There are many new and exciting applications for data analysis in the construction industry, the vast majority of which employ new data aggregation tools to quantify and analyze specific aspects of the built environment, often numerical aspects like square foot totals, or asset management counts. But there are other important uses for data tools for more abstract attributes of the built environment, such as tracking, analyzing and evaluating risk.
This case-study details a facilities assessment for a government client who needed to understand the range of risk types and impacts that could potentially occur in their buildings. The analysis was triggered when a single pipe failure on the 11th floor of one facility unleashed a cascade of unforeseen consequences as it made its way to ground, almost paralyzing the facility for several days. The consequences rippled through the facility long after the event.
As a result, the client, a proactive owner-occupier, commissioned a comprehensive assessment of their three largest facilities to help enumerate and understand other similar vulnerabilities in each facility, so as to avoid future similar exposures.
Evaluating the Facilities
As a first step, the team visited the three facilities, totaling over two million SF, and surveyed each system’s equipment and arrangement. Because each of the facilities was large, and built over several decades, the range of equipment and systems encountered varied from new to those which were teetering on the end of their useful life. All of this data was captured with a brief narrative for each item, as well as a mitigation strategy.
Once the list of infrastructure, equipment, layout and configurations of each facility was completed, the team assigned each of the identified issues a category, such as site work, building envelope, electrical equipment, mechanical systems and even security protocols. In addition, they further classified each item according to two important decision-oriented factors: 1) its likelihood to occur, and 2) the impact of a failure were it to occur. They then took the categorized items and assigned a rough dollar amount to address and fix each work item.
The data had several data categories, or “dimensions.”
When completed, the final spreadsheet was a lengthy inventory of future work-items arranged by category, cost, likelihood and severity. In data jargon, each of these traits – category, cost severity, likelihood, etc. - would be called ‘dimensions’, that is aspects of the item that help to understand the problem. Each dimension represents a way to slice the data. Thus, with the right tool an owner could start to drill into the hundreds of items, even with combinations of dimensions.
Leveraging Data Tools
With over 1,000 items cataloged and several dimensions to simultaneously evaluate, the next task was to address was how best to turn the data into information – that is actionable decisions to help address the facility needs. In its raw form, the initial spreadsheet report was rich with information but was somewhat cumbersome to navigate for everyday use by the facility manager.
ALSO SEE: BI(m): BIM data without models
In addition, with so many measures, the team needed the capability to drill down into the findings to be able to pose various questions:
• Which items were the most critical points of failure for service continuity?
• Were there certain categories of vulnerabilities that occurred frequently in each facility?
• What was the total capital cost by category, such as critical items and less critical items?
These were all valid questions that would take quite a while to deduce from a straight spreadsheet format. For the next step, the team imported the raw data into a data analysis application.
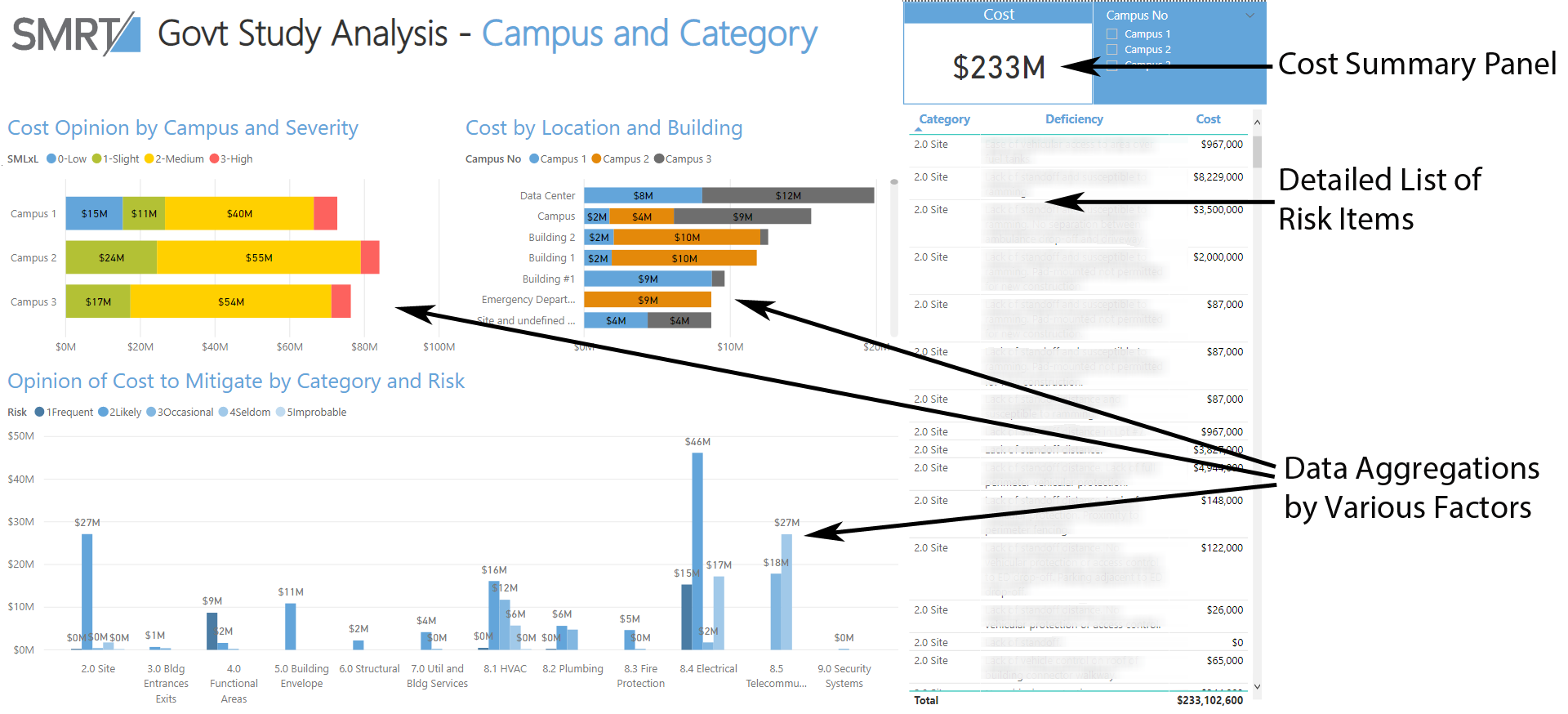
A collection of charts on a single page; each chart is interactive, so that clicking on it filters the surrounding charts.
By using the advanced pivoting and aggregation of data analytical tools, the engineering team was able to scrutinize the data and display it graphically in a way the facility manager could more readily comprehend. A diverse collection of tables and column charts, organized and colored by severity or category, told a far more vivid story of the work items for each facility. For example, it was easier to see which items needed to be addressed immediately and which were those that could happen sometime over a longer timeframe.
3D charts with a color legend can display four dimensions at once.
Using the data tools, the team was even able to create three-dimensional chart formats that provided a very rich assessment of each item by campus, capital cost, severity and likelihood of occurrence all in a single comprehensive view. Each item could also display additional information about the line item when the user hovered over it. Thus, the new data tools allowed the reader to comprehend major trends and highpoints in a highly integrated way.
Even after the site survey activity was complete, there were further opportunities to ‘extend’ - or enhance - the original raw survey data spreadsheet with other data points subsequent to the survey, such as an anticipated contract date for when each item might need to be performed. As a result, extending the data resulted in a date chart to gauge future expenditures for each year, and also an average yearly spend rate for the facilities. The team could see that in 15 years for example, a large sum of funds would be needed to avoid disruptions to services. This chart could be further analyzed by severity or impact.
An anticipated contract date was added to each work item to forecast capital expenditures over the next 25 years.
Seeing the Forest AND the Tree
The risk analysis study illustrated how risk mitigation studies can be greatly enhanced with new data tools. We like to say that the team sees the power of data analytics to be that the owner “can see the forest AND the tree” – meaning, - where previous typical reports either summarized the findings, (the Forest), or itemized them in individual detail, (the Trees), - these new tools allowed the forest of measures to be displayed at once, and then through drilldown and interactive graphics, enabled custom aggregations as well as isolation of individual trees. As such, data analysis tools constitute a significant leap for facility managers and building professionals to help catalog, understand and strategize around facility conditions and plan future capital expenditures to address risks and vulnerabilities.
The uses of data in construction go far beyond mere floor areas and quantities, - in this case evaluating the risk posed to critical facilities. What is most valuable about these tools is how they helped to make complex and abstract aspects of buildings more visible.
About the Author
John Tobin is the Albany, N.Y., Office Director for SMRT Architects and Engineers, headquartered in Portland, Maine. He has spent three decades spearheading new practice technologies, especially BIM and advanced delivery, and then as an AE technology and operations leader. Most recently, Tobin has begun integrating new data analysis techniques with BIM processes.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Mar 9, 2024
9 steps for implementing digital transformation in your AEC business
Regardless of a businesses size and type, digital solutions like workflow automation software, AI-based analytics, and integrations can significantly enhance efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
AEC Tech | Feb 28, 2024
How to harness LIDAR and BIM technology for precise building data, equipment needs
By following the Scan to Point Cloud + Point Cloud to BIM process, organizations can leverage the power of LIDAR and BIM technology at the same time. This optimizes the documentation of existing building conditions, functions, and equipment needs as a current condition and as a starting point for future physical plant expansion projects.
AEC Innovators | Feb 28, 2024
How Suffolk Construction identifies ConTech and PropTech startups for investment, adoption
Contractor giant Suffolk Construction has invested in 27 ConTech and PropTech companies since 2019 through its Suffolk Technologies venture capital firm. Parker Mundt, Suffolk Technologies’ Vice President–Platforms, recently spoke with Building Design+Construction about his company’s investment strategy.
AEC Tech | Feb 20, 2024
AI for construction: What kind of tool can artificial intelligence become for AEC teams?
Avoiding the hype and gathering good data are half the battle toward making artificial intelligence tools useful for performing design, operational, and jobsite tasks.
AEC Tech | Feb 20, 2024
ABC releases technology guide for AI in construction
Associated Builders and Contractors has released an artificial intelligence (AI) technology guide for the U.S. construction industry. AI in Construction — What Does It Mean for Our Contractors? outlines definitions, construction use cases, and considerations for the implementation of AI in construction.
AEC Tech | Jan 24, 2024
4 ways AEC firms can benefit from digital transformation
While going digital might seem like a playground solely for industry giants, the truth is that any company can benefit from the power of technology.
Modular Building | Jan 19, 2024
Building with shipping containers not as eco-friendly as it seems
With millions of shipping containers lying empty at ports around the world, it may seem like repurposing them to construct buildings would be a clear environmental winner. The reality of building with shipping containers is complicated, though, and in many cases isn’t a net-positive for the environment, critics charge, according to a report by NPR's Chloe Veltman.
AEC Tech | Jan 8, 2024
What's driving the surge of digital transformation in AEC today?
For centuries, the AEC industry has clung to traditional methods and legacy processes—seated patterns that have bred resistance to change. This has made the adoption of new technologies a slow and hesitant process.
Sustainability | Nov 1, 2023
Researchers create building air leakage detection system using a camera in real time
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a system that uses a camera to detect air leakage from buildings in real time.
Building Owners | Aug 23, 2023
Charles Pankow Foundation releases free project delivery selection tool for building owners, developers, and project teams
Building owners and project teams can use the new Building Owner Assessment Tool (BOAT) to better understand how an owner's decision-making profile impacts outcomes for different project delivery methods.















