SSOE Group, an international engineering, procurement, and construction management firm headquartered in Toledo, Ohio, recently completed the reconstruction of two Ford Motor Co. plants. The key to the project’s success was the use of new laser scanning technology that allowed the SSOE-led Building Team to capture untold millions of data points for integration into the 3D design model, thereby saving the client significant amounts of time and money.
Ford determined the two plants had exceeded their designed lifespans and opted to reconstruct and upgrade them rather than build new. All members of the Building Team—SSOE, laser-scanning vendor Troy Design & Manufacturing, Redford, Mich., Walbridge Construction Co., Detroit, and UK software developer Pointools Ltd.—had prior experience with laser scanning technology on smaller projects. What was daunting about these projects was the sheer size, totaling about 200,000 sf.
“Ford wanted us to work within their ‘as constructed’ environments, meaning we would be designing inside existing structures that needed to be cleared of old equipment,” says Joe Gerweck, project manager for SSOE Group.
Ford also required the Building Team to work with point cloud technology to reduce the number of construction coordination conflicts. To create the data points, the Building Team used a 3D laser scanner to capture the point clouds of existing equipment and construction in the plants.
LET THE TROUBLESHOOTING BEGIN!
Once the Building Team was defined, SSOE was tasked as the model integrator during the bid and construction phases to ensure the proper utilization of the 3D models and laser scans. This involved confirming software compatibility between subcontractors supplying 3D elements and collaborating the design intent, construction models, and laser scans.
Much to the surprise of the Building Team, there were few problems regarding software compatibility between the members of the Building Team.
“As with any new endeavor, there are always compatibility issues that need to be identified and resolved,” says Gerweck, who notes that, because point cloud technology and the supporting software are still in their infancy, there is no standard that exists between the technology vendors. “This limits the compatibility some, but it was not to the detriment of the Ford projects,” he says.
Having sidestepped the software compatibility problem, the next step for the Building Team was to scan the two manufacturing plants. This represented the most critical aspect of the job because these scanned data points would be used to compare and coordinate with new construction designs.
Traditional scanning methods and equipment were utilized for both Ford reconstruction projects. According to Neil Wakeman, SSOE Group’s BIM/CAD technical leader, stationary laser scanners on tripods were strategically mapped to encompass an area depending on the density or detail requested by the design engineers. The resulting data points were then imported into manageable files per building bay. The point clouds were then cleaned up and ultimately became the basic content used to create the reconstruction designs.
Architectural drawings utilized screen shots of the laser scans to identify elements for demolition versus elements that were to be reproduced in CAD. When using CAD, it is up to the user to interpret what they see on the screen, and identify it as a real world object such as a beam or column.
The laser scanning process, from on-site scanning to cleaning and organizing the raw scans into manageable files for the Building Team, was utilized during all phases of construction. This allowed improvements to the construction schedule, preplanning, and final design conducted by the Building Team both in the field and in the office.
LESSONS LEARNED ABOUT WORKING REMOTELY
Following the scans, the data was then integrated within the 3D modeling software, providing the Building Team with both a visual reference and actual reference to locate points in the 3D digital space. The result was the basis of the designs for updating the two Ford facilities. The entire Building Team was able to virtually see the design intent models, fabrication models, and laser scans overlaid in Navisworks for discussion before anything was assembled in the field.
Once the data points from the scans were transferred to the 3D modeling environment, the Building Team now had the capability to measure points and elevations virtually from a remote office during reconstruction. The scans from the Ford facilities were also used to coordinate the new utility layout with the existing utilities for such systems as HVAC, compressed air piping, coolant piping, domestic water piping, steam piping, electrical bus ducts, and electric cable tray. This resulted in a reduction of the number of hours the Building Team spent in the field verifying existing site conditions.
“The laser scanning technology was very effective,” says Gerweck. “During the design phase, it was much more efficient to review the laser scan results than to travel many hours to verify field conditions.”
Although having the laser scans reduced the number of overall trips to the job sites, thereby saving the client money in the long run, some site visits were still unavoidable. “It’s always beneficial for the Building Team to visit the site because there are instances where the laser scan does not fully describe the actual site condition based upon where the tripod was located for the scan,” says Gerweck.
During the laser scanning process, the Building Team learned another valuable lesson—that rescanning the buildings after the manufacturing equipment was removed proved to be much more efficient and accurate than editing the point clouds by hand to reflect the conditions prior to the new design. Wakeman says SSOE will be certain to incorporate this bit of wisdom into future scanning projects.
Perhaps the most important lesson from this case study is that, while the learning curve associated with new technology can be intimidating, once the Building Team is on same page technologically, the result can save a client significant time and money, thus benefiting everyone involved in the project. BD+C
Related Stories
| Mar 13, 2014
Austria's tallest tower shimmers with striking 'folded façade' [slideshow]
The 58-story DC Tower 1 is the first of two high-rises designed by Dominique Perrault Architecture for Vienna's skyline.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 10, 2014
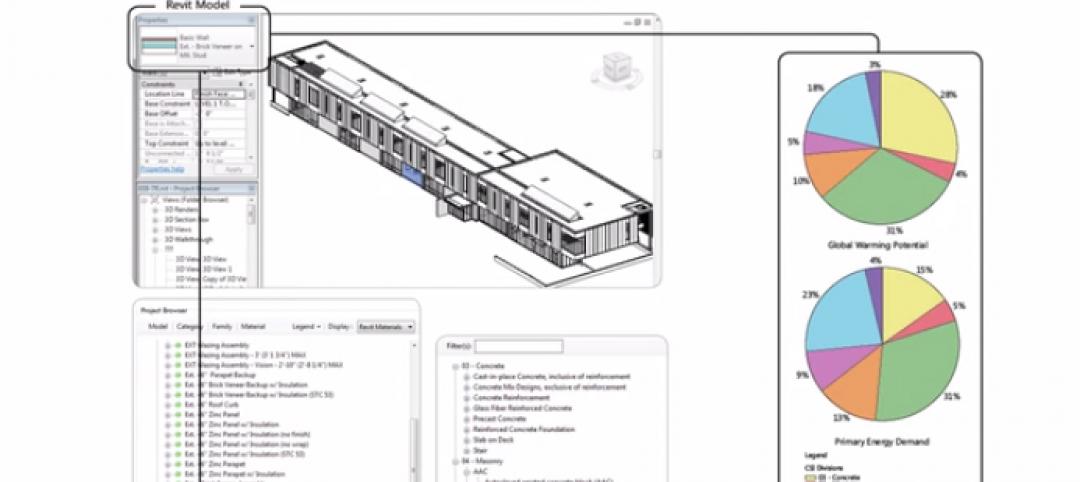
Meet Tally – the Revit app that calculates the environmental impact of building materials
Tally provides AEC professionals with insight into how materials-related decisions made during design influence a building’s overall ecological footprint.
| Mar 7, 2014
Thom Mayne's high-tech Emerson College LA campus opens in Hollywood [slideshow]
The $85 million, 10-story vertical campus takes the shape of a massive, shimmering aircraft hangar, housing a sculptural, glass-and-aluminum base building.
| Mar 4, 2014
How EIFS came to America
Design experts from Hoffmann Architects offer a brief history of exterior insulation and finish systems in the U.S.
| Feb 20, 2014
5 myths about cross laminated timber
A CLT expert clears up several common misconceptions and myths surrounding the use of wood as a building material.
| Feb 19, 2014
Harvard's 'termite robots' can build any thing, any way [video]
The robots build by observing thier environment and then obeying a set of traffic rules programmed by researchers.
| Feb 14, 2014
Scrap tires used to boost masonry blocks at Missouri University of S&T
Research could lead to blocks that use waste material and have seismic and insulating benefits.
| Feb 14, 2014
The Technology Report 2014: Top tech tools and trends for AEC professionals
In this special five-part report, Building Design+Construction explores how Building Teams throughout the world are utilizing advanced robotics, 3D printers, drones, data-driven design, and breakthroughs in building information modeling to gain efficiencies and create better buildings.
| Feb 14, 2014
Crowdsourced Placemaking: How people will help shape architecture
The rise of mobile devices and social media, coupled with the use of advanced survey tools and interactive mapping apps, has created a powerful conduit through which Building Teams can capture real-time data on the public. For the first time, the masses can have a real say in how the built environment around them is formed—that is, if Building Teams are willing to listen.