U.S. school districts are widely planning to use funds from last year’s American Rescue Plan (ARP) to upgrade or improve air filtration and heating/cooling systems, according to a report from the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC).
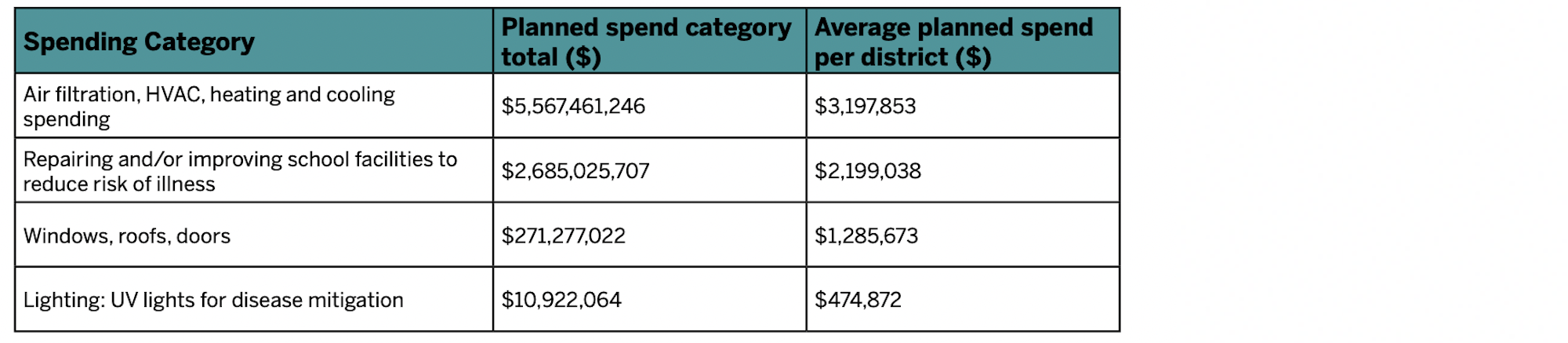
The report, School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic, says air filtration and HVAC upgrades are the top facility improvement choice for the 5,004 school districts included in the analysis. The top choice for spending federal funds was for staffing, followed by air filtration/HVAC at $5.5 billion.
Other categories of planned spending include $2.6 billion for repairing/improving school facilities; $271 million for upgrading windows, roofs, and doors; and nearly $11 million for UV lighting for disease mitigation. The average planned spending for air filtration and HVAC is about $260,000 per school. Around 500 school districts plan to spend over $1 million per school on one or more of these categories.
District interviewees said having substantial federal dollars was important to be able to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases. They also noted that they face constraints on their projects caused by the pandemic, associated supply chain issues, and the rising rate of inflation.
District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems.
More findings from the School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic study
- Although staff capacity, inflation and supply chain shortages are affecting infrastructure projects, school districts have prioritized significant ESSER III funding to support indoor air quality for their students and staff. Of all the funding categories tracked by Burbio, air filtration/HVAC was the second-highest category for district planned spending at $5.5 billion, just behind staffing/teachers/academic interventionists/guidance counselors.
- Of the 2,379 school districts that planned to spend any ESSER III funding on facilities, large districts planned to spend the lowest percentage (on average 22%) and small districts planned to spend the highest percentage of their total allocation (on average 30%).
- Small and medium-size districts (those with 20 or fewer schools) consistently reported more spending per school on facilities categories than their larger counterparts.
- In addition to filtration and HVAC improvements, in most cases, districts that planned to spend in this category also indicated plans to spend in at least one other facilities category, displaying a layered approach to addressing COVID at the building infrastructure level.
- The district interviewees highlighted the importance of having substantial federal dollars to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases.
- District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems. Similarly, interviewees reported positive results from spending in other facilities categories to reduce the spread of COVID.
The analysis included qualitative interviews with three school district facilities personnel and a quantitative analysis based on a data set of 5,004 school districts’ ESSER-III spending plans by the Burbio data service. The dataset contained information from school districts from all 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing approximately 74% of public-school students and roughly $83.1 billion in ESSER III funds.
Related Stories
K-12 Schools | Aug 1, 2017
This new high school is the first to be built on a tech company’s campus
Design Tech High School, located on Oracle Corporation’s Headquarters campus, will span 64,000 sf across two stories and have a capacity of 550 students.
Education Facilities | Jul 14, 2017
Youth education center in Baltimore gets first students
Students learn environmental skills, natural resource management, urban agriculture, and water quality monitoring.
Great Solutions | Jul 12, 2017
The writing on the wall: Maker spaces encourage students to take an active role
Maker spaces, dry-erase walls, and flexible furniture highlight Kinkaid’s new Learning Center.
Building Team Awards | Jun 7, 2017
Rebuilding to heal: Sandy Hook Elementary School
Gold Award: Community involvement was paramount as Newtown, Conn., replaced the school where a mass shooting occurred.
K-12 Schools | Jun 5, 2017
PK-8 school will be Denver’s first CHPS-certified building
A “learning stair” will connect the cafeteria to the main level.
K-12 Schools | May 31, 2017
NAC Architecture rolls out ‘Hack Your Classroom’ campaign
In collaboration with room2learn, NAC launched a campaign aimed at crowd-sourcing information on what teachers are doing in their classroom to improve the learning experience.
K-12 Schools | May 16, 2017
The future of schools: Net zero should be the norm
Students are helping drive change by focusing on the future.
K-12 Schools | May 1, 2017
Seattle’s first vertically-oriented middle school breaks ground
The building will provide 74,289 sf of space across its five-story classroom bar.
K-12 Schools | Apr 21, 2017
The stadium effect
School districts that invested in their athletic facilities over the last few years have seen a tremendous increase in student morale and health, growth in campus culture, and excitement within their communities.
K-12 Schools | Apr 7, 2017
Is an alternative project delivery method right for your K-12 school district?
With California’s increasingly busy—and costly—construction market, it’s becoming more difficult to predict costs with a typical design-bid-build delivery method.

















