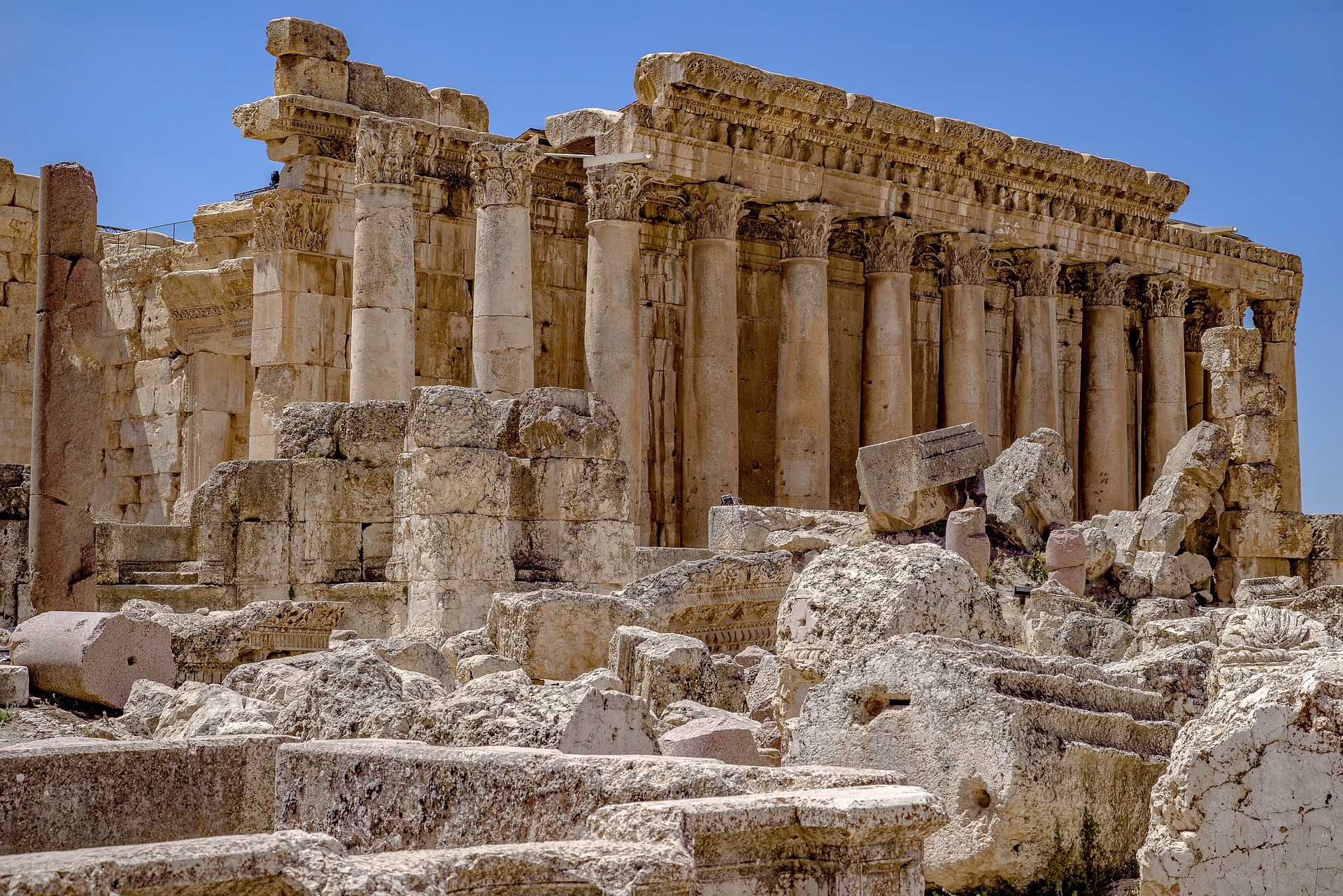
Researchers have turned to an ancient Roman concrete recipe to develop more durable concrete that lasts for centuries and can potentially reduce the carbon impact of the built environment.
To construct architectural marvels that still stand today, ancient Romans combined lime, volcanic ash, and aggregates with water to create concrete. A key difference from how modern concrete is processed is temperature.
Today, we use cold mixing—a process conducted under ambient temperatures—but Romans used hot mixing, heating the mixture to 180 degrees Fahrenheit. This resulted in a key change in the lime that provides concrete with the ability to self-heal.
“Due to hot mixing and creation of these tiny granules of lime due to hot mixing, eventually you create a mechanism that just naturally goes and fills the crack with the material and prevents water to flow and propagation of the crack,” an MIT professor told National Public Radio. If modern manufacturers can emulate the ancient method, the result would be longer lasting structures that in the long run will result in using less concrete which will correspond to less emissions.
Listen to the NPR Weekend Edition segment:
Related Stories
| May 15, 2014
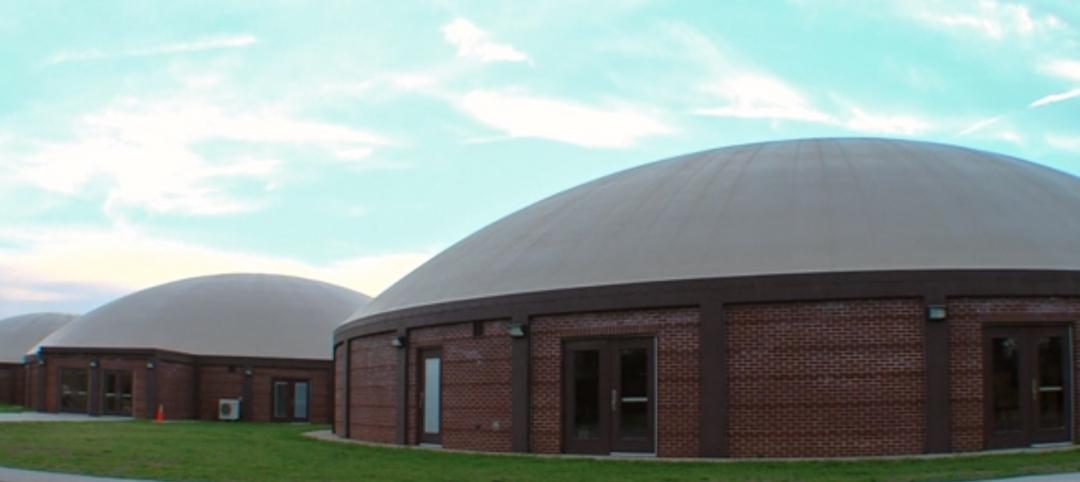
'Virtually indestructible': Utah architect applies thin-shell dome concept for safer schools
At $94 a square foot and "virtually indestructible," some school districts in Utah are opting to build concrete dome schools in lieu of traditional structures.
| Feb 14, 2014
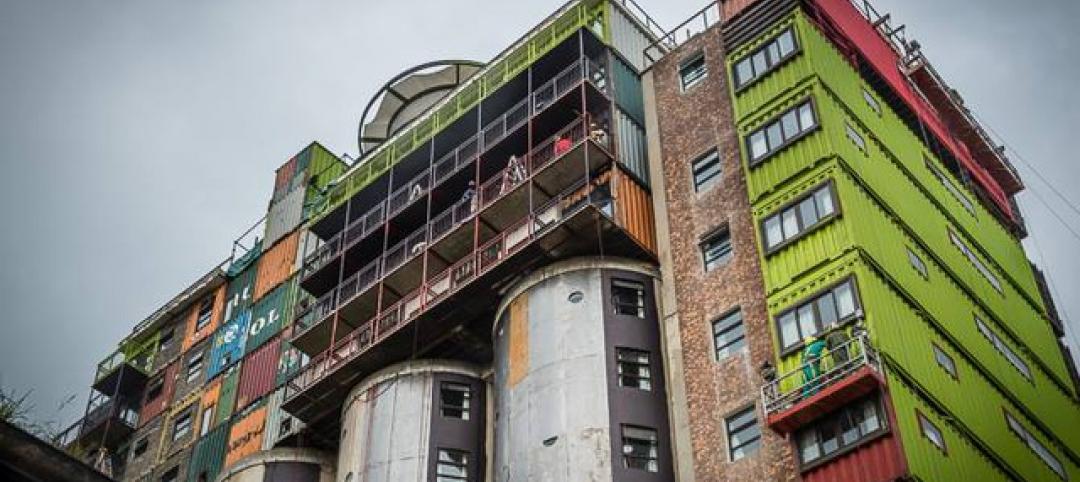
Must see: Developer stacks shipping containers atop grain silos to create student housing tower
Mill Junction will house up to 370 students and is supported by 50-year-old grain silos.
| Feb 5, 2014
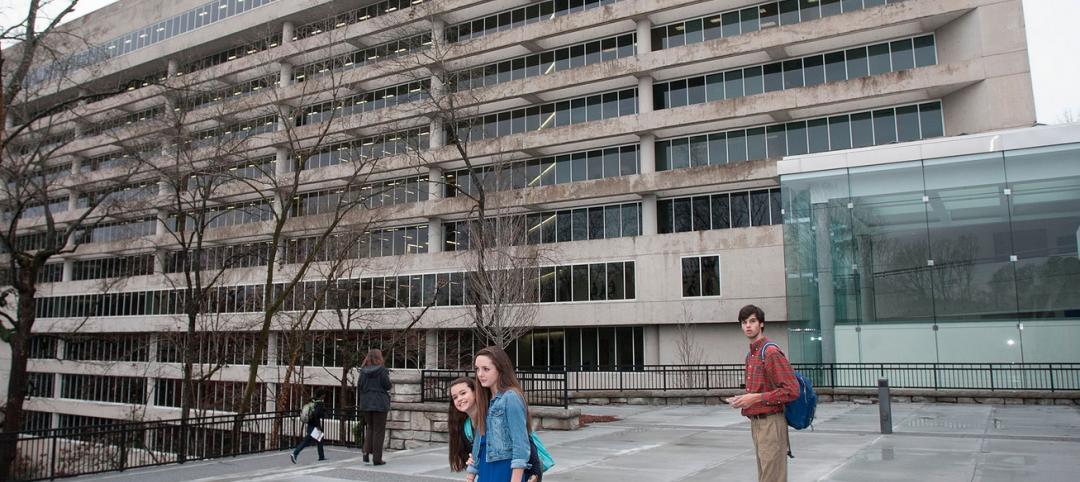
Extreme conversion: Atlanta turns high-rise office building into high school
Formerly occupied by IBM, the 11-story Lakeside building is the new home for North Atlanta High School.
| Feb 5, 2014
7 towers that define the 'skinny skyscraper' boom [slideshow]
Recent advancements in structural design, combined with the loosening of density and zoning requirements, has opened the door for the so-called "superslim skyscraper."
| Jan 28, 2014
2014 predictions for skyscraper construction: More twisting towers, mega-tall projects, and 'superslim' designs
Experts from the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat release their 2014 construction forecast for the worldwide high-rise industry.
| Jan 24, 2014
Structural concrete requirements under revision: ACI 318 standard
The American Concrete Institute (ACI), an organization whose mission is to develop and disseminate consensus-based knowledge on concrete and its uses, is finalizing a completely reorganized ACI 318-14: Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete.
| Jan 7, 2014
Concrete solutions: 9 innovations for a construction essential
BD+C editors offer a roundup of new products and case studies that represent the latest breakthroughs in concrete technology.
| Dec 12, 2013
Book announcement: The economic performance of sustainable construction
Thirty specialists from around the world challenge the question of (higher) costs related to sustainability of the built environment
| Dec 10, 2013
16 great solutions for architects, engineers, and contractors
From a crowd-funded smart shovel to a why-didn’t-someone-do-this-sooner scheme for managing traffic in public restrooms, these ideas are noteworthy for creative problem-solving. Here are some of the most intriguing innovations the BD+C community has brought to our attention this year.
| Nov 27, 2013
Wonder walls: 13 choices for the building envelope
BD+C editors present a roundup of the latest technologies and applications in exterior wall systems, from a tapered metal wall installation in Oklahoma to a textured precast concrete solution in North Carolina.