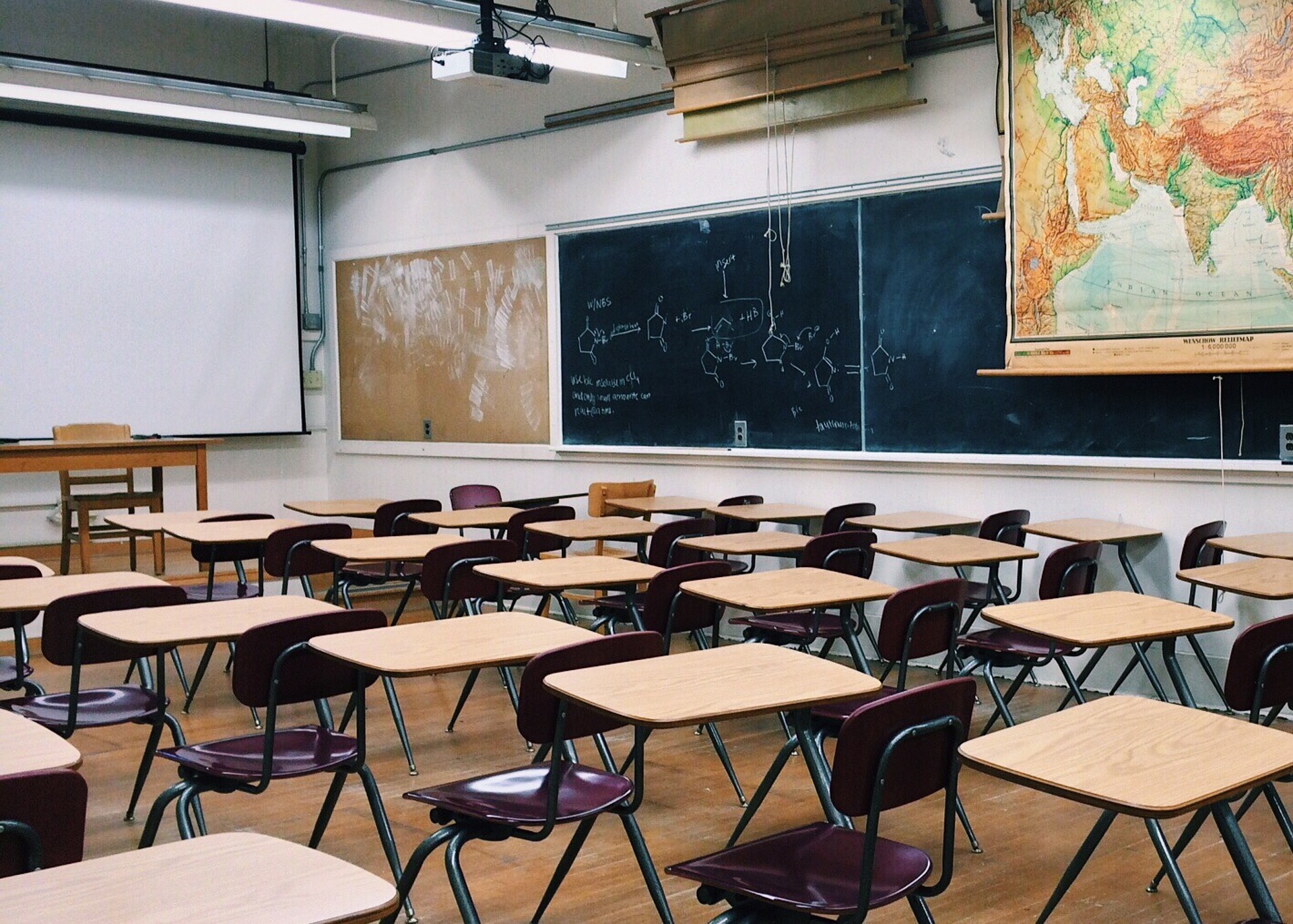
U.S. school districts are widely planning to use funds from last year’s American Rescue Plan (ARP) to upgrade or improve air filtration and heating/cooling systems, according to a report from the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC).
The report, School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic, says air filtration and HVAC upgrades are the top facility improvement choice for the 5,004 school districts included in the analysis. The top choice for spending federal funds was for staffing, followed by air filtration/HVAC at $5.5 billion.
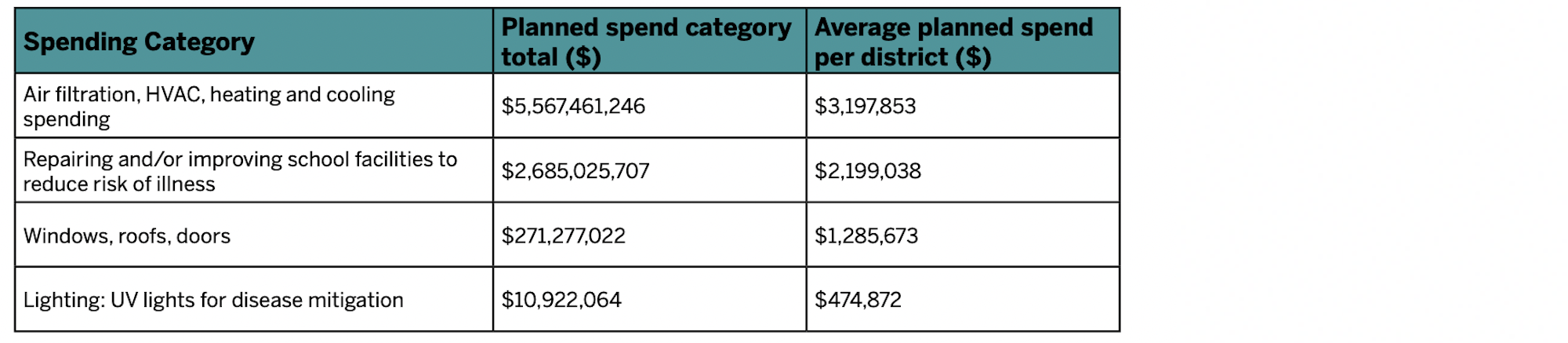
Other categories of planned spending include $2.6 billion for repairing/improving school facilities; $271 million for upgrading windows, roofs, and doors; and nearly $11 million for UV lighting for disease mitigation. The average planned spending for air filtration and HVAC is about $260,000 per school. Around 500 school districts plan to spend over $1 million per school on one or more of these categories.
District interviewees said having substantial federal dollars was important to be able to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases. They also noted that they face constraints on their projects caused by the pandemic, associated supply chain issues, and the rising rate of inflation.
District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems.
More findings from the School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic study
- Although staff capacity, inflation and supply chain shortages are affecting infrastructure projects, school districts have prioritized significant ESSER III funding to support indoor air quality for their students and staff. Of all the funding categories tracked by Burbio, air filtration/HVAC was the second-highest category for district planned spending at $5.5 billion, just behind staffing/teachers/academic interventionists/guidance counselors.
- Of the 2,379 school districts that planned to spend any ESSER III funding on facilities, large districts planned to spend the lowest percentage (on average 22%) and small districts planned to spend the highest percentage of their total allocation (on average 30%).
- Small and medium-size districts (those with 20 or fewer schools) consistently reported more spending per school on facilities categories than their larger counterparts.
- In addition to filtration and HVAC improvements, in most cases, districts that planned to spend in this category also indicated plans to spend in at least one other facilities category, displaying a layered approach to addressing COVID at the building infrastructure level.
- The district interviewees highlighted the importance of having substantial federal dollars to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases.
- District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems. Similarly, interviewees reported positive results from spending in other facilities categories to reduce the spread of COVID.
The analysis included qualitative interviews with three school district facilities personnel and a quantitative analysis based on a data set of 5,004 school districts’ ESSER-III spending plans by the Burbio data service. The dataset contained information from school districts from all 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing approximately 74% of public-school students and roughly $83.1 billion in ESSER III funds.
Related Stories
| Oct 12, 2011
BIM Clarification and Codification in a Louisiana Sports Museum
The Louisiana State Sports Hall of Fame celebrates the sporting past, but it took innovative 3D planning and coordination of the future to deliver its contemporary design.
| Oct 11, 2011
AIA introduces five new documents for use on sustainable projects
These new documents will be available in the first quarter of 2012 as part of the new AIA Contract Documents service and AIA Documents on Demand.
| Oct 11, 2011
Onex completes investment in JELD-WEN
With the completion of the JELD-WEN investment, Onex Partners III is approximately 40% invested.
| Oct 7, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: UL Environment releases industry-wide sustainability requirements for doors
ASSA ABLOY Trio-E door is the first to be certified to these sustainability requirements.
| Oct 7, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Transparent concrete makes its North American debut at Greenbuild
The panels allow interior lights to filter through, from inside.
| Oct 6, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Dow Corning features new silicone weather barrier sealant
Modular Design Architecture >Dow Corning 758 sealant used in GreenZone modular high-performance medical facility.
| Oct 6, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Kingspan Insulated Panels spotlights first-of-its-kind Environmental Product Declaration
Updates to Path to NetZero.
| Oct 5, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Sustainable construction should stress durability as well as energy efficiency
There is now a call for making enhanced resilience of a building’s structure to natural and man-made disasters the first consideration of a green building.
| Oct 5, 2011
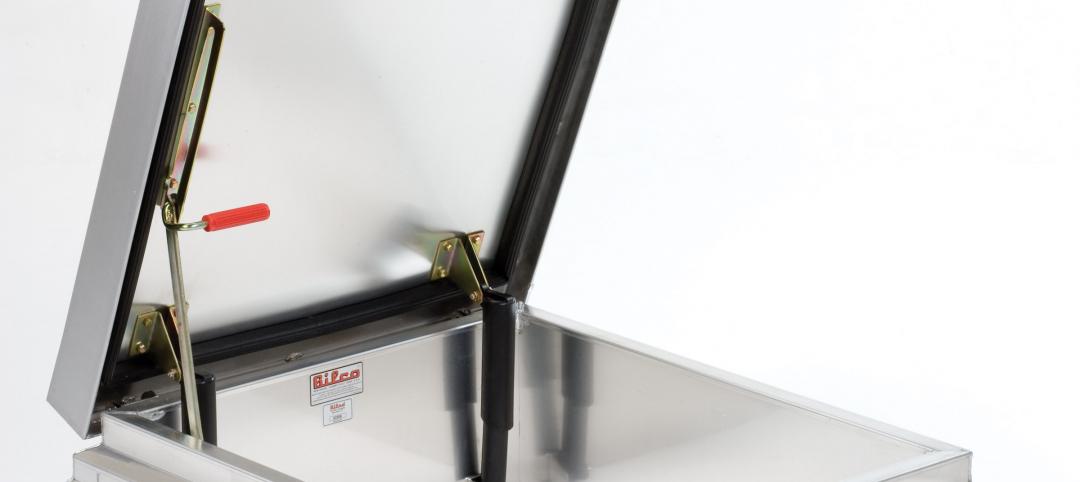
GREENBUILD 2011: Roof hatch designed for energy efficiency
The cover features a specially designed EPDM finger-type gasket that ensures a positive seal with the curb to reduce air permeability and ensure energy performance.
| Oct 4, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Large diameter polypropylene-random pipe unveiled
Available in North America for large scale piping applications including high-rise buildings, large chilled water systems, district energy, and water mains.