With student debt in the U.S. topping $1.2 trillion, and with recent graduates racking up an average $30,000 in loans, it’s no wonder college and university officials are under intense pressure to hold down costs. Campus building projects are hardly exempt from this imperative.
Critics of higher education point to “shiny new facilities” as contributing to ballooning tuition fees and room and board charges. Advocates for new buildings claim they are strategic assets in the battle to recruit and retain top students and faculty.
“Everybody agrees that higher ed is too expensive, but are we going to do without that fitness center and other amenities? No,” says Robert Schulz, AIA, Associate Vice President of Operations and University Architect at San Diego State University.
The tug of war between those seeking to control costs and those demanding ever more attractive campus facilities has put higher education officials in a bind. They continue to greenlight projects to upgrade building stock, but are using a wider breadth of cost-saving strategies to squeeze more value out of every capital dollar.
Here’s a look at how several representative institutions of higher learning are using alternate financing schemes, rigorous programming and design processes, and cost-containment measures to rein in building project expenses.
HOW institutions are using PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS to BRIDGe THE FINANCE GAP
Some schools are turning to so-called public-private partnerships to widen their financing capabilities. In a P3 arrangement, the institution contracts with a private developer to design, construct, and manage a new building for an extended period, usually 30 years. University P3 projects must have dedicated revenue streams, so only a few building types qualify: student housing, dining halls, parking facilities, and research centers with rent-paying private-sector tenants.
P3s allow universities to get projects built faster than through traditional design-bid-build, without assuming more debt. The P3 reduces the institution’s exposure to cost overruns, which become the responsibility of the private partner.
Some schools are starting to take the P3 plunge; others are just testing the waters. “This is a major wave of the future,” says John Finke, Senior Managing Director, National Development Council, a P3 owner/developer. Universities are ideal clients for P3 owners due to their stability and willingness to take on long-term leases, he says.
As a nonprofit entity working with nonprofit institutions, NDC uses tax-exempt 501c3 bonds for project funding. P3 specialists are exempt from public procurement rules at public colleges and universities in many states, making it easier to fast-track projects. These advantages mean that a P3 project can usually be built for 15-25% less than conventional design-bid-build projects without reducing quality, says Finke.
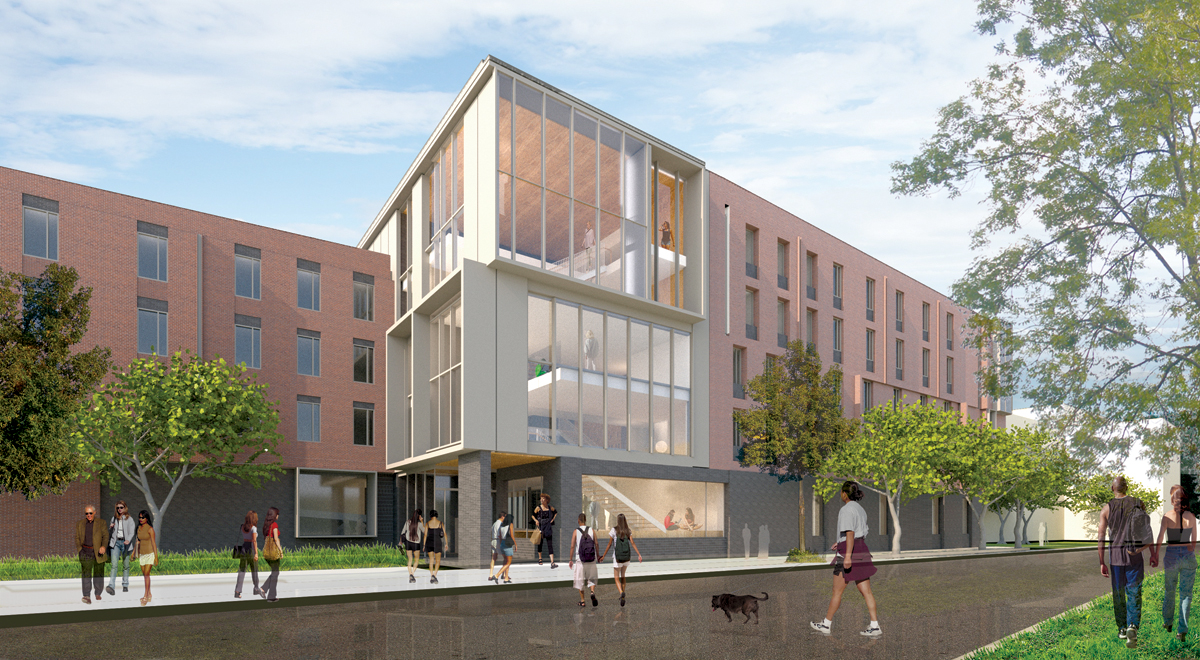
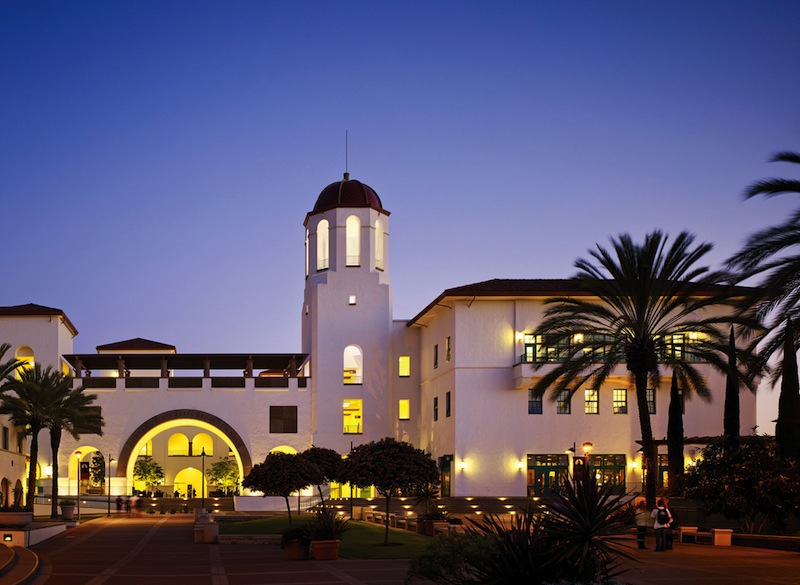 The $104 million, LEED Platinum Conrad Prebys Aztec Student Union at San Diego State University. The four-story, 206,000-sf union has a 300-seat theater, three dining facilities, retail space, a banquet hall, a bowling/games center, a fitness center, a 6,000-sf gym, 13 meeting rooms, and office spaces. The Building Team: CannonDesign (architect), P2S Engineering (MEP/telecom engineer), John A. Martin & Associates (SE), BWE/Burkett & Wong Engineers (CE), Kaplan Gehring McCaroll Architectural Lighting, Carter Romanek Landscape Architects, and Sundt Construction (CM). Photo: © Nick Merrick / Hedrich Blessing
The $104 million, LEED Platinum Conrad Prebys Aztec Student Union at San Diego State University. The four-story, 206,000-sf union has a 300-seat theater, three dining facilities, retail space, a banquet hall, a bowling/games center, a fitness center, a 6,000-sf gym, 13 meeting rooms, and office spaces. The Building Team: CannonDesign (architect), P2S Engineering (MEP/telecom engineer), John A. Martin & Associates (SE), BWE/Burkett & Wong Engineers (CE), Kaplan Gehring McCaroll Architectural Lighting, Carter Romanek Landscape Architects, and Sundt Construction (CM). Photo: © Nick Merrick / Hedrich Blessing
Last August, the University of Alaska Fairbanks partnered with NDC to complete its first P3 project, a renovation and 43,000-sf dining hall expansion of the Wood Center student union. The university’s primary motivation for going the P3 route was fast access to capital. “It gave us a way to jump positions on our capital project funding list,” says Jenny Campbell, PE, Director of UAF’s Division of Design and Construction.
The UAF project is owned by Community Properties Alaska, which was created and staffed by NDC. CPA and NDC sold the bonds on behalf of the university. Under the agreement, UAF will pay the owner $1.45 million a year for about 30 years, well under the $1.6 million a year cap approved by the university’s board of trustees. The fee covers $1.37 million a year in bond payments, plus additional management fees for CPA.
The downside to P3s for universities is loss of control over building design and project management. Under the P3 model, the owner/developer hires the architect and GC. The university may retain some influence over design, but it does not have final say. Campbell says that giving up control wasn’t easy. “We’re experienced in construction management,” she says. “Giving control to a third party was difficult for us.”
“Everybody agrees that higher ed is too expensive, but are we going to do without that fitness center and other amenities? No.” —Robert Schulz, AIA, Associate Vice President of Operations and University Architect at San Diego State University
Campbell says the university is pleased with the overall look and functionality of the $27.5 million building, which recently won a SCUP AIA/CAE Excellence in Architecture Merit Award. “We have a beautiful facility,” she says. “It was built on time and came in at about a million dollars under budget.”
But Campbell acknowledges that her division would have done some things differently had they managed the project. She says that UAF relies heavily on the recommendations of the nearby Cold Climate Housing Research Center with regard to building envelope standards. “They are experts on building envelopes in arctic and subarctic climates,” she says.
Campbell says the design team took the center’s recommendations to heart, but some building envelope details were less than optimal. She says the university strives for tight continuity in the vapor barrier, particularly at duct penetrations. “We’re very precise about those details,” Campbell says. “We had to work very closely with the contractor [GHEMM] and the architect [P+W] to ensure that our building envelope requirements were met.” The university manages the building and pays all utility costs, so this was not a trivial matter.
UAF will consider P3 for future projects, with some fixes, says Campbell. “If we do P3 again, I believe we should work to improve the construction phase communication process outlined in the agreement with the developer and owner that outlines how communication works,” she says. She would also like the university to have more control over design decision making, but acknowledges that the owner may be hesitant to give up control.
Design and construction firms that want to participate in P3 projects should step up their networking efforts with P3 owner/developers. “Design partner matches are often made well in advance of the advertisement,” says David Damon, AIA, LEED AP, Principal and Higher Education Practice Leader with Perkins+Will. “You need to have established relationships.”
developing new STRATEGIES FOR HOLDING DOWN COSTS
San Diego State University initially thought that renovating its student union rather than building a new one seemed like a money-saving option. Students approved the fee increase for the project in 2006, but “as we dove into the design, we realized that the renovation would cost significantly more than we had planned,” says University Architect Schulz. The budget was $50 million; renovation would have cost $76 million. Schulz says the existing building was “not beloved,” so there was no constituency to preserve it. After it became clear that SDSU could get a newer, better building for about the same price as a renovated one, the decision to build new became obvious.
Students were intimately involved in the programming phase for the 206,000-sf Conrad Prebys Aztec Student Union. To introduce a dose of reality into their wish lists, Schulz imposed a strict rule: “Nobody was allowed to voice additions to the program until they had a plan that included the budget impact,” he says. “That added a lot of honesty to the process.”
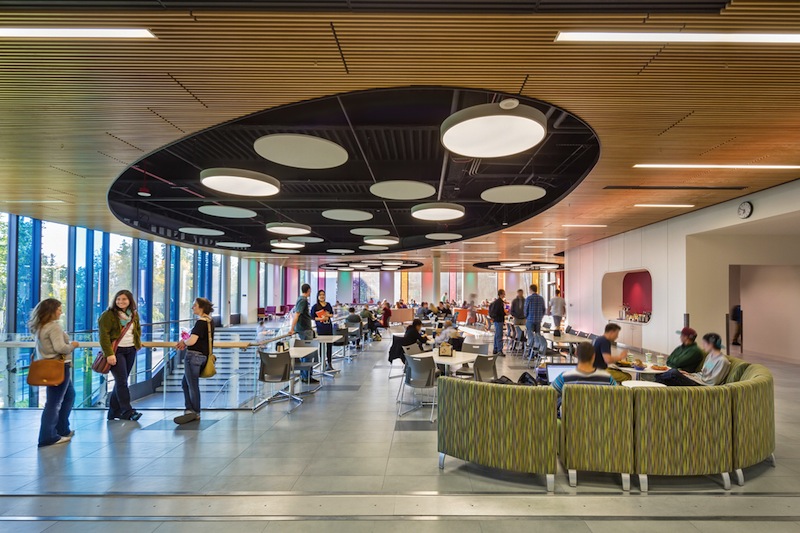 Perkins+Will (architect) led the Building Team for the 43,000-sf Wood Center, the renovated and expanded student union at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. The dining facility added 420 seats; several student organizations gained office space. Also on the team: Community Properties Alaska Inc. (owner), Lorig Associates (development manager), Patrick Mechanical Inc. (mechanical engineer), Fullford Electric (electrical engineer), Bucher Glass (glazing/fenestration), Florcraft (flooring), HVAC Inc. (HVAC contractor), and GHEMM Company (GC). Photo: Kevin Smith
Perkins+Will (architect) led the Building Team for the 43,000-sf Wood Center, the renovated and expanded student union at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. The dining facility added 420 seats; several student organizations gained office space. Also on the team: Community Properties Alaska Inc. (owner), Lorig Associates (development manager), Patrick Mechanical Inc. (mechanical engineer), Fullford Electric (electrical engineer), Bucher Glass (glazing/fenestration), Florcraft (flooring), HVAC Inc. (HVAC contractor), and GHEMM Company (GC). Photo: Kevin Smith
On projects that require student approval, it’s best to start with a fairly fleshed-out program with a realistic budget before asking students to vote. “If you start with the fee vote, you may not get best value for the project,” says CannonDesign’s Craig A. Hamilton, FAIA, LEED AP, a Project Principal. The danger is that students could okay a fee for a building that winds up disappointing everyone in the long run.
As the SDSU student union design process progressed, the project team kept a close watch on costs. “We had a design evolution log at every meeting,” says Schulz. “There was a projector on the wall showing the most recent full-on estimate.” The tab was updated in real time after every significant design decision. “We’ve made this process a model for future projects,” he says.
DESIGN EFFICIENCIES can yield LONG-TERM energy SAVINGS
Colleges and universities are in the building game for the long run, and therefore place high value on lifetime savings from energy-efficient systems. Comparing projected savings with first costs is a calculation that can change frequently as new technologies and building products and systems come on line during the course of the project.
The goal at the University of Kansas is to build to 30% above ASHRAE standards, says James Modig, University Architect and Director of Design and Construction Management. To reach that mark, KU is moving away from large, centralized chilled water plants to smaller district plants that serve multiple buildings. This system will allow operators to scale service up or down based on need. In a group of three chillers, when two units operating at 80–90% of capacity can provide enough cooling for the district, the third can remain essentially inactive. That’s much more efficient than running all three at lower capacity.
The desire to achieve high-level environmental goals can lead to a call for value engineering. Keene (N.H.) State College hopes to meet the Architecture 2030 Challenge in a new 350-bed living/learning residence currently under design. The college wants the building to operate without fossil fuels. “With costs on the table, there is pressure to make cuts,” says Perkins+Will’s Damon. Some scaling back of the design may be enough to offset the higher costs of highly efficient features such as geothermal heating and cooling. “You won’t notice that we took one cantilever off and reduced corridor width by one foot,” says Damon.
Designers, engineers, and contractors should be prepared to offer cost-shaving options to university clients in order to free up funds for high-efficiency systems. Clients driven by environmental goals may be willing to cut back on features like common area space and high-end finishes to pay for high-efficiency HVAC, lighting, and plumbing features.
Building Teams can also help universities use bulk buying of materials to stretch construction budgets. KU’s Modig is negotiating with manufacturers for multi-year agreements with suppliers to maximize the university’s buying power. He says that he’d also like to leverage the buying power of large general contracting firms to secure even better procurement deals.
Colleges and universities are looking everywhere for ways to stretch construction dollars. Building Teams that can help these institutional clients maximize value on projects stand a greater chance to thrive in this dynamic market sector.
Related Stories
Architects | Jun 22, 2023
Keith Hempel named President of LPA Design Studios
LPA Design Studios today announced the promotion of Chief Design Officer Keith Hempel, FAIA, to president of the 58-year-old integrated design firm. Hempel, who joined LPA in 1995, has been an integral part of the firm’s growth, helping to develop an integrated design process that has produced industry-leading results.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Virtual Reality | Jun 16, 2023
Can a VR-enabled AEC Firm transform building projects?
With the aid of virtual reality and 3D visualization technologies, designers, consultants, and their clients can envision a place as though the project were in a later stage.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Office Buildings | Jun 15, 2023
An office building near DFW Airport is now home to two Alphabet companies
A five-minute drive from the Dallas-Fort Worth International Airport, the recently built 2999 Olympus is now home to two Alphabet companies: Verily, a life sciences business, and Wing, a drone delivery company. Verily and Wing occupy the top floor (32,000 sf and 4,000 sf, respectively) of the 10-story building, located in the lakeside, work-life-play development of Cypress Waters.
Transit Facilities | Jun 15, 2023
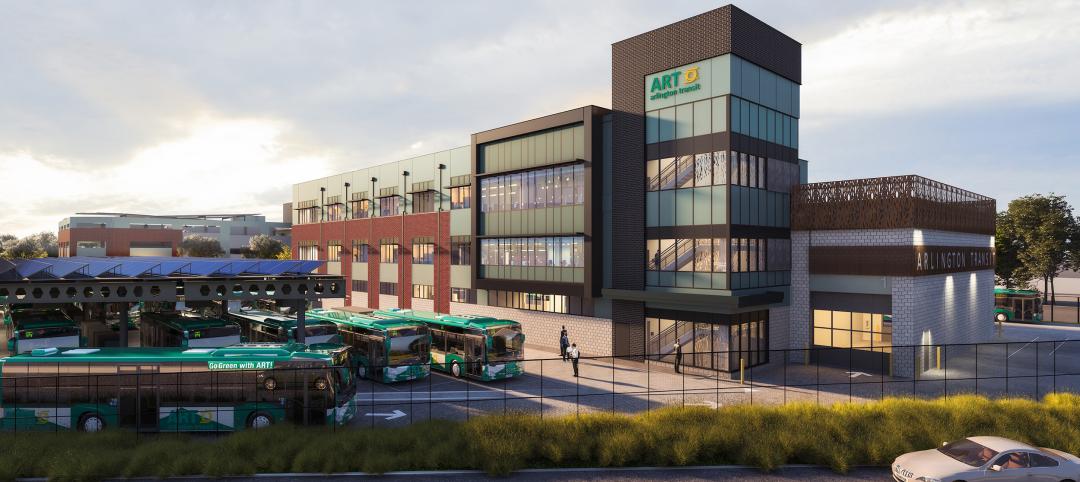
Arlington, Va., transit station will support zero emissions bus fleet
Arlington (Va.) Transit’s new operations and maintenance facility will support a transition of their current bus fleet to Zero Emissions Buses (ZEBs). The facility will reflect a modern industrial design with operational layouts to embrace a functional aesthetic. Intuitive entry points and wayfinding will include biophilic accents.
Urban Planning | Jun 15, 2023
Arizona limits housing projects in Phoenix area over groundwater supply concerns
Arizona will no longer grant certifications for new residential developments in Phoenix, it’s largest city, due to concerns over groundwater supply. The announcement indicates that the Phoenix area, currently the nation’s fastest-growing region in terms of population growth, will not be able to sustain its rapid growth because of limited freshwater resources.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 15, 2023
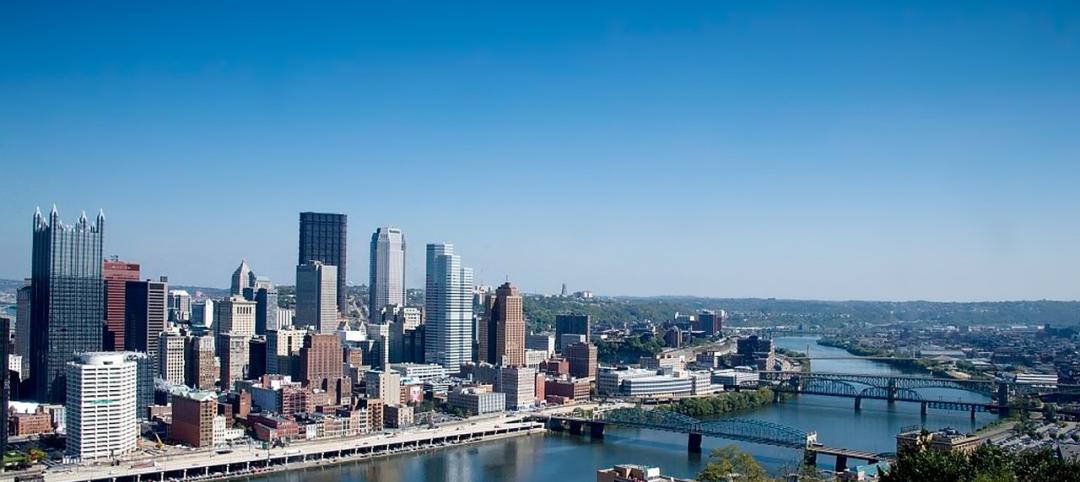
Alliance of Pittsburgh building owners slashes carbon emissions by 45%
The Pittsburgh 2030 District, an alliance of property owners in the Pittsburgh area, says that it has reduced carbon emissions by 44.8% below baseline. Begun in 2012 under the guidance of the Green Building Alliance (GBA), the Pittsburgh 2030 District encompasses more than 86 million sf of space within 556 buildings.
Industry Research | Jun 15, 2023
Exurbs and emerging suburbs having fastest population growth, says Cushman & Wakefield
Recently released county and metro-level population growth data by the U.S. Census Bureau shows that the fastest growing areas are found in exurbs and emerging suburbs.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 14, 2023
Design considerations for behavioral health patients
The surrounding environment plays a huge role in the mental state of the occupants of a space, especially behavioral health patients whose perception of safety can be heightened. When patients do not feel comfortable in a space, the relationships between patients and therapists are negatively affected.