In the rush to slash energy consumption in power-hungry data centers, design teams, equipment manufacturers, and tech companies have been developing clever, low-energy cooling solutions—from Facebook’s open-rack server setup with exposed motherboards, to Skanska’s eOPTI-TRAX liquid refrigerant coil system, to Google’s evaporative cooling schemes.
Solutions like these have helped data center facility operators achieve unprecedented energy performance levels, with power utilization effectiveness (PUE) ratios dipping below 1.10 in some instances. This means that less than 10% of the total energy consumption in a facility is attributed to noncomputing functions, such as air-conditioning and lighting.
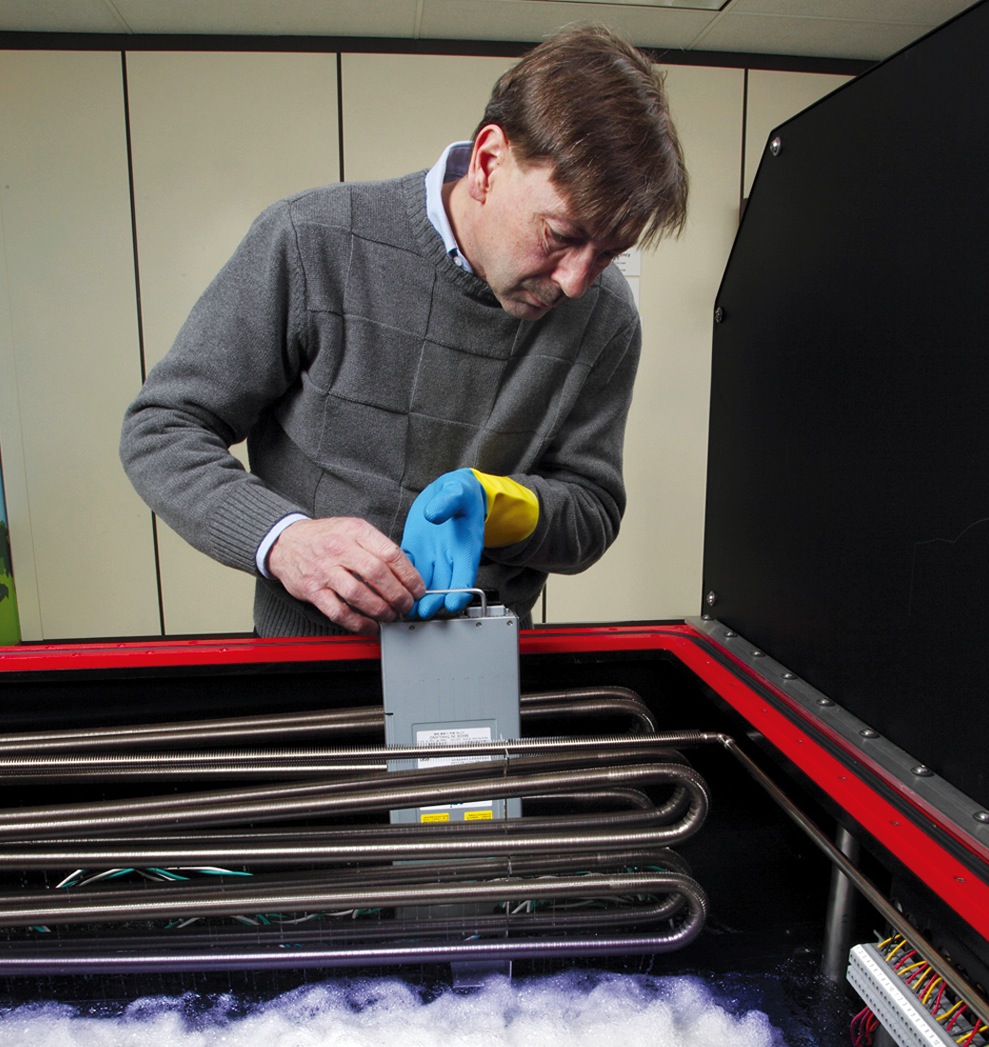
Now, a new technology promises to push the limits of data center energy efficiency even further. Called immersive cooling, it uses a liquid instead of air to cool the servers. LiquidCool Solutions, Green Revolution, and 3M are among the pioneers of this technology. Each system works a bit differently, but the basic idea is to submerge the motherboards in tanks filled with nonconductive fluid, which absorbs the heat generated by the processors.
LiquidCool Solutions, for example, uses an enclosed server module and pumps dielectric fluid through the server enclosure. Green Revolution uses a tub full of dielectric oil and circulates the liquid through the tubs. 3M also uses the tub approach, but the fluid boils and then is condensed to reject the heat.
By using liquid-based cooling at the server level, the need for air-conditioning is greatly reduced, or even eliminated in some climates. The same goes for traditional HVAC equipment and systems—chillers, fan units, raised floors, and so on.
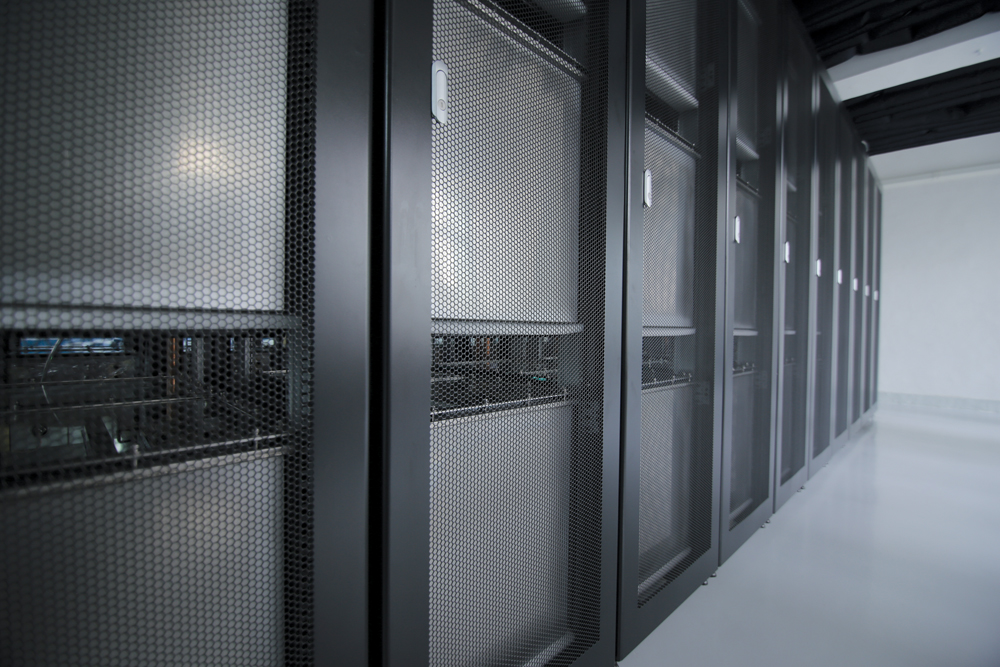

The Allied Control 500 kW immersion-cooled data center in Hong Kong is capable of delivering a PUE of just 1.02. The standard, 19-inch server racks use 3M Novec Engineered Fluids to enable tight component packaging for greater computing power in less space, according to Allied. Its open-bath design permits easy access to hardware and eliminates the need for pressure vessel enclosures and charging/recovery systems. PHOTO: COURTESY ALLIED CONTROL
“In most parts of the world, compressorized cooling would not be required with immersive cooling, since the liquid temperatures can be at a level where direct heat rejection using outdoor condensers or cooling towers would be sufficient,” says Thomas Squillo, PE, LEED AP, Vice President with Environmental Systems Design, who is currently researching the technology for the firm’s data center clients. “The fan energy is also eliminated, both in the HVAC system and in the server itself. Fluid pumping energy is very low.”
Other advantages of the cooling technology, according to Squillo:
• Increased performance and service life of the computer chips by eliminating heat buildup and problems related to contaminated air and dust.
• Ability to deploy data centers in extremely harsh environments without greatly impacting energy performance.
• Potential construction cost savings by downsizing or eliminating traditional HVAC systems.
Other than a few pilot projects, including a Bitcoin mining data center in Hong Kong and a Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory-led installation in Chippewa Falls, Wis., immersive cooling technology is largely untested. A year into the Bitcoin pilot, the data center operator reported a 95% reduction in cooling costs.
AEC professionals are starting to realize the potential for immersive cooling, especially for high-performance computing centers and consolidated, high-density data centers.
“Large data centers that have many homogenous machines at high density—like those operated by Internet and cloud providers—are a good application,” says Squillo. “Small footprint and minimal energy use are very important due to the volume of servers. These can be deployed in remote areas where space and energy are cheap, but where air quality may be a concern, without having to worry about the data center air.”
TRICKY DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Before the technology can be implemented, says Squillo, several nettlesome design factors specific to immersive cooling have to be addressed:
• Piping distribution to the racks and cooling units requires redundancy and valving to accommodate equipment maintenance without disrupting server performance.
• Additional equipment and space are needed to drain fluid from the tanks for server maintenance.
• Local code requirements may limit the amount of fluid that can be stored in a single room.
• For the foreseeable future, it’s unlikely that a large data center would be 100% liquid-immersion cooled. This means provisions will have to be made for both air- and liquid-cooling systems, which will require additional space in the data hall and mechanical room.
“I think that some form of this technology will definitely be the direction the data center market will take in the future,” says Squillo. “The market just needs to mature enough for owners to trust the technology and demand servers that are designed for a particular type of liquid cooling. In the short term, I see large companies and server manufacturers doing small-scale installations to test the concept, before wanting to implement it at a large scale.”
Related Stories
Project + Process Innovation | Mar 22, 2023
Onsite prefabrication for healthcare construction: It's more than a process, it's a partnership
Prefabrication can help project teams navigate an uncertain market. GBBN's Mickey LeRoy, AIA, ACHA, LEED AP, explains the difference between onsite and offsite prefabrication methods for healthcare construction projects.
Women in Design+Construction | Mar 21, 2023
Two leading women in construction events unite in 2023
The new Women in Residential + Commercial Construction Conference (WIR+CC) will take place in Nashville, Tenn., October 25-27, 2023. Combining these two long-standing events aligns with our mission to create an event most impactful for women in the $1.4 trillion U.S. commercial and residential design and construction industry.
Mass Timber | Mar 19, 2023
A 100% mass timber construction project is under way in North Carolina
An office building 100% made from mass timber has started construction within the Live Oak Bank campus in Wilmington, N.C. The 67,000-sf structure, a joint building venture between the GCs Swinerton and Wilmington-headquartered Monteith Construction, is scheduled for completion in early 2024.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 17, 2023
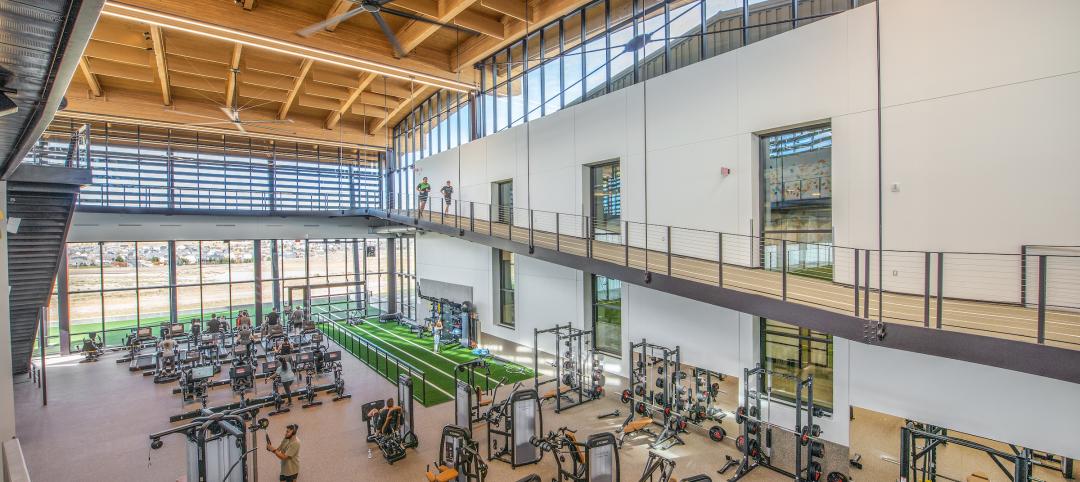
Aurora, Colo., recreation center features city’s first indoor field house, unobstructed views of the Rocky Mountains
In January, design firm Populous and the City of Aurora, Colo. marked the opening of the Southeast Aurora Recreation Center and Fieldhouse. The 77,000-sf facility draws design inspiration from the nearby Rocky Mountains. With natural Douglas Fir structure and decking, the building aims to mimic the geography of a canyon.
Architects | Mar 16, 2023
HKS launches partner diversity program to create a more diverse workforce and partnership network
Design firm HKS has launched a new partner diversity program that will work to build a more diverse AEC ecosystem. The HKS xBE program will give xBE firms (a term encompassing all disadvantaged businesses) and their members “access to opportunities to build relationships, pursue new work, and bolster innovation within the architecture and design professions,” according to HKS.
Sustainability | Mar 16, 2023
Lack of standards for carbon accounting hamper emissions reduction
A lack of universally accepted standards for collecting, managing, and storing greenhouse gas emissions data (i.e., carbon accounting) is holding back carbon reduction efforts, according to an essay published by the Rocky Mountain Institute.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
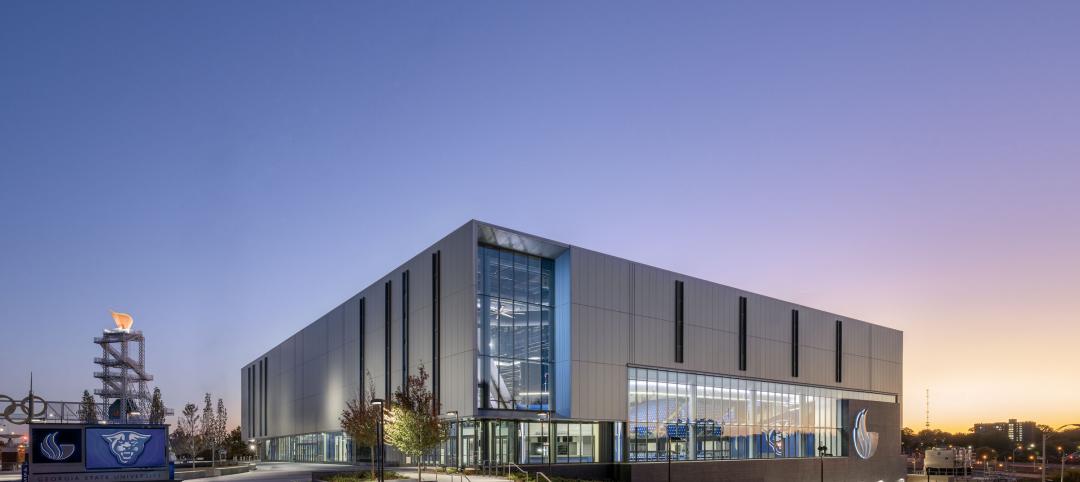
Georgia State University Convocation Center revitalizes long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood
Georgia State University’s new Convocation Center doubles the arena it replaces and is expected to give a shot in the arm to a long-neglected Atlanta neighborhood. The new 200,000 sf multi-use venue in the Summerhill area of Atlanta is the new home for the university’s men’s and women’s basketball teams and will also be used for large-scale academic and community events.
Sponsored | Cladding and Facade Systems | Mar 15, 2023
Metal cladding trends and innovations
Metal cladding is on a growth trajectory globally. This is reflected in rising demand for rainscreen cladding and architectural metal coatings. This course covers the latest trends and innovations in the metal cladding market.
Education Facilities | Mar 15, 2023
DLR Group’s Campus Planning Studio defines new leadership
Linsey Graff named Campus Planning Leader. Krisan Osterby transitions to Senior Planner.
Building Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Reaping the benefits of offsite construction, with ICC's Ryan Colker
Ryan Colker, VP of Innovation at the International Code Council, discusses how municipal regulations and inspections are keeping up with the expansion of off-site manufacturing for commercial construction. Colker speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield.