Related Stories
University Buildings | Dec 5, 2023
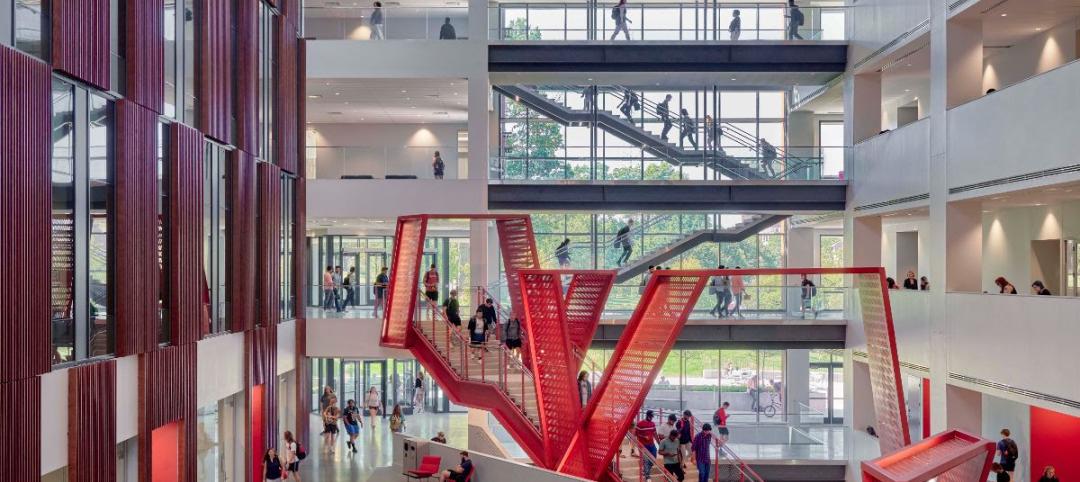
The University of Cincinnati builds its largest classroom building to serve its largest college
The University of Cincinnati’s recently completed Clifton Court Hall unifies the school’s social science programs into a multidisciplinary research and education facility. The 185,400-sf structure is the university’s largest classroom building, serving its largest college, the College of Arts and Sciences.
MFPRO+ News | Dec 5, 2023
DOE's Zero Energy Ready Home Multifamily Version 2 released
The U.S. Department of Energy has released Zero Energy Ready Home Multifamily Version 2. The latest version of the certification program increases energy efficiency and performance levels, adds electric readiness, and makes compliance pathways and the certification process more consistent with the ENERGY STAR Multifamily New Construction (ESMFNC) program.
Architects | Dec 5, 2023
Populous celebrates its 40th anniversary with a photo exhibit of its works
The firm partnered with Getty Images to assemble more than 60 images, many capturing fan ardor.
Office Buildings | Dec 1, 2023
Amazon office building doubles as emergency housing for Seattle families
The unusual location for services of this kind serves over 300 people per day. Mary's Place spreads across eight of the office's floors—all designed by Graphite—testing the status quo for its experimental approach to homelessness support.
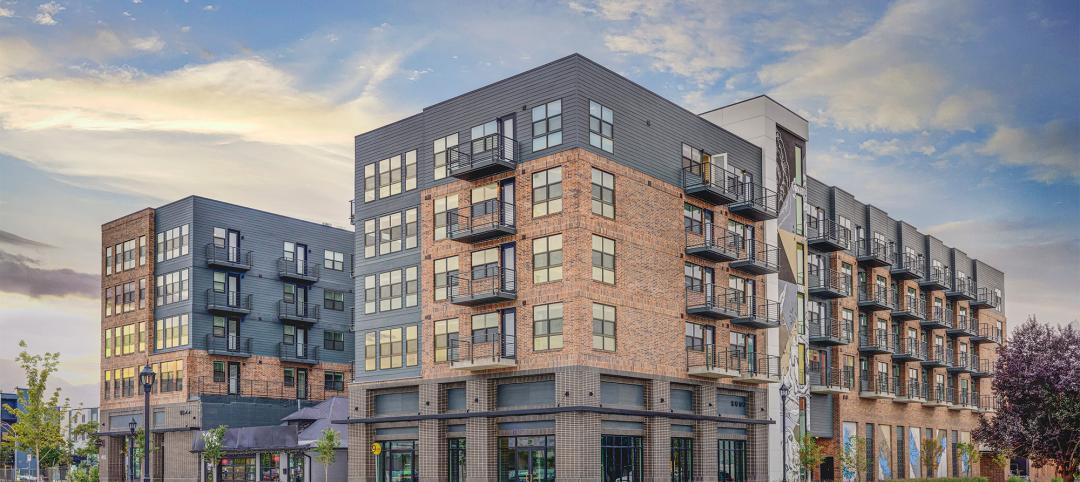
Mixed-Use | Nov 29, 2023
Mixed-use community benefits from city amenities and ‘micro units’
Salt Lake City, Utah, is home to a new mixed-use residential community that benefits from transit-oriented zoning and cleverly designed multifamily units.
Giants 400 | Nov 28, 2023
Top 100 Laboratory Design Firms for 2023
HDR, Flad Architects, DGA, Elkus Manfredi Architects, and Gensler top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest laboratory architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Engineers | Nov 27, 2023
Kimley-Horn eliminates the guesswork of electric vehicle charger site selection
Private businesses and governments can now choose their new electric vehicle (EV) charger locations with data-driven precision. Kimley-Horn, the national engineering, planning, and design consulting firm, today launched TREDLite EV, a cloud-based tool that helps organizations develop and optimize their EV charger deployment strategies based on the organization’s unique priorities.
Market Data | Nov 27, 2023
Number of employees returning to the office varies significantly by city
While the return-to-the-office trend is felt across the country, the percentage of employees moving back to their offices varies significantly according to geography, according to Eptura’s Q3 Workplace Index.
Resiliency | Nov 27, 2023
All levels of government need to act to cope with climate-driven flooding and sea level rise
The latest National Climate Assessment highlights the need for local, state, and federal governments to adopt policies to mitigate the effects of climate-driven flooding and sea level rise, according to a policy expert with the National Resources Defense Council.
Data Centers | Nov 22, 2023
How is artificial intelligence impacting data center design?
As AI is reshaping how we interact with machines and the world around us, the design of data centers needs to adapt to this fast-changing landscape. So, Page pairs expert thinking with high-performing solutions to meet the needs of rapidly advancing technologies.