Conventional windows have long been considered the weak link in the building envelope. According to the U.S. Department of Energy’s Building Technologies Program Multi-Year Program Plan 2011-2015, approximately 4.4 quadrillion Btu of energy in the U.S. is lost through windows in the form of heating and air-conditioning loads.
The DOE plan suggests that regardless of orientation or climate, window systems have the potential to outperform the best-insulated wall or roof in terms of annual energy performance, peak demand reduction, and cost.
UNIVERSITY FINDS A SOLUTION TO INEFFICIENT WINDOWS
The University of Minnesota’s Folwell Hall, a fixture on the National Register of Historic Places, recently underwent three years of extensive renovation.
Before the renovation, students, staff, and faculty who met in Folwell Hall were at the mercy of wildly fluctuating temperatures caused by outdated, inefficient windows, and an antiquated HVAC system.
The Building Team of Miller Dunwiddie Architects and construction manager McGough Construction, both of Minneapolis, set out to remedy this problem by replacing 400 existing windows with energy-efficient units. In order to meet state sustainability guidelines, window distributor National Window Associates Inc., Rogers, Minn., recommended Kolbe’s Ultra Series Sterling double-hung units with standard LoE2-270 double-pane insulating glass.
“Two of the main goals for Folwell Hall were to protect its historic significance and improve its energy efficiency,” says Denita Lemmon, AIA, project manager with Miller Dunwiddie. “The window system met both the aesthetic and performance specifications.”
In the 1980s, Folwell Hall’s century-old wood windows had been replaced with a basic aluminum system, which hid some of the historic architectural details. The replacement window system integrated aluminum-clad windows with custom aluminum panning to replicate the original architectural vision.
“To retain as much of the historical nature of the window openings, the interior trim was left in place,” says Tim Mahanna, project superintendent with McGough Construction.
The renovation of Folwell Hall was completed in August 2011. In addition to the new windows, the building’s HVAC system was updated to create an energy-efficient, temperature-controlled environment year-round. According to University of Minnesota officials, the indoor environment in Folwell Hall has been dramatically improved in terms of the HVAC, acoustics, and comfort.
COMMERCIAL RETROFIT KEEPS NOISE, ENERGY LOSS LOW
The 400 Market Street building in Philadelphia is an example of one of the countless buildings in the U.S. that are 30-60 years old where reglazing for aesthetic, environmental, or practical reasons is called for.
Constructed in 1972, the 12-story building is owned and managed by local property firm Kaiserman Co. As energy costs rose, along with tenant complaints regarding street noise, Kaiserman opted to install the Renovate by Berkowitz window retrofit system.
Glass fabricator J.E. Berkowitz manufactures an on-site window retrofit system that converts existing single-pane windows into energy-saving, triple-glazed insulating glass units. The retrofit system costs about 50% less than ripping out and replacing old windows.
Carolyn Pfeiffer, property manager of 400 Market Street, says the investment in the retrofit system is already paying dividends beyond cost and energy savings.
“Even without the energy savings, we’ve received positive feedback from our tenants, who are pleased with how much quieter and more comfortable the building is,” says Pfeiffer. The installation team worked with the tenants to minimize disruption to their workplace. “This not only made the tenants happy, but saved time and the cost of relocating them as well,” she says.
The retrofit took about 50 working days. In comparison, a traditional rip-out/replace project can take between 100-150 days for a similar 12-story structure.
AESTHETICS, THERMAL PERFORMANCE APPEAL TO MIDDLE SCHOOL
Beaty-Warren Middle School in Warren, Pa., recently completed an extensive renovation to update the 80-year-old facility. In addition to numerous structural and aesthetic updates, more than 300 high-performance, energy-efficient windows were installed.
Contractor Architectural Windows Concepts, Export, Pa., was given a six-month schedule to remove the existing windows and replace them with windows manufactured by Wausau Windows and Wall Systems.
Originally designed in 1930, the school experienced three building expansions to accommodate a growing student population. During each reconstruction phase, the windows were replaced on an as-needed basis, resulting is dissimilar styles and performance.
In 2010, the Warren County School District voted to replace the school’s windows and selected Hallgren, Restifo, Loop & Coughlin Architects, Erie, Pa., to design the reconstruction project.
“Our goal was to bring back the original intent and character of the building’s design,” says Chris Coughlin, lead architect. “We knew the windows would be an important piece to anchor the original design aesthetic and tie together the building’s many additions.”
Among the difficulties was creating profiles for more than 65 different window sizes and replicating the original shapes and colors of the window frames.
Mimicking the look of the school’s original windows, Wausau’s INvent Series units were fabricated for Beaty-Warren with a beveled face, muntin grids, and custom panning. Offset glass panes replicate the historic double-hung sash while offering easy operation, weatherability, and performance. The window’s triple-glazed, high thermal performance contributes to both the environmental and financial goals of the school. Following installation, interior temperatures at the school increased an average of 4-5 degrees Fahrenheit in the classrooms during the winter heating season. In the warmer months, the windows can be opened for natural ventilation.
To manage daylight, the windows were installed with one-inch, between-glass blinds. This allows staff to control glare, which may be evident on computer screens.
“Our office is very pleased with the design aesthetic,” says Coughlin. “The windows reflect the aesthetics that would be expected on a school from this particular era, yet add the performance we expect today.” +
Related Stories
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 2, 2010
Historic changes to commercial building energy codes drive energy efficiency, emissions reductions
Revisions to the commercial section of the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) represent the largest single-step efficiency increase in the history of the national, model energy. The changes mean that new and renovated buildings constructed in jurisdictions that follow the 2012 IECC will use 30% less energy than those built to current standards.
| Nov 1, 2010
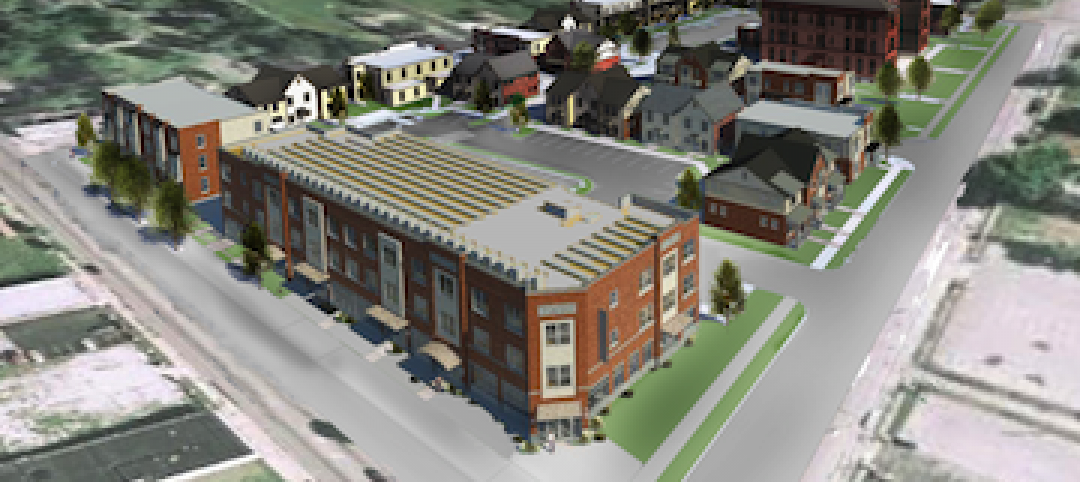
Sustainable, mixed-income housing to revitalize community
The $41 million Arlington Grove mixed-use development in St. Louis is viewed as a major step in revitalizing the community. Developed by McCormack Baron Salazar with KAI Design & Build (architect, MEP, GC), the project will add 112 new and renovated mixed-income rental units (market rate, low-income, and public housing) totaling 162,000 sf, plus 5,000 sf of commercial/retail space.
| Nov 1, 2010
John Pearce: First thing I tell designers: Do your homework!
John Pearce, FAIA, University Architect at Duke University, Durham, N.C., tells BD+C’s Robert Cassidy about the school’s construction plans and sustainability efforts, how to land work at Duke, and why he’s proceeding with caution when it comes to BIM.
| Nov 1, 2010
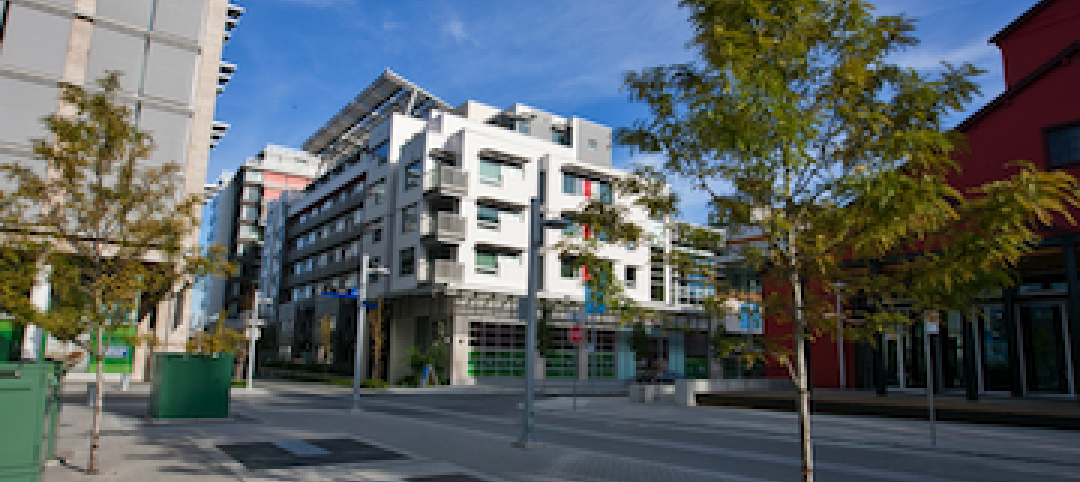
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 27, 2010
Grid-neutral education complex to serve students, community
MVE Institutional designed the Downtown Educational Complex in Oakland, Calif., to serve as an educational facility, community center, and grid-neutral green building. The 123,000-sf complex, now under construction on a 5.5-acre site in the city’s Lake Merritt neighborhood, will be built in two phases, the first expected to be completed in spring 2012 and the second in fall 2014.
| Oct 21, 2010
GSA confirms new LEED Gold requirement
The General Services Administration has increased its sustainability requirements and now mandates LEED Gold for its projects.
| Oct 18, 2010
World’s first zero-carbon city on track in Abu Dhabi
Masdar City, the world’s only zero-carbon city, is on track to be built in Abu Dhabi, with completion expected as early as 2020. Foster + Partners developed the $22 billion city’s master plan, with Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture, Aedas, and Lava Architects designing buildings for the project’s first phase, which is on track to be ready for occupancy by 2015.