In 2009, we met with Senior Facility Managers of four U.S. national laboratories to discuss a major limitation in the way they summarized their capital needs. As with most large organizations, they expressed capital needs in terms of deferred maintenance projects—things that needed to be fixed as determined by condition assessment (inspection or prescribed schedule). To put these needs in perspective, they computed a facility condition index (FCI), which is the ratio of deferred maintenance (D.M) costs to the replacement value of a building or portfolio.
Several years later, following the acquisition of Whitestone Research by CBRE Inc., it quickly became clear that major healthcare organizations around the world oftentimes employ a similar FCI based approach to their capital planning and prioritization decisions.
FACILITY CONDITION INDEX BREAKDOWN
According to a well-known scale developed initially for educational facilities in 1991, a facility is considered in poor condition if its FCI exceeds 90%. The shortcomings of the FCI approach are well-known, as results are not easily compared with alternative condition assessment approaches, and it does not contemplate methodologies for determining replacement values. These choices can become highly political for an organization that uses, as many do, the FCI as a key policy metric.
The basic concern of the laboratory facility managers was that the FCI did not represent the true condition of the facility in terms of safety, security, mission relevance, and other criteria that actually guide their decisions. FCI is also not a forecast or leading indicator that demonstrates consequences of alternative actions. These concerns led to a series of small projects that would eventually define a new approach to summarizing facility condition and prioritizing capital expenditures.
The new method, Risk Scanning, meets three requirements identified in our original meeting. The process must not rely on expensive inspections, must incorporate multiple (customizable) criteria, and the outcomes must be expressed as a simple monetary value.
This approach has universal applicability for laboratories and for large, corporate occupiers. In addition, we have found this approach to be particularly relevant for healthcare organizations today, given the extraordinary economic and regulatory pressures that have become a reality for the industry.
RISK SCANNING
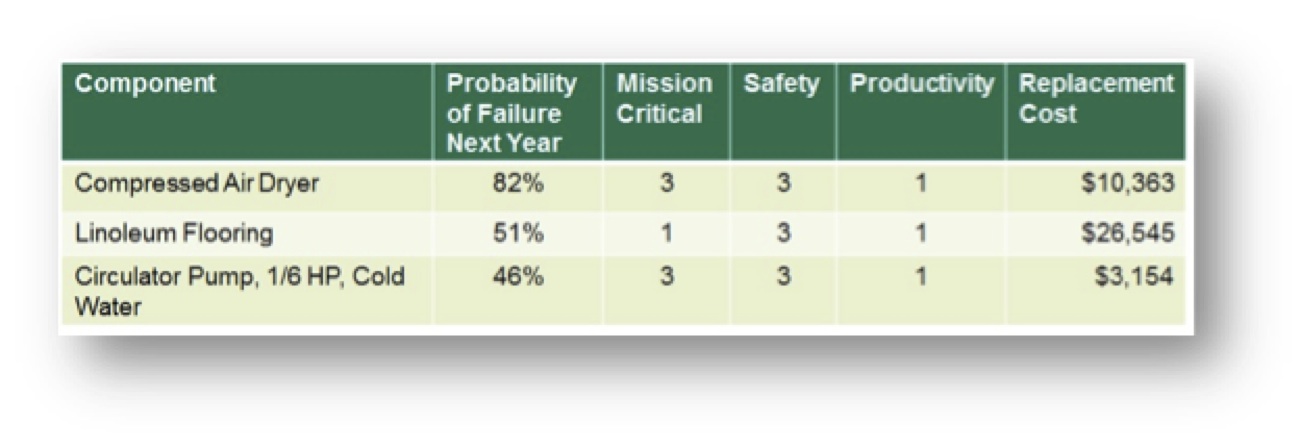
Risk Scanning assumes that buildings or other assets can be reduced to an inventory of components (roof, HVAC equipment, plumbing fixtures, etc.). Each component has a “survivor” curve that relates its age to the likelihood of its failure in the future, little different than an actuarial calculation for an insurance policy. And each component, should it fail, could have consequences for the building operation. Below, Figure 1 illustrates how this data could be used as a simple sort by probability of failure, consequence of failure, or replacement cost.
A more useful view of this data combines knowledge of the probability of failure and the potential consequences as the Risk Facility Managers implicitly consider when scheduling repairs. For example, a new light bulb in a closet would be low risk (low likelihood of failure, low impact on safety, security, mission, etc.), while a roof or electrical panel, far beyond their expected service life would be a high risk. Individual component risk ratings can be aggregated into risk maps by building, consequence type, or aggregated at the portfolio level.
Another example is a risk scan of a data center built in 1980, as shown in Figure 2. Risk is summarized by three consequences or threats of failure – mission, productivity and safety. The “Loss Intensity” is the measure (low, medium, high) of the impact of failure. Each cell in the tables is the sum of the replacement value of each component. For instance, in the first table there are high risk (red) components with replacement values totaling $374,210.
Figure 2: Dashboard showing risk by consequence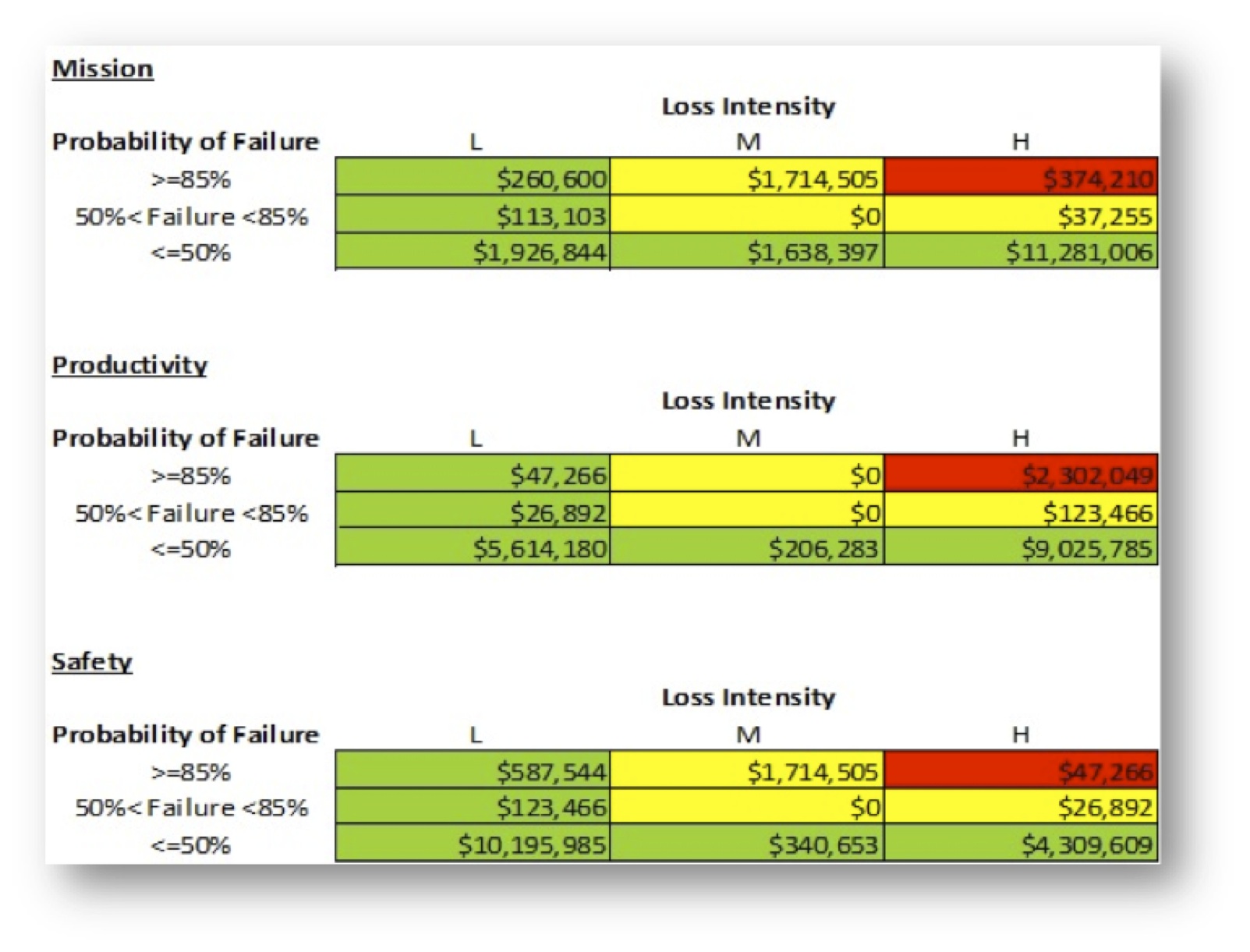
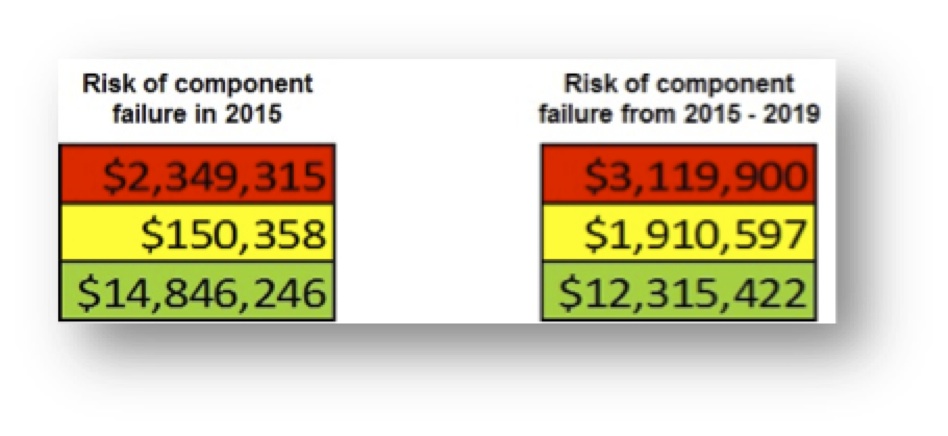
One way to represent overall risk is to sum across the individual tables in Figure 2, by risk category (red = high, yellow = moderate, green = low) to produce a single risk column, as shown in Figure 3. This shows that the costs to replace components rated high risk in 2015 for any reason (mission, productivity, or safety) were $2,349,315. Note that some components are high risk for multiple reasons.
The calculation of the column can be modified for different purposes. The ratings from the dashboard could be weighted to reflect management priorities. The likelihood of failure, and consequent migration of risk ratings, could be estimated for a range of years, as shown for the period 2015-2019.
COMPARING THE FCI WITH RISK SCANNING
The data center example provides a useful comparison of the output from a simple condition assessment with the additional data provided by Risk Scanning.
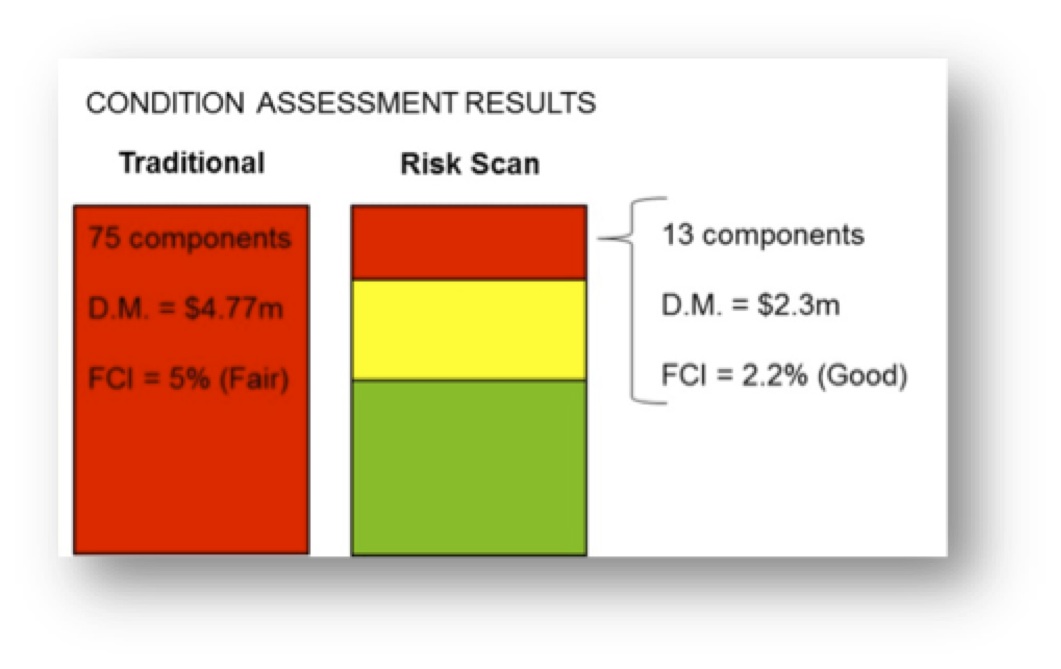
A conventional facility condition assessment using a life cycle cost model indicated that 75 components had exceeded their service life. The costs of replacing these would be $4,771,159. Considering this amount to be deferred maintenance (D.M.), the FCI would be 5% (given $100 million replacement value). This would be summarized as a building in “fair” condition.
A Risk Scan of the component inventory indicates that 13 components are at high risk, and the costs of replacing these would be $2,349,315. This is less than half the costs of replacements by a simple service life-assessment. An FCI based on high risk components would be 2.2%, indicating a building in “good” condition.
In this case, with the additional information provided by Risk Scanning, the facility would be considered in better condition than with the simple condition assessment. Moreover, the risk scan would provide a rating for all components—including those not yet considered as deferred maintenance—as a basis for anticipating future needs and prioritization.
CONCLUSION
The Risk Scanning approach uses well-known risk analytics applied to pre-existing facility data to provide a richer view of facility condition more consistent with actual management decision making. In practice, limited funding is directed to those repairs and replacements that address corporate priorities, such as safety, security, and mission achievement. For healthcare systems, this approach can provide critical insight for decision-making about capital deployment where actionable criteria are not established or where data is limited.
About the Authors
Peter Lufkin is Senior Managing Director and Luca Romani is Senior Analyst with CBRE Whitestone.
Related Stories
Adaptive Reuse | Sep 12, 2024
White paper on office-to-residential conversions released by IAPMO
IAPMO has published a new white paper titled “Adaptive Reuse: Converting Offices to Multi-Residential Family,” a comprehensive analysis of addressing housing shortages through the conversion of office spaces into residential units.
Mixed-Use | Sep 10, 2024
Centennial Yards, a $5 billion mixed-use development in downtown Atlanta, tops out its first residential tower
Centennial Yards Company has topped out The Mitchell, the first residential tower of Centennial Yards, a $5 billion mixed-use development in downtown Atlanta. Construction of the apartment building is expected to be complete by the middle of next year, with first move-ins slated for summer 2025.
Healthcare Facilities | Sep 9, 2024
Exploring the cutting edge of neuroscience facility design
BWBR Communications Specialist Amanda Fisher shares the unique considerations and challenges of designing neuroscience facilities.
Office Buildings | Sep 6, 2024
Fact sheet outlines benefits, challenges of thermal energy storage for commercial buildings
A U.S. Dept. of Energy document discusses the benefits and challenges of thermal energy storage for commercial buildings. The document explains how the various types of thermal energy storage technologies work, where their installation is most beneficial, and some practical considerations around installations.
Office Buildings | Sep 5, 2024
Office space downsizing trend appears to be past peak
The office downsizing trend may be past its peak, according to a CBRE survey of 225 companies with offices in the U.S., Canada, and Latin America. Just 37% of companies plan to shrink their office space this year compared to 57% last year, the survey found.
University Buildings | Sep 4, 2024
UC San Diego’s new Multidisciplinary Life Sciences Building will support research and teaching in both health and biological sciences
The University of California San Diego has approved plans for a new Multidisciplinary Life Sciences Building, with construction starting this fall. The 200,000-sf, six-level facility will be the first building on the UC San Diego campus to bridge health science research with biological science research and teaching.
Codes and Standards | Sep 3, 2024
Atlanta aims to crack down on blighted properties with new tax
A new Atlanta law is intended to crack down on absentee landlords including commercial property owners and clean up neglected properties. The “Blight Tax” allows city officials to put levies on blighted property owners up to 25 times higher than current millage rates.
Resiliency | Sep 3, 2024
Phius introduces retrofit standard for more resilient buildings
Phius recently released, REVIVE 2024, a retrofit standard for more resilient buildings. The standard focuses on resilience against grid outages by ensuring structures remain habitable for at least a week during extreme weather events.
Construction Costs | Sep 2, 2024
Construction material decreases level out, but some increases are expected to continue for the balance Q3 2024
The Q3 2024 Quarterly Construction Insights Report from Gordian examines the numerous variables that influence material pricing, including geography, global events and commodity volatility. Gordian and subject matter experts examine fluctuations in costs, their likely causes, and offer predictions about where pricing is likely to go from here. Here is a sampling of the report’s contents.
Adaptive Reuse | Aug 29, 2024
More than 1.2 billion sf of office space have strong potential for residential conversion
More than 1.2 billion sf of U.S. office space—14.8% of the nation’s total—have strong potential for conversion to residential use, according to real estate software and services firm Yardi. Yardi’s new Conversion Feasibility Index scores office buildings on their suitability for multifamily conversion.