U.S. school districts are widely planning to use funds from last year’s American Rescue Plan (ARP) to upgrade or improve air filtration and heating/cooling systems, according to a report from the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC).
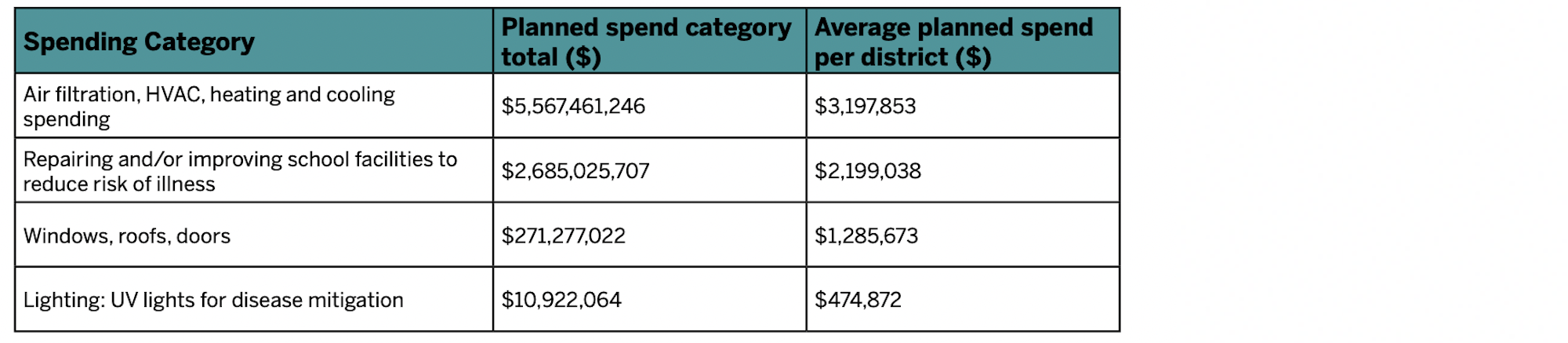
The report, School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic, says air filtration and HVAC upgrades are the top facility improvement choice for the 5,004 school districts included in the analysis. The top choice for spending federal funds was for staffing, followed by air filtration/HVAC at $5.5 billion.
Other categories of planned spending include $2.6 billion for repairing/improving school facilities; $271 million for upgrading windows, roofs, and doors; and nearly $11 million for UV lighting for disease mitigation. The average planned spending for air filtration and HVAC is about $260,000 per school. Around 500 school districts plan to spend over $1 million per school on one or more of these categories.
District interviewees said having substantial federal dollars was important to be able to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases. They also noted that they face constraints on their projects caused by the pandemic, associated supply chain issues, and the rising rate of inflation.
District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems.
More findings from the School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic study
- Although staff capacity, inflation and supply chain shortages are affecting infrastructure projects, school districts have prioritized significant ESSER III funding to support indoor air quality for their students and staff. Of all the funding categories tracked by Burbio, air filtration/HVAC was the second-highest category for district planned spending at $5.5 billion, just behind staffing/teachers/academic interventionists/guidance counselors.
- Of the 2,379 school districts that planned to spend any ESSER III funding on facilities, large districts planned to spend the lowest percentage (on average 22%) and small districts planned to spend the highest percentage of their total allocation (on average 30%).
- Small and medium-size districts (those with 20 or fewer schools) consistently reported more spending per school on facilities categories than their larger counterparts.
- In addition to filtration and HVAC improvements, in most cases, districts that planned to spend in this category also indicated plans to spend in at least one other facilities category, displaying a layered approach to addressing COVID at the building infrastructure level.
- The district interviewees highlighted the importance of having substantial federal dollars to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases.
- District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems. Similarly, interviewees reported positive results from spending in other facilities categories to reduce the spread of COVID.
The analysis included qualitative interviews with three school district facilities personnel and a quantitative analysis based on a data set of 5,004 school districts’ ESSER-III spending plans by the Burbio data service. The dataset contained information from school districts from all 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing approximately 74% of public-school students and roughly $83.1 billion in ESSER III funds.
Related Stories
| May 18, 2011
One of Delaware’s largest high schools seeks LEED for Schools designation
The $82 million, 280,000-sf Dover (Del.) High School will have capacity for 1,800 students and feature a 900-seat theater, a 2,500-seat gymnasium, and a 5,000-seat football stadium.
| May 17, 2011
Sustainability tops the syllabus at net-zero energy school in Texas
Texas-based firm Corgan designed the 152,200-sf Lady Bird Johnson Middle School in Irving, Texas, with the goal of creating the largest net-zero educational facility in the nation, and the first in the state. The facility is expected to use 50% less energy than a standard school.
| May 16, 2011
USGBC and AIA unveil report for greening K-12 schools
The U.S. Green Building Council and the American Institute of Architects unveiled "Local Leaders in Sustainability: A Special Report from Sundance," which outlines a five-point national action plan that mayors and local leaders can use as a framework to develop and implement green schools initiatives.
| May 10, 2011
Greenest buildings: K-12 and commercial markets
Can you name the nation’s greenest K-12 school? How about the greenest commercial building? If you drew a blank, don’t worry because our friends at EarthTechling have all the information on those two projects. Check out the Hawai’i Preparatory Academy’s Energy Lab on the Big Island and Cascadia Green Building Council’s new Seattle headquarters.
| Mar 15, 2011
Passive Strategies for Building Healthy Schools, An AIA/CES Discovery Course
With the downturn in the economy and the crash in residential property values, school districts across the country that depend primarily on property tax revenue are struggling to make ends meet, while fulfilling the demand for classrooms and other facilities.
| Feb 23, 2011
“School of Tomorrow” student design competition winners selected
The American Institute of Architecture Students (AIAS) and Kawneer Company, Inc. announced the winners of the “Schools of Tomorrow” student design competition. The Kawneer-sponsored competition, now in its fifth year, challenged students to learn about building materials, specifically architectural aluminum building products and systems in the design of a modern and creative school for students ranging from kindergarten to sixth grade. Ball State University’s Susan Butts was awarded first place and $2,500 for “Propel Elementary School.”
| Feb 15, 2011
LAUSD commissions innovative prefab prototypes for future building
The LA Unified School District, under the leadership of a new facilities director, reversed course regarding prototypes for its new schools and engaged architects to create compelling kit-of-parts schemes that are largely prefabricated.
| Feb 9, 2011
Gen7 eco-friendly modular classrooms are first to be CHPS verified
The first-ever Gen7 green classrooms, installed at Bolsa Knolls Middle School in Salinas, California, have become the nation's first modular classrooms to receive Collaborative for High Performance Schools (CHPS) Verified recognition for New School Construction. They are only the second school in California to successfully complete the CHPS Verified review process.
| Dec 17, 2010
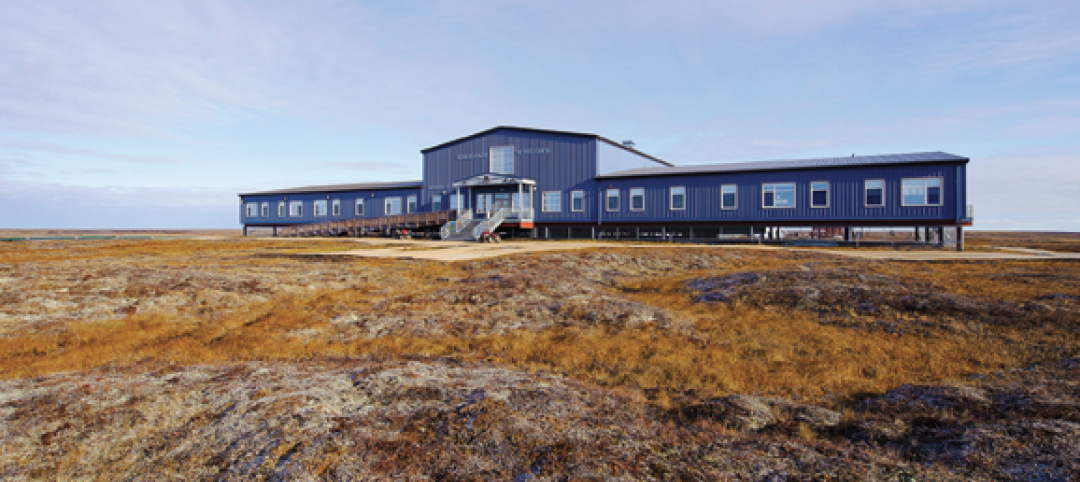
Alaskan village school gets a new home
Ayagina’ar Elitnaurvik, a new K-12 school serving the Lower Kuskikwim School District, is now open in Kongiganak, a remote Alaskan village of less than 400 residents. The 34,000-sf, 12-classroom facility replaces one that was threatened by river erosion.
| Dec 6, 2010
Honeywell survey
Rising energy costs and a tough economic climate have forced the nation’s school districts to defer facility maintenance and delay construction projects, but they have also encouraged districts to pursue green initiatives, according to Honeywell’s second annual “School Energy and Environment Survey.”