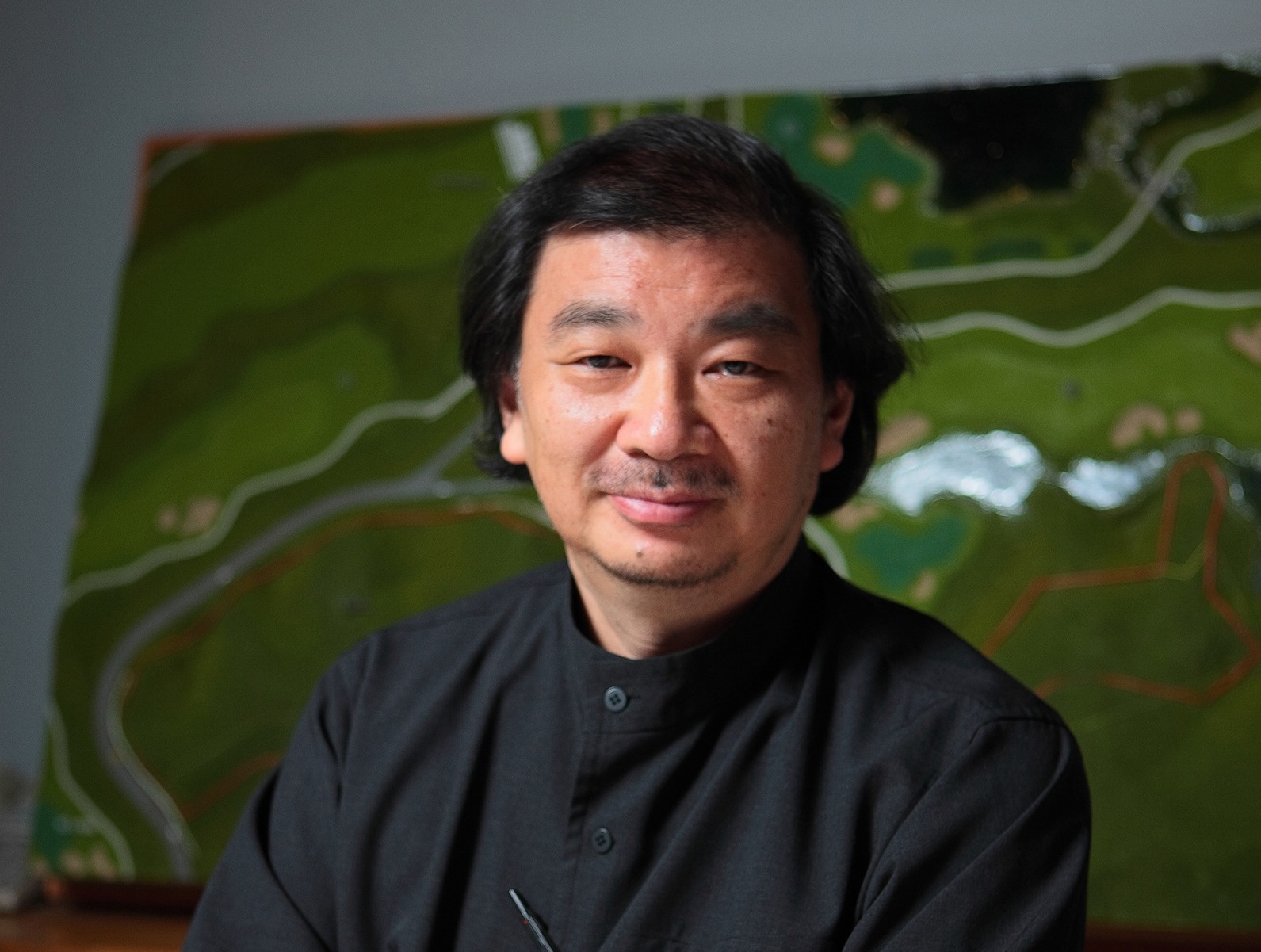
Shigeru Ban will receive the 2014 Pritzker Architecture Prize. Tom Pritzker, Chairman and President of The Hyatt Foundation, which sponsors the prize, made the announcement on Monday.
Shigeru Ban, a Tokyo-born, 56-year-old architect with offices in Tokyo, Paris, and New York, is rare in the field of architecture. He designs elegant, innovative work for private clients, and uses the same inventive and resourceful design approach for his extensive humanitarian efforts.
For 22 years Ban has traveled to sites of natural and man-made disasters around the world, to work with local citizens, volunteers, and students, to design and construct simple, dignified, low-cost, recyclable shelters and community buildings for the disaster victims.
“Receiving this prize is a great honor, and with it, I must be careful," said Shigeu Ban. "I must continue to listen to the people I work for, in my private residential commissions and in my disaster relief work. I see this prize as encouragement for me to keep doing what I am doing – not to change what I am doing, but to grow."
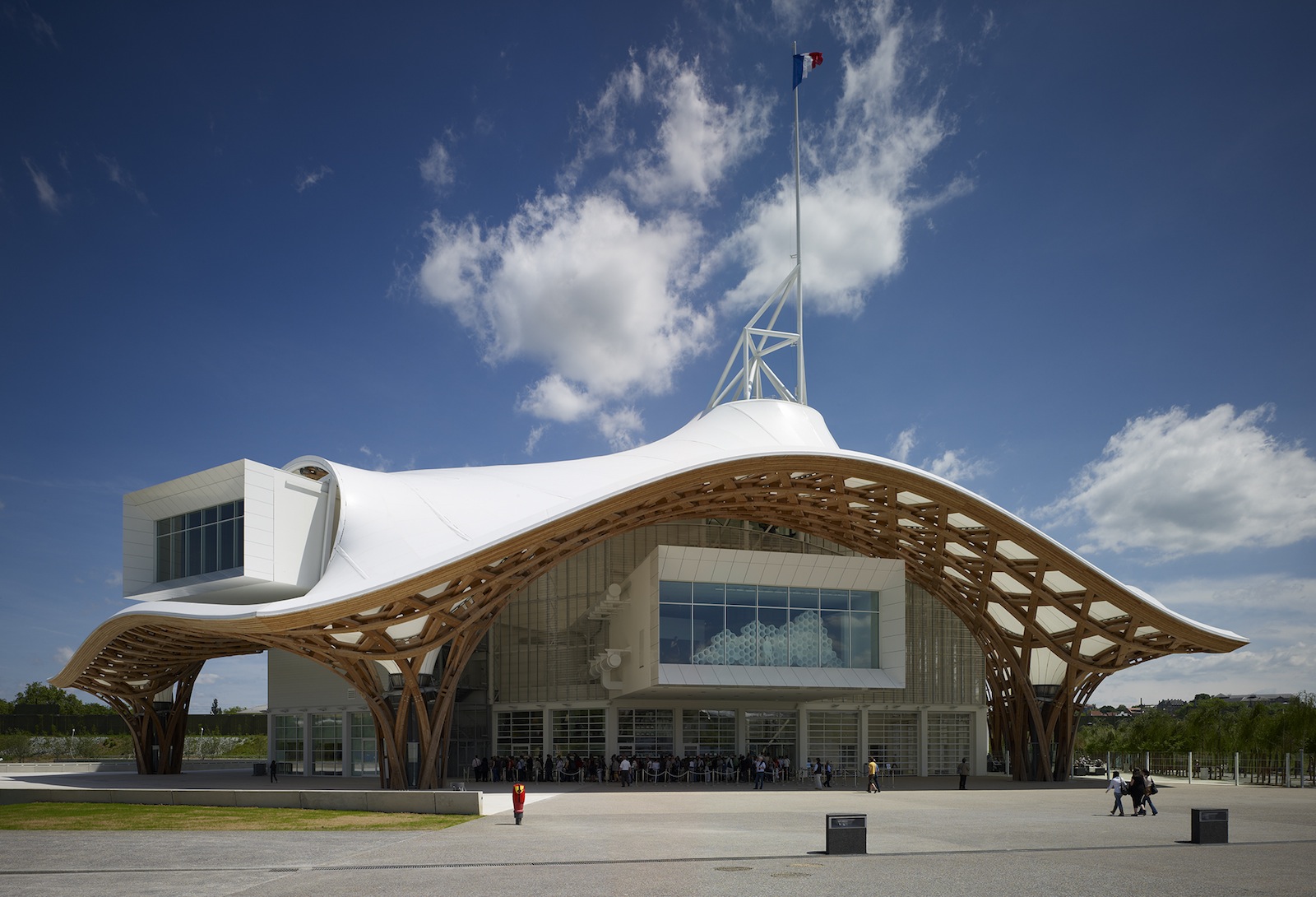

Centre Pompidou-Metz, 2010, France; Photo by Didier Boy de la Tour
In all parts of his practice, Ban finds a wide variety of design solutions, often based around structure, materials, view, natural ventilation, and light, and a drive to make comfortable places for the people who use them.
From private residences and corporate headquarters, to museums, concert halls and other civic buildings, Ban is known for the originality, economy, and ingeniousness of his works, which do not rely on today’s common high-tech solutions.
The Swiss media company Tamedia asked Ban to create pleasant spaces for their employees. He responded by designing a seven-story headquarters with the main structural system entirely in timber. The wooden beams interlock, requiring no metal joints.
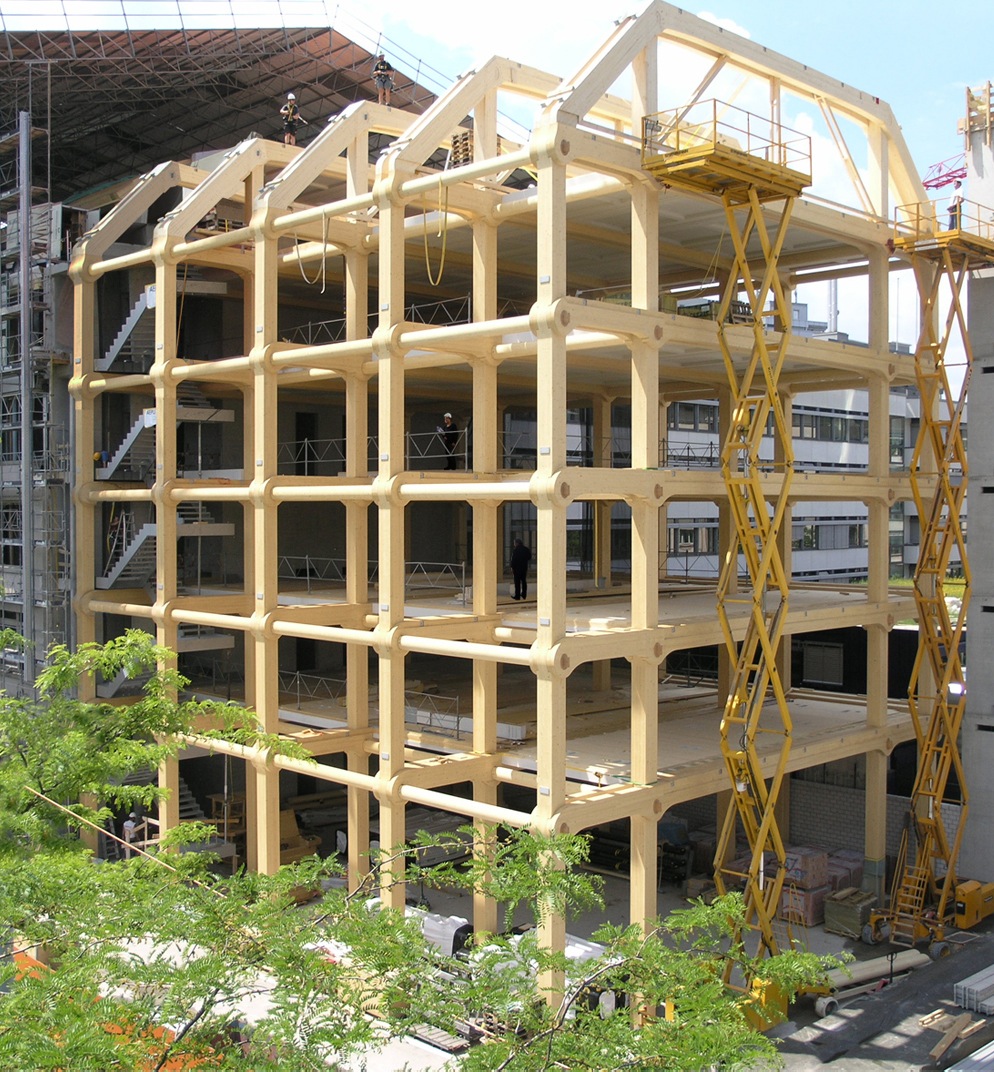

Tamedia Building, 2013, Zurich, Switzerland; Photo by Shigeru Ban Architects Europe
For the Centre Pompidou-Metz, in France, Ban designed an airy, undulating latticework of wooden strips to form the roof, which covers the complex museum program underneath and creates an open and accessible public plaza.
To construct his disaster relief shelters, Ban often employs recyclable cardboard paper tubes for columns, walls, and beams, as they are locally available, inexpensive, easy to transport, mount and dismantle, and they can be water- and fire-proofed, and recycled. He says that his Japanese upbringing helps account for his wish to waste no materials.
As a boy, Shigeru Ban observed traditional Japanese carpenters working at his parents’ house and to him their tools, the construction, and the smells of wood were magic. He would save cast aside pieces of wood and build small models with them. He wanted to become a carpenter. But at age eleven, his teacher asked the class to design a simple house and Ban’s was displayed in the school as the best. Since then, to be an architect was his dream.
Ban’s humanitarian work began in response to the 1994 conflict in Rwanda, which threw millions of people into tragic living conditions. Ban proposed paper-tube shelters to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees and they hired him as a consultant.

Cardboard Cathedral, 2013, Christchurch, New Zealand; Photo by Stephen Goodenough
After the 1995 earthquake in Kobe, Japan, he again donated his time and talent. There, Ban developed the “Paper Log House,” for Vietnamese refugees in the area, with donated beer crates filled with sandbags or the foundation, he lined up the paper cardboard tubes vertically, to create the walls of the houses.
Ban also designed “Paper Church,” as a community center of paper tubes for the victims of Kobe. It was later disassembled and sent to Taiwan, and reconstructed there, in 2008.
Ban works with local victims, students, and other volunteers to get these disaster relief projects built. In 1995, he founded a non-governmental organization (NGO) called VAN: Voluntary Architects’ Network. With VAN, following earthquakes, tsunami, hurricanes, and war, he has conducted this work in Japan, Turkey, India, Sri Lanka, China, Haiti, Italy, New Zealand, and currently, the Philippines.
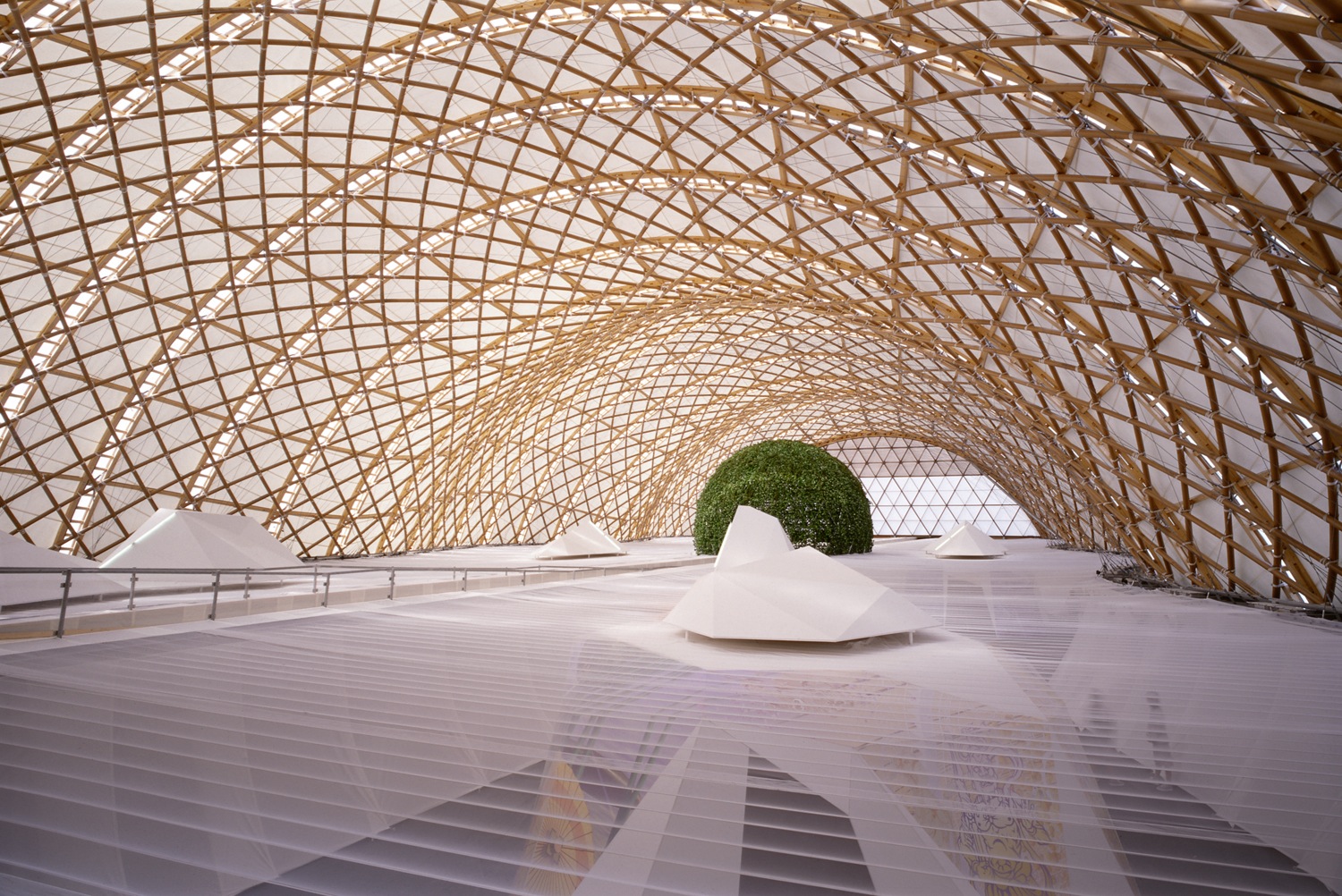

Japan Pavilion, Expo 2000 Hannover, 2000, Germany; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
Pritzker Prize jury chairman, The Lord Palumbo, said, “Shigeru Ban is a force of nature, which is entirely appropriate in the light of his voluntary work for the homeless and dispossessed in areas that have been devastated by natural disasters. But he also ticks the several boxes for qualification to theArchitectural Pantheon -- a profound knowledge of his subject with a particular emphasis on cutting-edge materials and technology; total curiosity and commitment; endless innovation; an infallible eye; an acute sensibility -- to name but a few.”
The citation from the Pritzker Prize jury underscores Ban’s experimental approach to common materials such as paper tubes and shipping containers, his structural innovations, and creative use of unconventional materials such as bamboo, fabric, paper, and composites of recycled paper fiber and plastics.
The jury cited Naked House (2000) in Saitama, Japan, in which Ban clad the external walls in clear corrugated plastic and sections of white acrylic stretched internally across a timber frame. The layering of translucent panels evokes the glowing light of shoji screens.
The client asked for no family member to be secluded, so the house consists of one unique large space, two-stories high, in which four personal rooms on casters can be moved about freely.
Ban is the seventh Japanese architect to become a Pritzker Laureate – the first six beingthe late Kenzo Tange in 1987, Fumihiko Maki in 1993, Tadao Ando in 1995, the team of Kazuyo Sejima and Ryue Nishizawa in 2010, and Toyo Ito in 2013.
The award ceremony will take place on June 13, 2014, at the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
For more, visit: http://www.pritzkerprize.com/laureates/2014
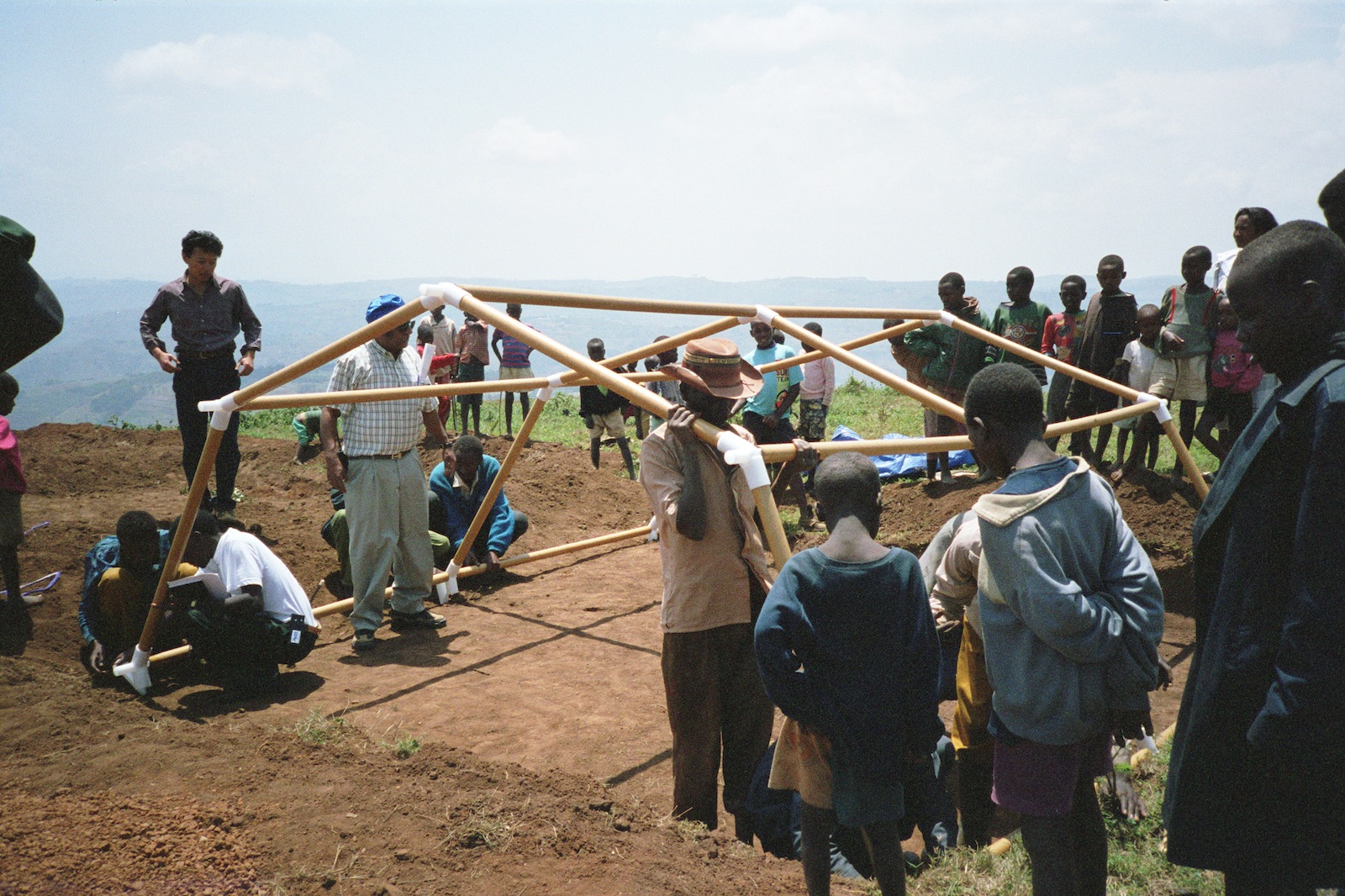

Paper Refugee Shelters for Rwanda, 1999, Byumba Refugee Camp, Rwanda; Photo by Shigeru Ban Architects
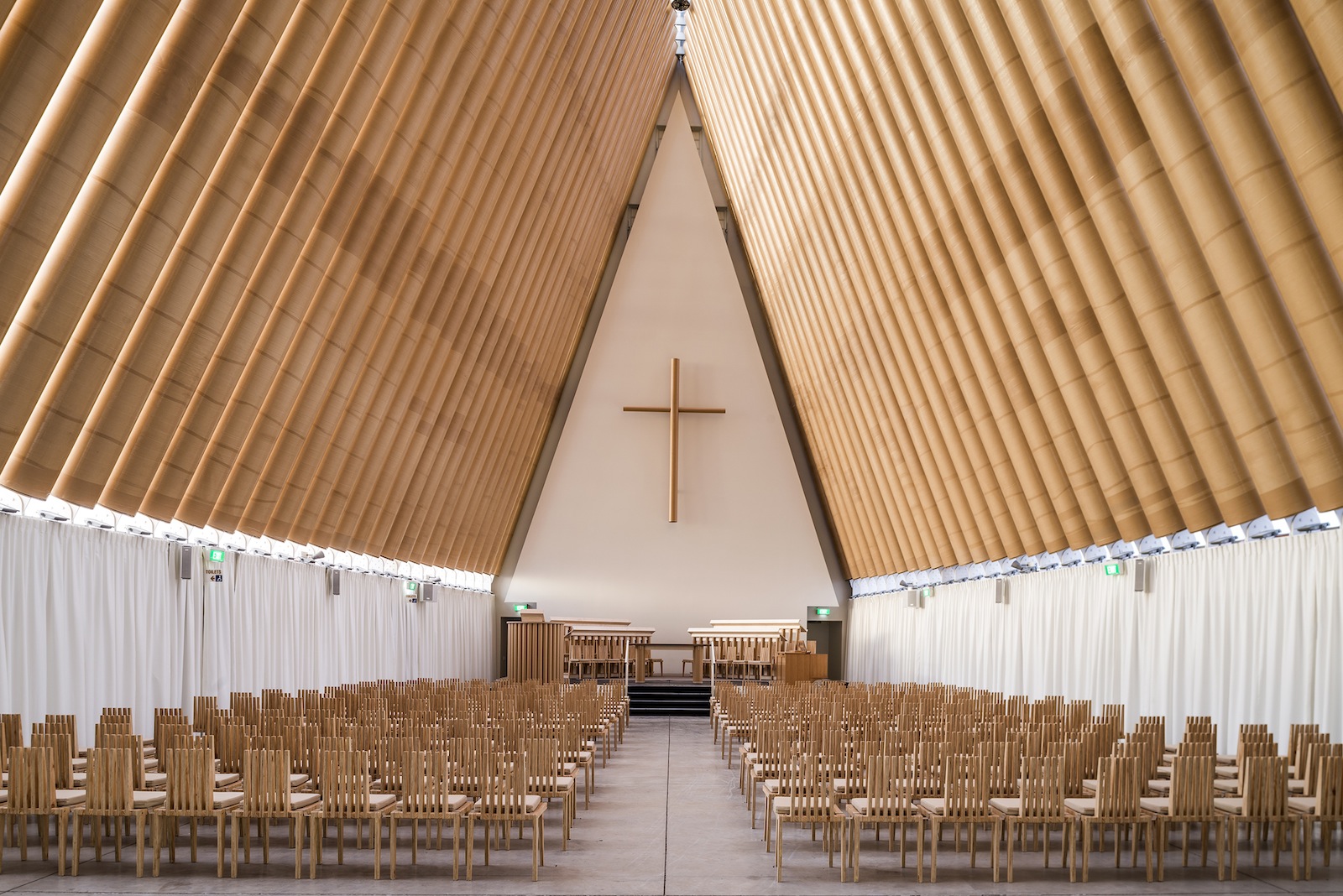

Cardboard Cathedral, 2013, Christchurch, New Zealand; Photo by Stephen Goodenough
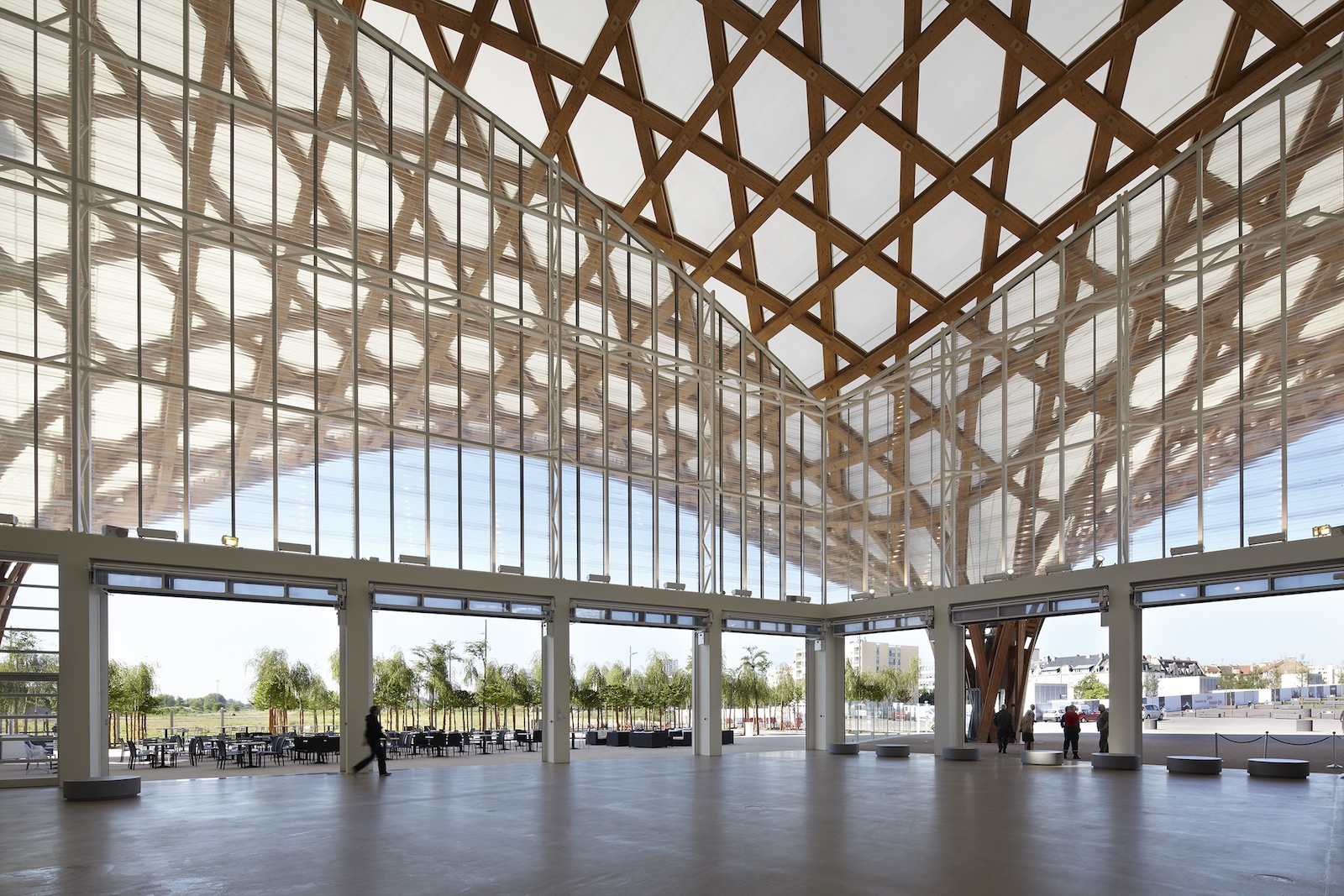

Centre Pompidou-Metz, 2010, France; Photo by Didier Boy de la Tour
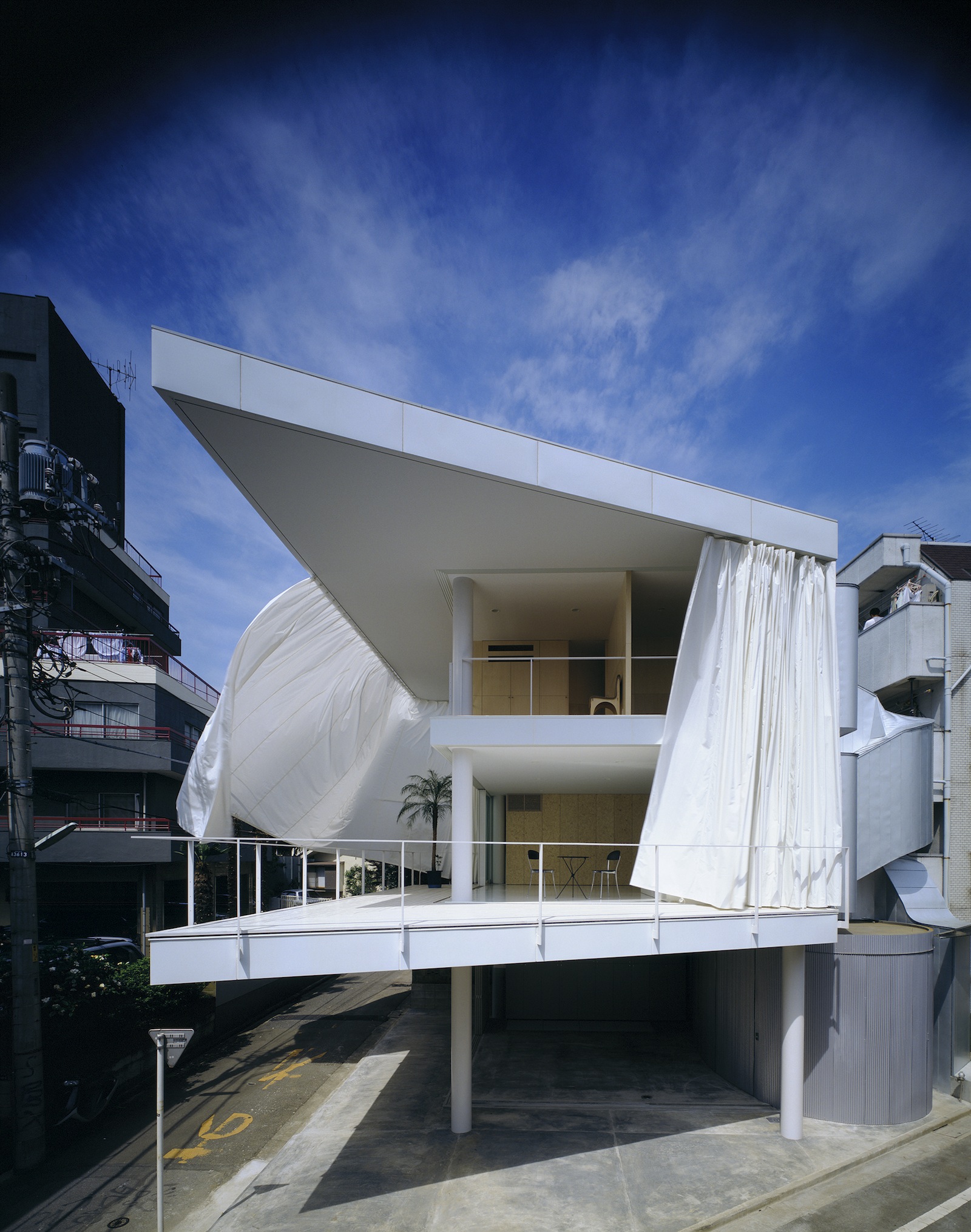

Curtain Wall House, 1995, Tokyo, Japan; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
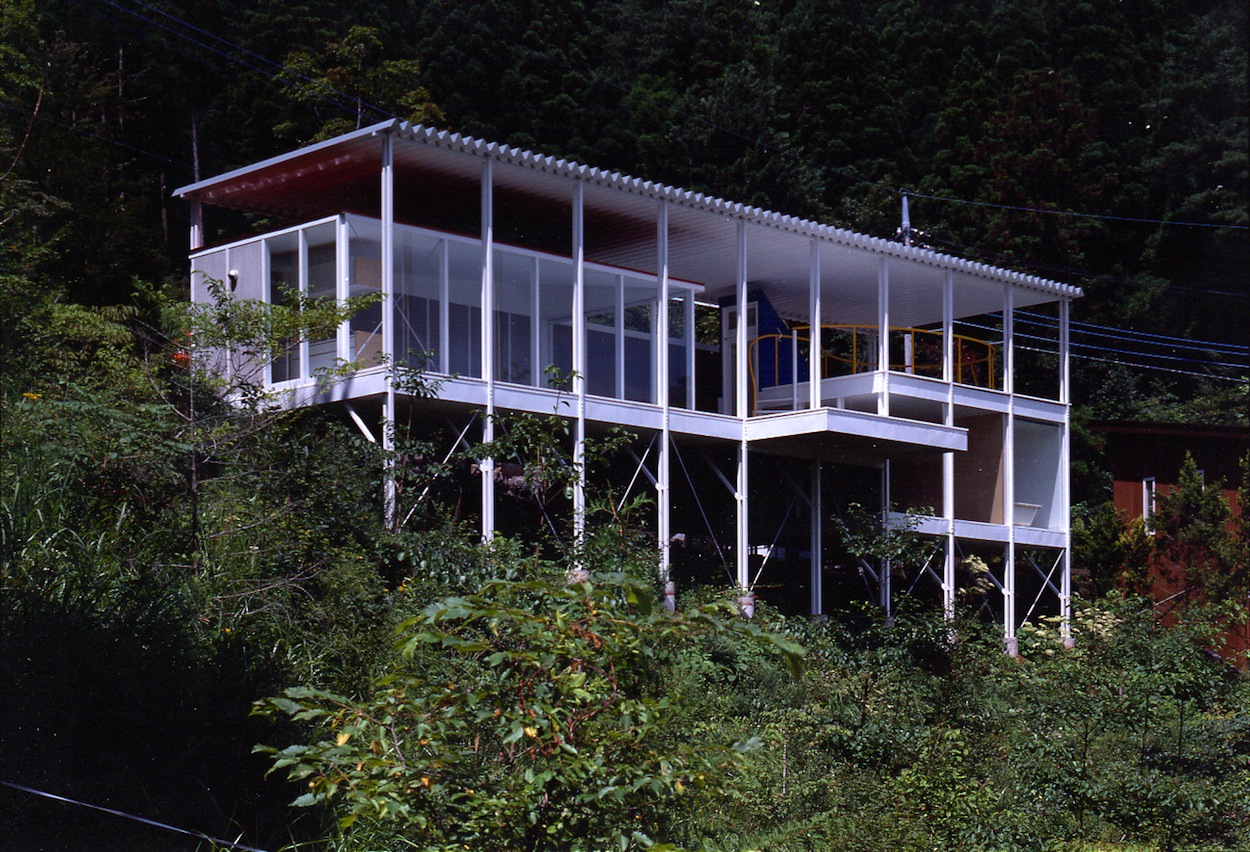

House of Double-Roof, 1993, Yamanashi, Japan; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
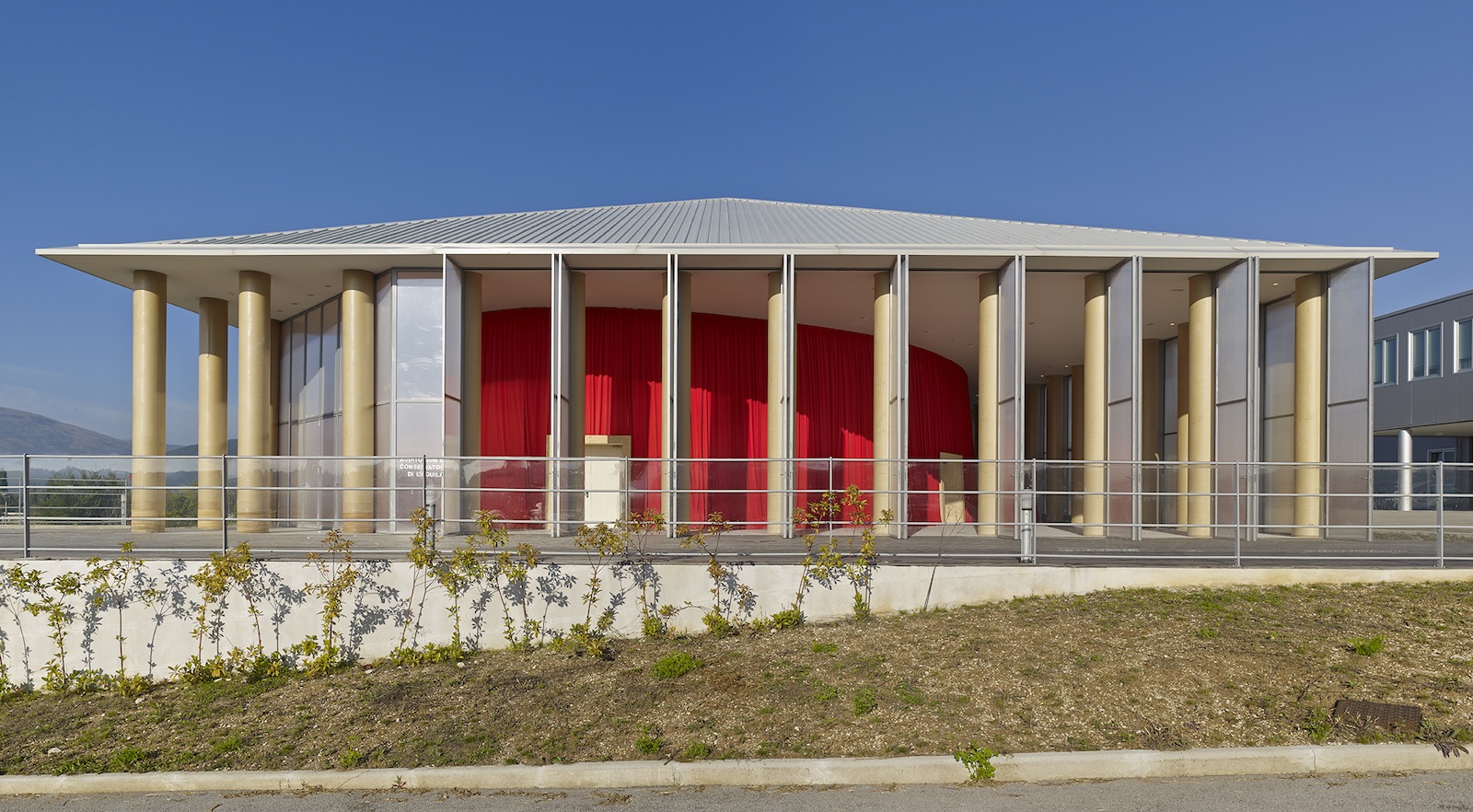

Paper Concert Hall, 2011, L’Aquila, Italy; Photo by Didier Boy de la Tour
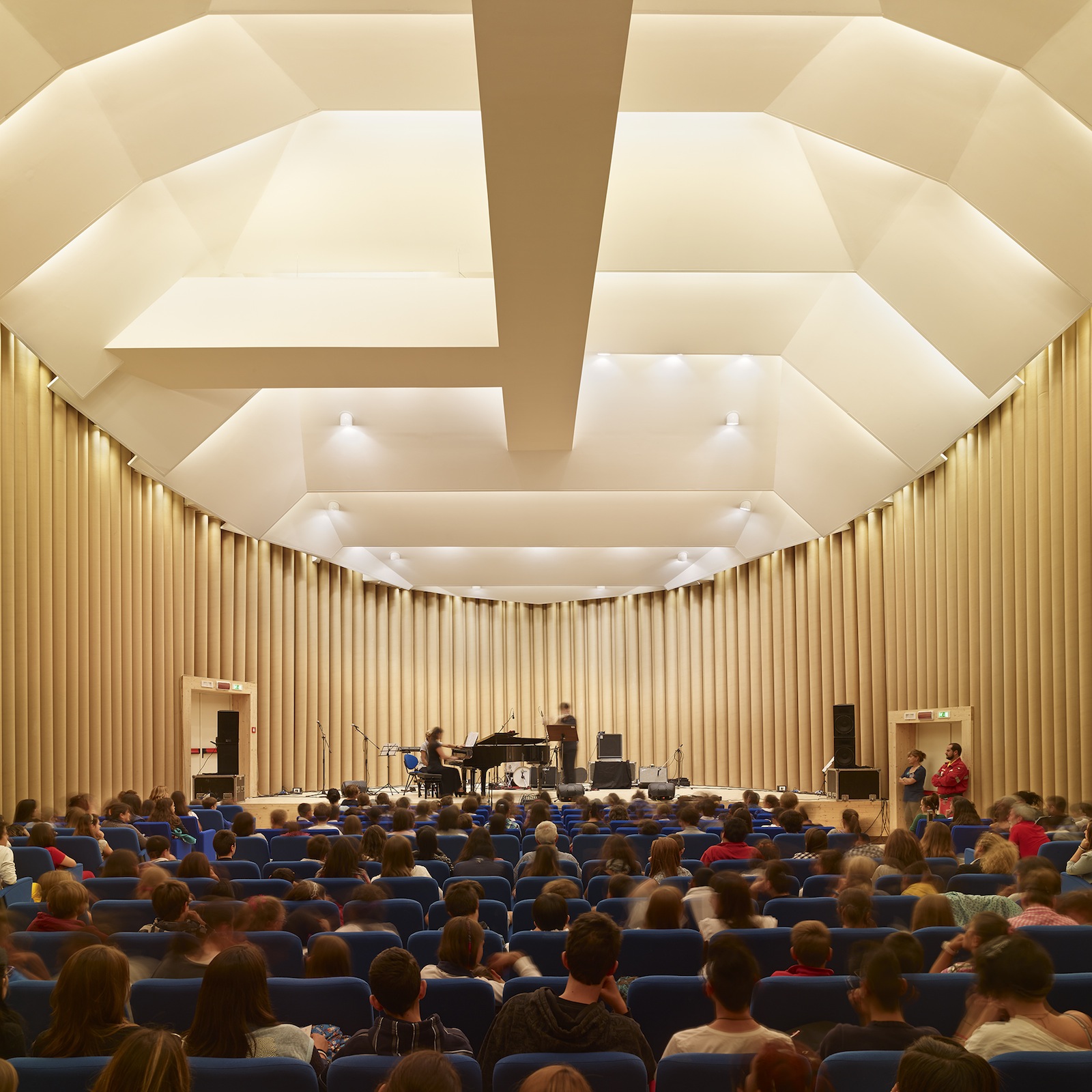

Paper Concert Hall, 2011, L’Aquila, Italy; Photo by Didier Boy de la Tour
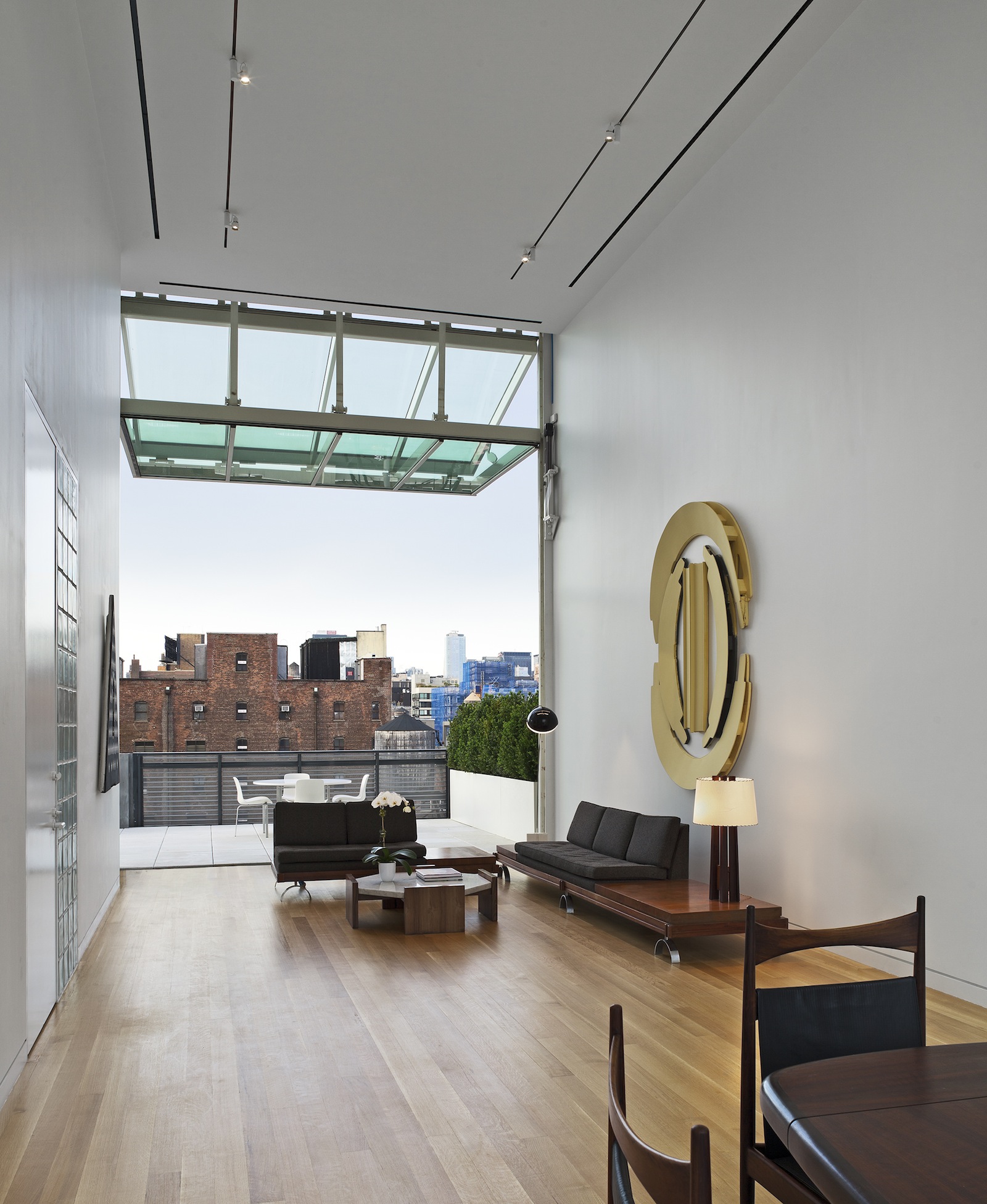

Metal Shutter House, 2010, New York; Photo by Michael Moran
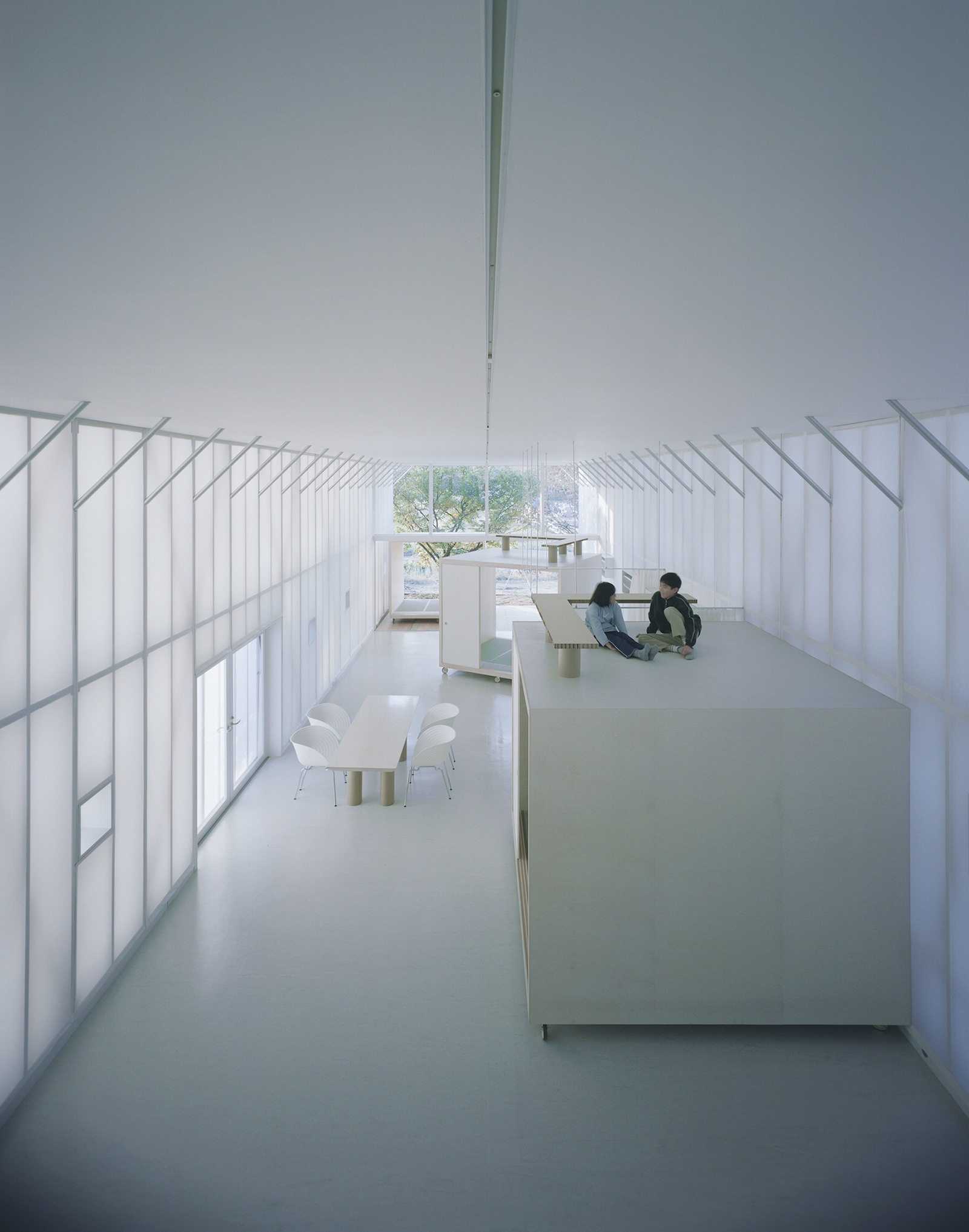

Naked House, 2000, Saitama, Japan; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
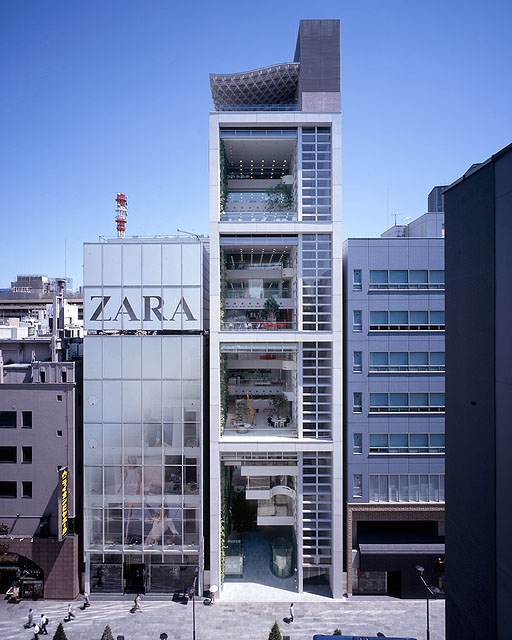

Nicolas G. Hayek Center, 2007, Tokyo, Japan; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
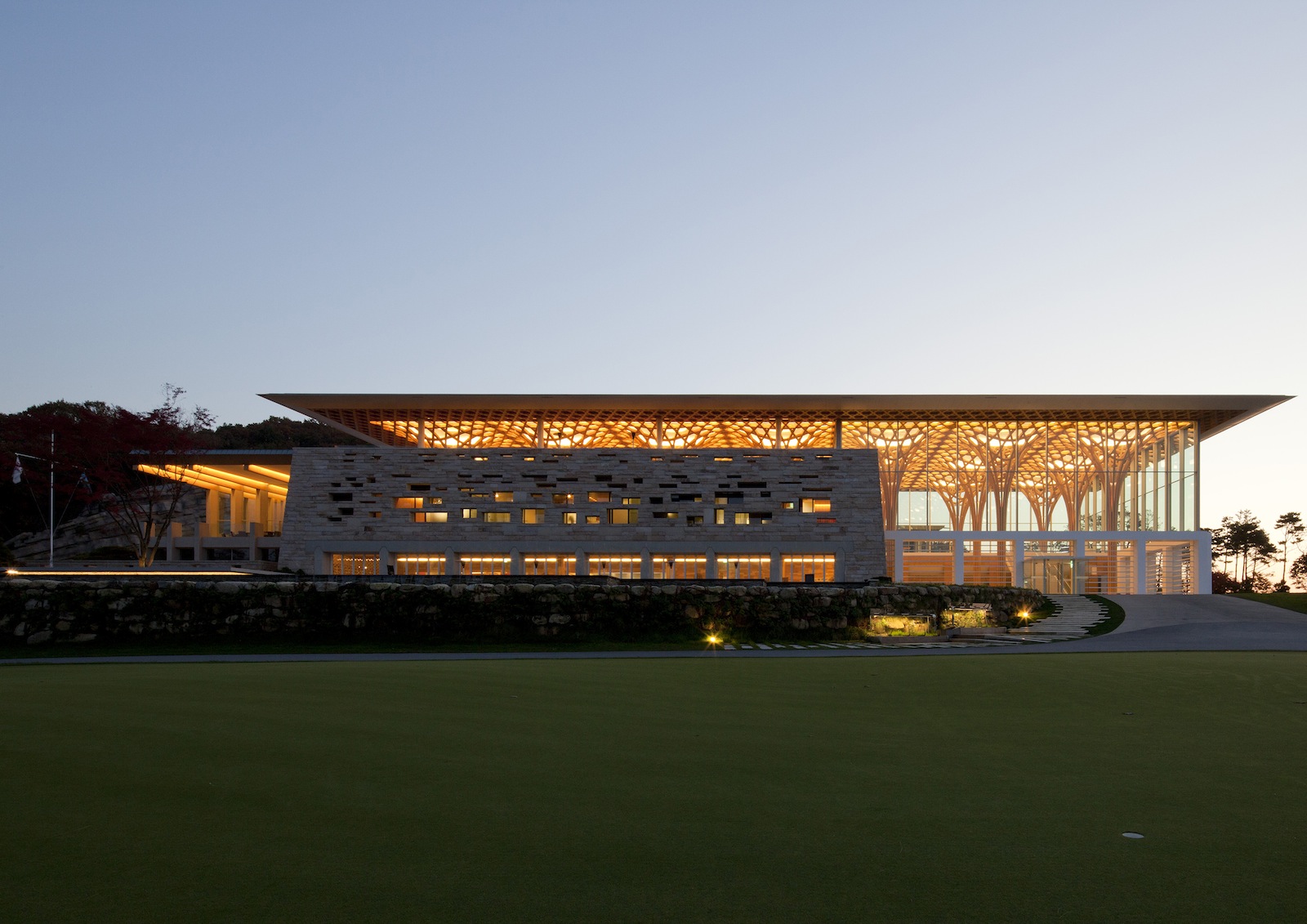

Haesley Nine Bridges Golf Club House, 2010, Korea; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
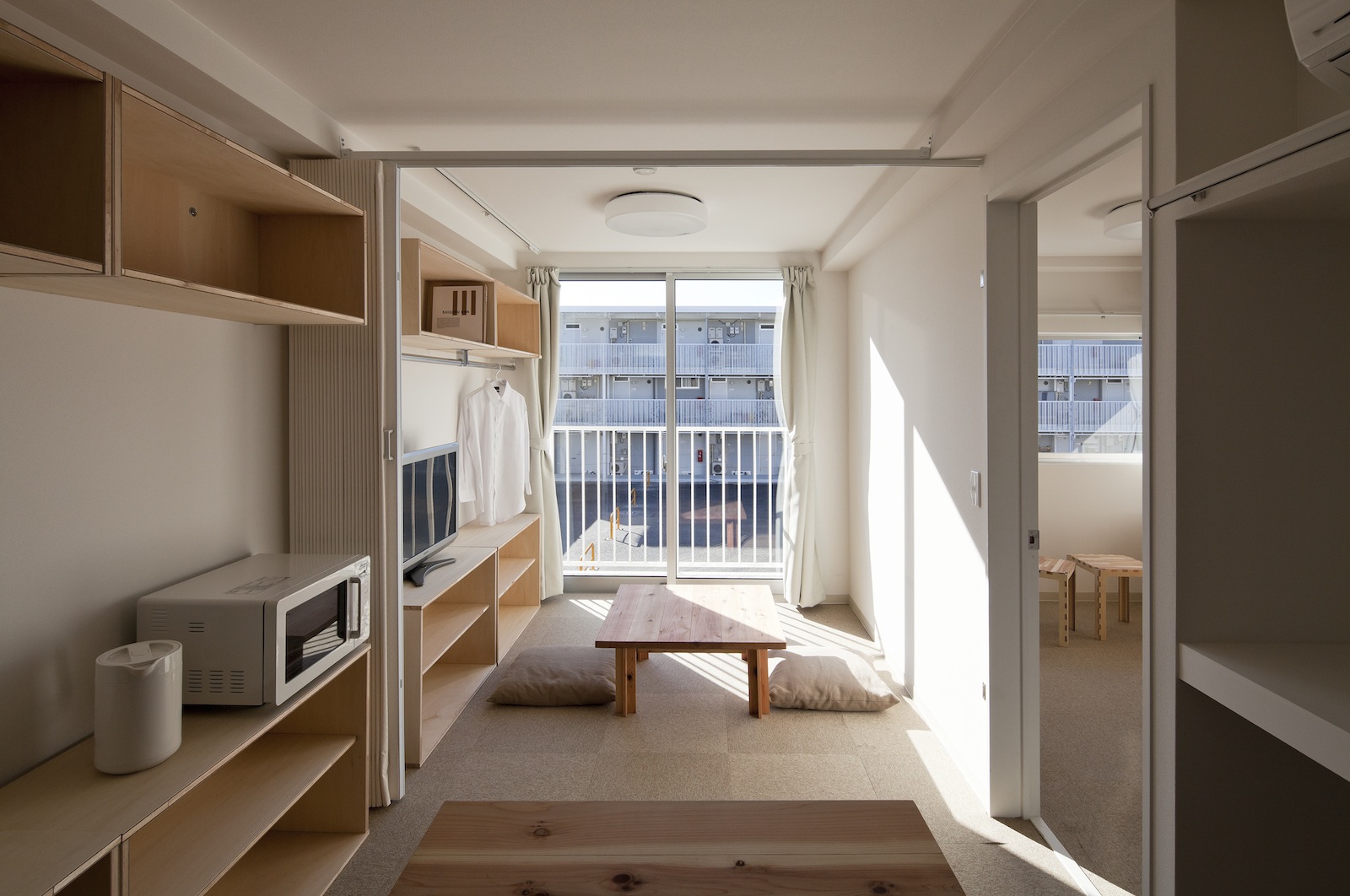

Container Temporary Housing, 2011, Onagawa, Miyagi, Japan; Photo by Hiroyuki Hirai
Related Stories
| Nov 2, 2010
Energy Analysis No Longer a Luxury
Back in the halcyon days of 2006, energy analysis of building design and performance was a luxury. Sure, many forward-thinking AEC firms ran their designs through services such as Autodesk’s Green Building Studio and IES’s Virtual Environment, and some facility managers used Honeywell’s Energy Manager and other monitoring software. Today, however, knowing exactly how much energy your building will produce and use is survival of the fittest as energy costs and green design requirements demand precision.
| Nov 2, 2010
Yudelson: ‘If It Doesn’t Perform, It Can’t Be Green’
Jerry Yudelson, prolific author and veteran green building expert, challenges Building Teams to think big when it comes to controlling energy use and reducing carbon emissions in buildings.
| Nov 2, 2010
Historic changes to commercial building energy codes drive energy efficiency, emissions reductions
Revisions to the commercial section of the 2012 International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) represent the largest single-step efficiency increase in the history of the national, model energy. The changes mean that new and renovated buildings constructed in jurisdictions that follow the 2012 IECC will use 30% less energy than those built to current standards.
| Nov 1, 2010
Sustainable, mixed-income housing to revitalize community
The $41 million Arlington Grove mixed-use development in St. Louis is viewed as a major step in revitalizing the community. Developed by McCormack Baron Salazar with KAI Design & Build (architect, MEP, GC), the project will add 112 new and renovated mixed-income rental units (market rate, low-income, and public housing) totaling 162,000 sf, plus 5,000 sf of commercial/retail space.
| Nov 1, 2010
John Pearce: First thing I tell designers: Do your homework!
John Pearce, FAIA, University Architect at Duke University, Durham, N.C., tells BD+C’s Robert Cassidy about the school’s construction plans and sustainability efforts, how to land work at Duke, and why he’s proceeding with caution when it comes to BIM.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 27, 2010
Grid-neutral education complex to serve students, community
MVE Institutional designed the Downtown Educational Complex in Oakland, Calif., to serve as an educational facility, community center, and grid-neutral green building. The 123,000-sf complex, now under construction on a 5.5-acre site in the city’s Lake Merritt neighborhood, will be built in two phases, the first expected to be completed in spring 2012 and the second in fall 2014.
| Oct 21, 2010
GSA confirms new LEED Gold requirement
The General Services Administration has increased its sustainability requirements and now mandates LEED Gold for its projects.
| Oct 18, 2010
World’s first zero-carbon city on track in Abu Dhabi
Masdar City, the world’s only zero-carbon city, is on track to be built in Abu Dhabi, with completion expected as early as 2020. Foster + Partners developed the $22 billion city’s master plan, with Adrian Smith + Gordon Gill Architecture, Aedas, and Lava Architects designing buildings for the project’s first phase, which is on track to be ready for occupancy by 2015.