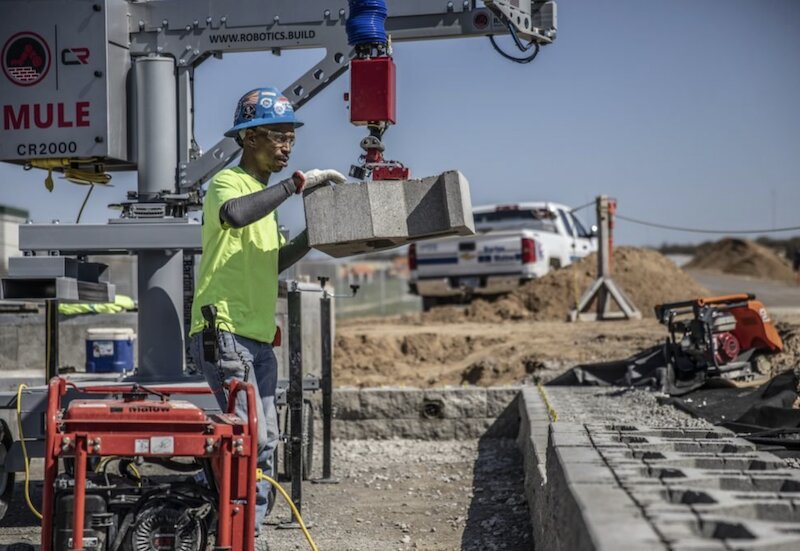
A 166,000-sf barracks with 300 bedrooms for 600 military personnel is under construction at the Great Lakes Naval Base in Illinois with the help of robots that can lay bricks every seven to 10 seconds and can lift and place foundation blocks weighing up to 135 lbs.
This $52 million project, started last March and scheduled for completion in October 2020, represents the debut of semi-robotic construction for the general contractor Clark Construction Group. Construction Robotics, a Victor, N.Y.-based manufacturer that launched in 2007, is providing the machines, which are called MULE (for Material Unit Lift Enhancer) and SAM (for Semiautomated Mason). Blinderman Constuction is Clark's partner on this project.
This is also the first construction project in the country to use MULE and SAM technology in tandem.
There are currently more than 130 MULEs operating in the field, and 11 SAMs, with more under production, says Scott Peters, president and cofounder of Construction Robotics. His company has worked with more than 80 contractors, from large GCs like Barton Malow and Wilhelm Construction, to local masonry subcontractors like Leidal & Hart Mason Contractors in Michigan and Jimmy ‘Z Masonry in Crystal Lake, Ill., the latter of which is working on the abovementioned barracks project, and reportedly advocated for the use of robots.

The SAM robot can lay brick at a pace of one every 7-10 seconds.
Construction Robotics’ machines have installed more than one million sf of wall, says Peters, whose training is in engineering. His partner, Nate Podkaminer, has a background in architecture and construction.
Tyler Shawcross, Clark’s senior project manager, says that his company first met with Construction Robotics’ principals about five years ago. “Our R&D team is always looking for ways to build smarter,” he says.
When asked how this technology benefits masons at a time when workers are losing their jobs to automation in many industries, Shawcross notes that masonry, like many other construction trades, is suffering from labor shortages and an aging workforce. Plus, he adds, these trades simply are not attracting younger workers.
Construction Robotics has had a training program for masons in place since 2018. Both Peters and Shawcross agree that the technology not only has the potential for extending the work longevity of masons, but also might entice younger workers to consider entering the profession.
MULEs cost between $70,000 to $80,000 to purchase and are relatively simple to operate. For the barracks project, the MULE grabs the 32-inch blocks (which Oldcastle developed specifically for this job). The mason positions the hoisted block onto the foundation row. “It’s like an extension of your hand,” says Shawcross.
SAMs are more complicated machines that require three-to-five days of training to operate. The machines are generally leased by the week, month, or longer. Peters is reluctant to discuss pricing because, he explains, each project is different and requires customized software coding. (Peters notes that SAMs can be programmed to lay bricks in complex patterns and color sequences.)
To view videos of MULE and SAM in action, click here.
Construction Robotics claims SAMs reduce labor costs by at least 30%. Shawcross couldn’t quantify the time and cost savings from using the robots. He notes, though, that the machines provide a reliable production rate. “We see it as an opportunity to drive cost certainty into a project. I don’t think it’s a large cost reducer, but it could be a scheduling reducer.”
Peters says that robotics are most effective in construction when they are factored into the building process early in the planning stage. “That’s why we engage with GCs like Clark.” He concedes, however, that the construction industry in general is slow to change. “Companies need to think about new technology, and use their money to learn.”
Shawcross believes that robotics will become more prevalent on jobsites for performing repetitive tasks. Peters says that on another project, a MULE was used to move concrete form panels into place. “It’s one of those rare products that provides both speed and safety,” he says.
Related Stories
| Jan 24, 2017
BD+C Accelerate Live! AEC Innovation Conference
Building Design+Construction's inaugural Accelerate Live!
AEC Tech | Dec 22, 2016
The success of your data strategy depends on healthy business practices
Data and digital tools are an absolute given to today’s building design and construction process. But creating a true data-driven workflow requires more than just a solid strategy, writes Proving Ground’s Nathan Miller.
AEC Tech | Dec 18, 2016
Customized future weather data now available for online purchase
Simulation tool, developed by Arup and Argos Analytics, is offered to help owners and AEC firms devise resilience strategies for buildings.
Virtual Reality | Nov 16, 2016
Converting 3D model files to VR, with one click
IrisVR offers two new products to simplify and enhance the application of virtual reality for designing projects.
AEC Tech | Sep 6, 2016
Innovation intervention: How AEC firms are driving growth through R&D programs
AEC firms are taking a page from the tech industry, by infusing a deep commitment to innovation and disruption into their cultural DNA.
Hardware | Aug 11, 2016
Kyocera introduces the DuraForce PRO, a rugged smartphone equipped with an HD action camera (UPDATED)
The Super Wide View HD Action Camera and rugged design allow users to capture their adventures on land, air, or sea.
AEC Tech | Jun 27, 2016
If ‘only the paranoid survive,’ what does it take to thrive?
“Sooner or later, something fundamental in your business world will change.” The late Andrew Grove (1936-2016), Co-founder of tech giant Intel Corp., lived by these words.
AEC Tech | Jun 17, 2016
Driverless cars could soon start impacting commercial, retail project design
Offsite parking and more space for valet parking lines are among the foreseeable changes.
3D Printing | Jun 14, 2016
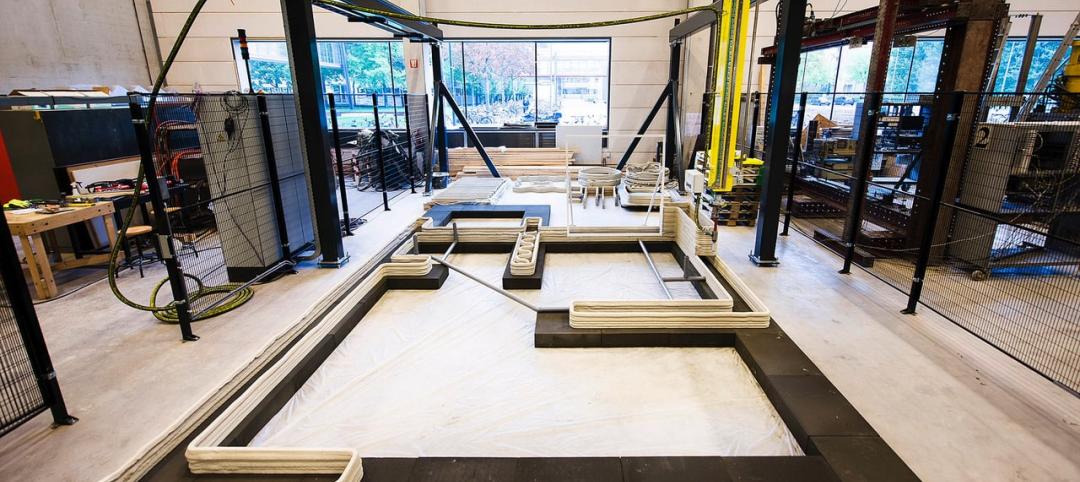
By 2021, 3D concrete printing is projected to be a $56.4 million industry
The 3D concrete printing industry is expected to more than double in size within the next five years.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 13, 2016
The race to digitize the globe with 3D imagery
Tech firms are creating a highly-detailed virtual planet available instantly for those who would like to scrutinize it. SmithGroupJJR's Stephen Conschafter details the new technologies being used to map our world.