrances to the amphitheater were created by designing a unique and strategically placed system of tunnels through the tree-covered slopes. Guest amenities, an updated service and stage entrance, a stage building with a canopy cover to protect the performers, and upgraded lighting and sound infrastructure were also included in the redesign.
When the amphitheater opens without any social distancing restrictions up to 8,000 guests can be accommodated.
Related Stories
| Jun 12, 2014
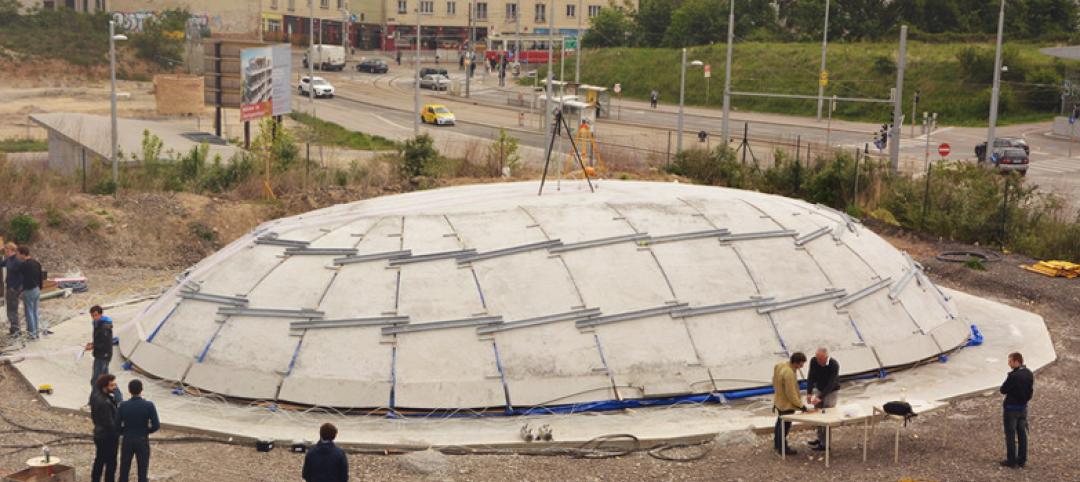
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 9, 2014
Green Building Initiative launches Green Globes for Sustainable Interiors program
The new program focuses exclusively on the sustainable design and construction of interior spaces in nonresidential buildings and can be pursued by both building owners and individual lessees of commercial spaces.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| May 2, 2014
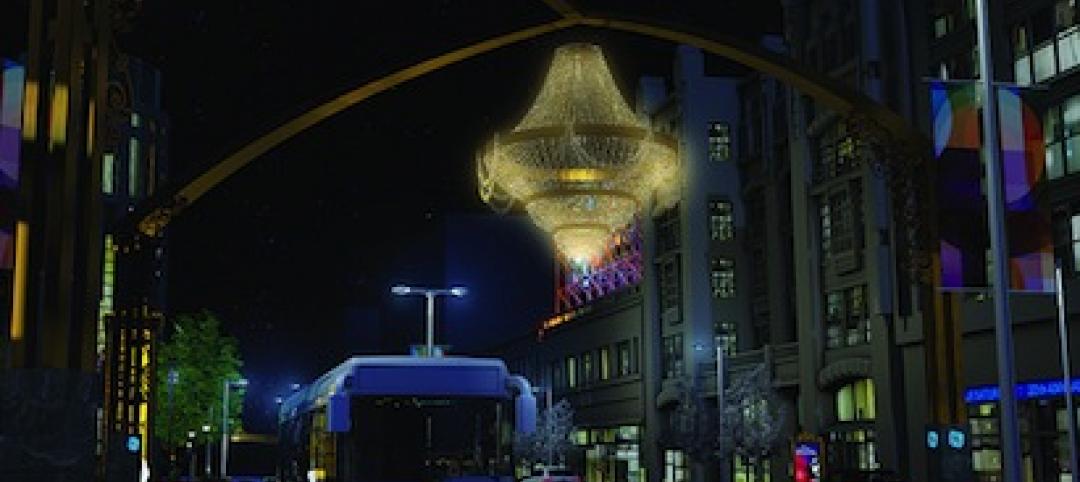
World's largest outdoor chandelier tops reworked streetscape for Cleveland's PlayhouseSquare
Streetscape project includes monumental gateway portals, LED signage, and a new plaza, fire pit, sidewalk café, and alfresco dining area.
| Apr 29, 2014
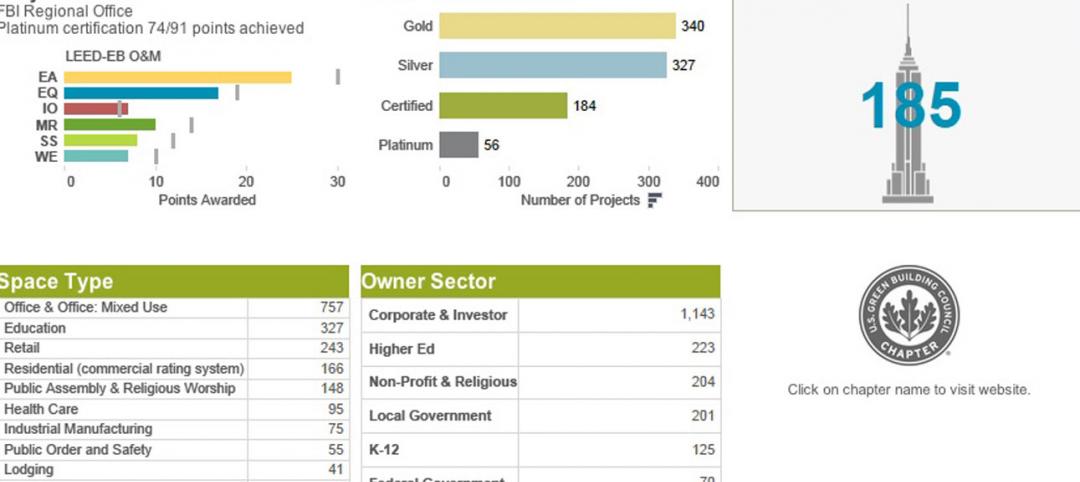
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
| Apr 16, 2014
Upgrading windows: repair, refurbish, or retrofit [AIA course]
Building Teams must focus on a number of key decisions in order to arrive at the optimal solution: repair the windows in place, remove and refurbish them, or opt for full replacement.