Rochester, Minn., home to the famed Mayo Clinic, is about to embark on what would be the largest economic development initiative in this state’s history.
The state government, the Mayo Clinic, and private investment partners are prepared to spend $6.5 billion on a 20-year plan whose goal is to elevate Rochester into a global biotech hub. The plan is also intended to rejuvenate Rochester’s downtown, promote open transit, and reconnect the city with its waterfront.
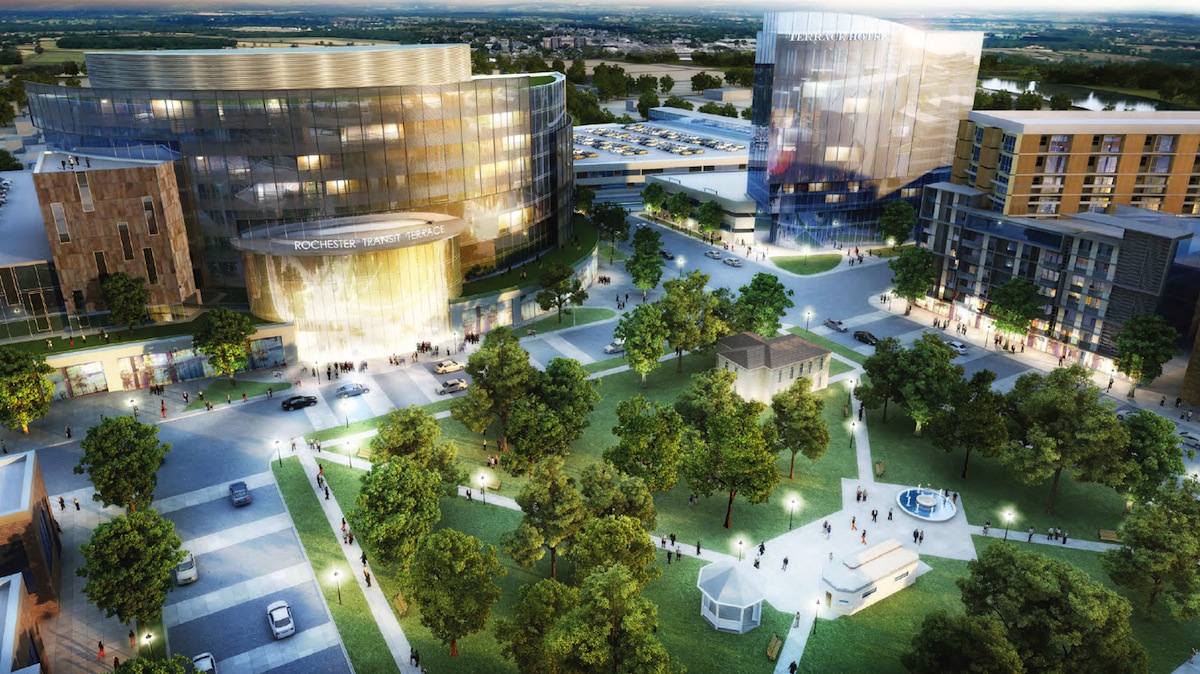
On April 23, the Board of Directors of the Destination Medical Center Corporation formally adopted the development plan for Destination Medical Center (DMC), which would be comprised of six districts spread across 550 acres. The vertical construction would support a diverse mixed-use environment that complements Mayo’s existing facilities, which already provide care for one million patients annually.
The state government, the Mayo Clinic, and private investment partners are prepared to spend $6.5 billion on a 20-year plan whose goal is to elevate Rochester into a global biotech hub. The plan is also intended to rejuvenate Rochester’s downtown, promote open transit, and reconnect the city with its waterfront.
The six districts identified in the development plan include:
• The Heart of the City: The plan would convert the downtown area into a place of “connected urban experiences” that build off of the city’s existing walkable attributes, with enhanced areas and mixed-use buildings
• Discovery Square: Steps from Mayo Medical School, this would be the address for the expansion of science, research, tech, and entrepreneurism;
• Downtown Waterfront: This would be located where the Zumbro River and Second Street intersect. It would be a cultural and historical center, and provide live-work opportunities;
• Central Station: A nexus of transportation for the downtown area, with an intermodal transit station that is incorporated into mixed-use development;
• UMR and Recreation Area: On the south edge of downtown, this location would encompass the University of Minnesota-Rochester campus and Soldier’s Memorial Field; and
• St. Mary’s Place: A new public space in the downtown’s western corner.
Peter Cavaluzzi, FAIA, Principal and Board Member for Perkins Eastman, this project’s lead designer, thinks The Heart of the City will be the most critical component, and have the biggest impact, early on. “The first phase of every large-scale project has to be bold enough to have an impact, but at the same time be small enough that it can be achieved.”
Perkins Eastman says the initial phase will start at the city’s 1st Street and 1st Avenue, in the middle of Peace Plaza, where a grand dining terrace will span the Avenue and connect to the historic Chateau Theater.
A breakdown of Destination Medical Center shows that it would have 6.8 million sf of healthcare facilities, 1.02 million sf of biotech, 310,000 sf of offices, a 1,380-room hotel, 2,850 units of residential, 354,000 sf of educational space, and 117,000 sf of transit, which would include 22,850 new parking spaces. Fast Company reports that there is also a possibility of a rail link between Rochester and Minneapolis, 90 miles away.
Rochester officials see this project as a way for their city to get out from under the shadow cast by the Minneapolis-St. Paul metroplex. DMC could also give Mayo Clinic a leg up on other healthcase hubs like Cleveland Clinic and Johns Hopkins that are all vying for what’s known as medical “tourists,” affluent foreign patients seeking the best treatment available.
Lisa Clarke, DMC’s executive director, estimates that this development would create between 25,000 and 40,000 jobs over 20 years, plus significantly more tax revenue.
Fast Company reports that $6 billion of the project’s cost would be raised from the private sector, and state and local taxpayers would contribute $585 million. Foreign companies, many with ties with Mayo Clinic, are expected to provide much of the private funding.
The Destination Medical Center, though, is controversial. For one thing, the plan calls for the downtown area to be “winterized” with skywalks, heated sidewalks, and underground passageways. There’s nothing in the plan that stipulates construction of affordable housing (which could be a real problem if, as estimated, this urban development project causes Rochester’s population to double from its current 111,000 people). And some residents fear that local cultural structures, like the public library and downtown theater, could ultimately be destined for the wrecking ball.
Related Stories
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Sustainability | Apr 20, 2023
13 trends, technologies, and strategies to expect in 2023
Biophilic design, microgrids, and decarbonization—these are three of the trends, technologies, and strategies IMEG’s market and service leaders believe are poised to have a growing impact on the built environment.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 17, 2023
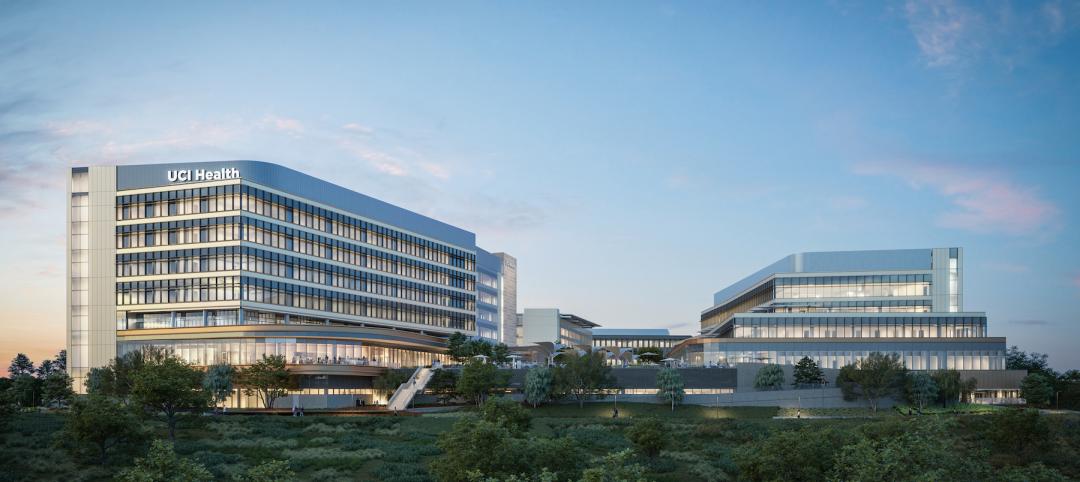
UC Irvine takes sustainability to new level with all-electric medical center
The University of California at Irvine (UCI) has a track record for sustainability. Its under-construction UCI Medical Center is designed, positioned, and built to preserve the nearby San Joaquin Marsh Reserve, to reduce the facility’s solar gain by 85%, and to be the first medical center in the country to operate on an all-electric central plant.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Healthcare construction costs for 2023
Data from Gordian breaks down the average cost per square foot for a three-story hospital across 10 U.S. cities.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 13, 2023
Urgent care facilities: Intentional design for mental and behavioral healthcare
The emergency department (ED) is the de-facto front door for behavior health crises, and yet these departments are understaffed, overwhelmed, and ill-equipped to navigate the layered complexities of highly demanding physical and behavioral health needs.
Urban Planning | Apr 12, 2023
Watch: Trends in urban design for 2023, with James Corner Field Operations
Isabel Castilla, a Principal Designer with the landscape architecture firm James Corner Field Operations, discusses recent changes in clients' priorities about urban design, with a focus on her firm's recent projects.
Market Data | Apr 11, 2023
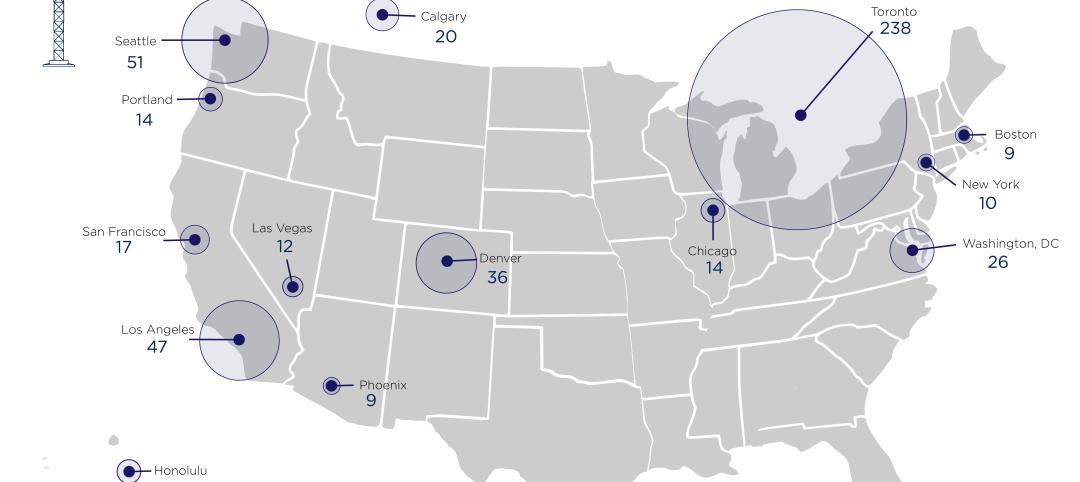
Construction crane count reaches all-time high in Q1 2023
Toronto, Seattle, Los Angeles, and Denver top the list of U.S/Canadian cities with the greatest number of fixed cranes on construction sites, according to Rider Levett Bucknall's RLB Crane Index for North America for Q1 2023.
Contractors | Apr 10, 2023
What makes prefabrication work? Factors every construction project should consider
There are many factors requiring careful consideration when determining whether a project is a good fit for prefabrication. JE Dunn’s Brian Burkett breaks down the most important considerations.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.