HIGHER ED’S ‘EDIFICE COMPLEX’
Describing American colleges and universities as suffering from an “Edifice Complex,” in 2012 the New York Times reported that, “A decade-long binge to build academic buildings, dormitories and recreation facilities – some of them inordinately lavish to attract new students – has left colleges and universities saddled with large amounts of debt.”
One calculation at the time showed that the amount of campus space per student had nearly tripled since 1974.
It was clear then, as it is now, that this kind of growth is unsustainable. And yet despite deep cuts in state funding and flattening enrollment, this building spree has continued. In 2015, American colleges and universities went on to spend a record $11.5 billion on construction, creating 21 million SF of new space even as they faced a record $30 billion shortfall in deferred maintenance costs on existing facilities.
What’s driving campus growth is clear. As public funding for higher education has fallen and colleges and universities find themselves ever more dependent on tuition dollars, they’ve relied on debt financing to build the kinds of spaces, they hope, will attract and retain more students (State of Facilities in Higher Education).
With COVID-19 putting additional pressures on budgets and shutting down or restricting campus access, endless campus expansions are even less tenable. At the same time, the near universal adoption of remote learning in Spring 2020 has opened new pedagogical opportunities that may lessen the demand for more space – not just this year but into 2022 and beyond. Given this confluence of events, it’s likely that colleges’ appetite for new construction will be diminished for the foreseeable future.
A pivot from ever-expanding campuses towards more compact and better-utilized ones cannot resolve the underlying funding issue, but it can help control most colleges and universities’ second largest expense: their facilities. This transition will inevitably involve university architects, planners, and administrators reconsidering—and repurposing—their existing space. There is no one-size-fits-all strategy for managing a campus’s spatial needs. Your institution’s plan needs to reflect its character. However, there are some key considerations to account for when making decisions to ensure the resiliency and adaptability of your campus.

CONSIDERATIONS FOR SMART GROWTH
Mission. Your college or university’s mission should be at the heart of any space planning decisions that are made. What is the mission of the university? How do time and circumstance shape that mission? The answers to these questions should guide your planning process.
Space Typology. It’s important to understand the priority and characteristics of your campus spaces. Your campus likely requires a mix of research labs, learning spaces, libraries, student life spaces, and administrative offices. When evaluating how to develop, allocate, or repurpose campus spaces, you should consider the likelihood that the need for them will endure, the frequency of their use, their relative value to those who use them, and their ability to double as immersive communities.
Space Funding. What spaces are revenue generating? This concern shouldn’t diminish all others, but you also don’t want to interrupt a valuable funding stream. Most universities and colleges have a grant-tracking system in place. Correlating space data with your grant-tracking system can create a useful metric for evaluating a space’s effectiveness.
How are your rooms and buildings paid for? Are you using grants, funding from alumni, donors, etc.? While you may want to repurpose a space (and may be physically be able to do so), it’s important to understand whether it’s reserved or off-limits due to its funding source.
Flexibility, Adaptability, “Repurposeability.” For planning a resilient, robustly-used campus, two key spatial characteristics are flexibility and adaptability. Flexibility is a measure of a space’s capacity to support different uses over the course of a day or week, while adaptability is a longer-term measure of its ability to support fundamental use changes with minimal architectural intervention to the infrastructure. Taken together—and combined with other factors that affect space planning (funding sources, revenue-generation, space utilization data, etc.)—these factors determine what we call the “repurposeability” of a space.
Most colleges plan for flexibility. Some plan for adaptability. Few, if any, bring all of these factors together into a comprehensive analysis that provides a holistic view of an institution’s future space needs. But this type of analysis could help campuses avoid costly expansion or repurposing while existing spaces are underutilized.
DATA-DRIVEN PLANNING
But before you make these decisions, it’s imperative to determine how you can measure the use of existing spaces, and what data you have available—or can generate—in order to evaluate what kinds of spaces you actually need (vs. what you already have). Be resourceful! It may not be simple or centralized as you begin to gather this data, but you’d be surprised how much you already have at hand.
Once data is identified and analyzed, variables can be assigned to key questions and a space’s “repurposeability” can be rated. Spaces can then be plotted along a “repurposeability” spectrum. See example below.

As you begin to measure the “repurposeability” of your space, maintain focus on what factors are influencing the decisions within your college or university and what are the best, most cost-effective, and judicious actions that you can take to forward your institution’s mission.
PREPARING FOR THE FUTURE
While there’s no perfect formula or single answer that will work for all campuses, what has been made clear by COVID-19 is the need for spaces that can change to meet changing needs. Further, the reliance on data to make informed decisions is critical – and although you may have some segment of this data now in an ad-hoc collection of systems or spreadsheets, you should consider how to make that data usable for all your space planning needs. As your institution continues to repurpose existing spaces or build new ones, it’s also advisable to develop a plan for generating and storing space-related data in a centralized, easily accessible, and user-friendly format to simplify this process in the future.
If COVID-19 and its impacts on the spring and fall semesters of 2020 has taught us anything, it’s that it is impossible to predict future events. But data-driven planning that integrates the concept of “repurposeability” can help universities manage the financial, social, and pedagogical impacts of an unpredictable future.
Related Stories
Education Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
DLR Group’s Campus Planning Studio defines new leadership
Linsey Graff named Campus Planning Leader. Krisan Osterby transitions to Senior Planner.
Student Housing | Mar 13, 2023
University of Oklahoma, Missouri S&T add storm-safe spaces in student housing buildings for tornado protection
More universities are incorporating reinforced rooms in student housing designs to provide an extra layer of protection for students. Storm shelters have been included in recent KWK Architects-designed university projects in the Great Plains where there is a high incidence of tornadoes. Projects include Headington and Dunham Residential Colleges at the University of Oklahoma and the University Commons residential complex at Missouri S&T.
Virtual Reality | Feb 27, 2023
Surfing the Metaversity: The future of online learning?
SmithGroup's tour of the Metaversity gives us insight on bringing together physical and virtual campuses to create a cohesive institution.
University Buildings | Feb 23, 2023
Johns Hopkins shares design for new medical campus building named in honor of Henrietta Lacks
In November, Johns Hopkins University and Johns Hopkins Medicine shared the initial design plans for a campus building project named in honor of Henrietta Lacks, the Baltimore County woman whose cells have advanced medicine around the world. Diagnosed with cervical cancer, Lacks, an African-American mother of five, sought treatment at the Johns Hopkins Hospital in the early 1950s. Named HeLa cells, the cell line that began with Lacks has contributed to numerous medical breakthroughs.
Sustainability | Feb 9, 2023
University of Southern California's sustainability guidelines emphasize embodied carbon
A Buro Happold-led team recently completed work on the USC Sustainable Design & Construction Guidelines for the University of Southern California. The document sets out sustainable strategies for the design and construction of new buildings, renovations, and asset renewal projects.
University Buildings | Feb 9, 2023
3 ways building design can elevate bold thinking and entrepreneurial cultures
Mehrdad Yazdani of CannonDesign shares how the visionary design of a University of Utah building can be applied to other building types.
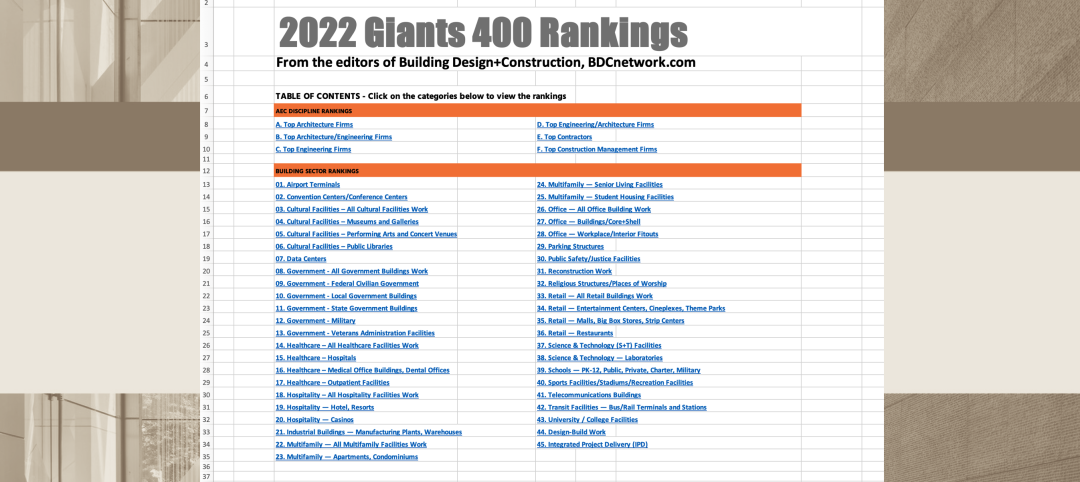
Giants 400 | Feb 9, 2023
New Giants 400 download: Get the complete at-a-glance 2022 Giants 400 rankings in Excel
See how your architecture, engineering, or construction firm stacks up against the nation's AEC Giants. For more than 45 years, the editors of Building Design+Construction have surveyed the largest AEC firms in the U.S./Canada to create the annual Giants 400 report. This year, a record 519 firms participated in the Giants 400 report. The final report includes 137 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
University Buildings | Feb 8, 2023
STEM-focused Kettering University opens Stantec-designed Learning Commons
In Flint, Mich., Kettering University opened its new $63 million Learning Commons, designed by Stantec. The new facility will support collaboration, ideation, and digital technology for the STEM-focused higher learning institution.
University Buildings | Feb 7, 2023
Kansas City University's Center for Medical Education Innovation can adapt to changes in medical curriculum
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) at Kansas City University was designed to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy. The project program supported the mission of training leaders in osteopathic medicine with a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training.
Giants 400 | Feb 6, 2023
2022 Reconstruction Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. building reconstruction and renovation sector
Gensler, Stantec, IPS, Alfa Tech, STO Building Group, and Turner Construction top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest reconstruction sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2022 Giants 400 Report.