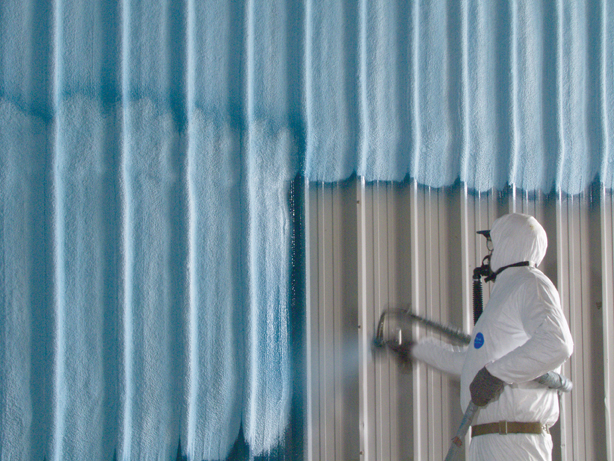
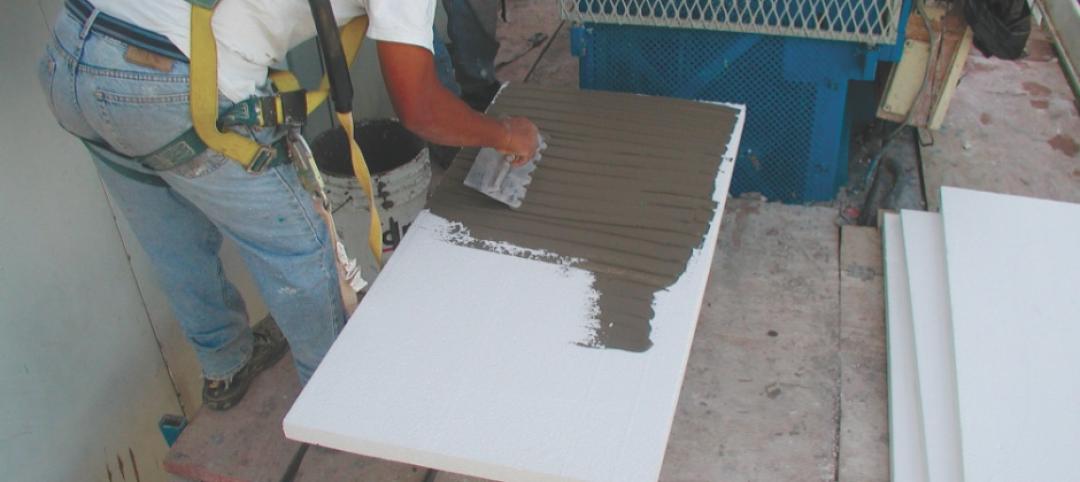
In the nonresidential sector, spray polyurethane foam (SPF) has been used most often for re-roofing existing buildings. While SPF is hardly a new product (it’s been around for at least 35 years), the applications for both open-cell and closed-cell foam have been growing steadily as Building Teams grasp its potential to improve energy efficiency, interior comfort and durability in all types of structures.
Demand for SPF is increasing in both new construction and retrofit applications in North America, says Brian Troy, commercial market manager for Icynene. “On the new construction side, the increase can be quantified by the sheer number of new specifications coming out every day, calling for SPF within the published construction documents,” he says.
LEED certification is also pushing more architects, contractors, and developers to use spray foam in the walls and building envelope as well as on the roof, says Michael Sievers, business manager for spray polyurethane foams at BASF Corp. That’s because SPF has multiple attributes, notably air sealing, thermal performance, and structural performance. “Instead of being a niche product, it’s becoming more of a mainstream product,” says Sievers.
The introduction of renewable-based SPF products that reduce the need for petroleum-based polyols has probably had the most significant impact on commercial applications, as architects, designers and building owners look for additional opportunities toward total point contributions on LEED-registered projects. This is especially true for government facilities that must comply with mandates for energy efficiency. “Spray foam is 25-30% more energy efficient because it’s seamless and monolithic, so it’s often used in building retrofits,” says Rick Tucker, global business manager for Honeywell’s TerraStrong, a closed-cell SPF.
Because spray foam is often 10-15% more expensive than other types of insulation, it’s sometimes used in combination with products such as rigid board insulation in order to achieve higher R-values. “If you want R-20 or R-30, you can use board stock on the exterior and foam on the interior,” says Tucker. “It’s an effective way to reduce or eliminate thermal bridging.”
Let’s take a look at some recent projects where Building Teams—and their clients—benefited from using SPF.
THE SEARCH FOR ‘ULTRA-INSULATION’
For the New Century International Elementary School in Cumberland County, N.C., SfL+a Architects, Raleigh, N.C., wanted the project to be more than just another LEED Platinum building: They wanted it to serve as a model for future buildings that will save their owners millions of dollars in the long term. The school is designed for net-zero energy use, meaning that it will generate more energy than it consumes. Among the sustainable features is a closed-loop geothermal HVAC system, solar panels that will generate electricity and heat water, controlled lighting systems, and NCFI’s InsulBloc spray foam insulation for the building envelope.
“We wanted ultra-insulation, air and vapor barriers in a single product,” says Robert W. Ferris, AIA, REFP, LEED AP, CEO and president of SfL+A. “With board insulation, there are a lot of joints that have to be taped to prevent water from entering. Foam eliminates all the joints. The primary benefits are increased R-values and decreased infiltration losses, and we get a nice waterproofing over our block.”
EXTRA : Spray Foam Insulation Trends |
At 175-185 Wyman Street, a new corporate campus in Waltham, Mass., Columbia Construction Co., North Reading, Mass., used NCFI’s InsulBloc for the first time in conjunction with a terra cotta rainscreen system. The project consists of two buildings with a variety of exterior surfaces, including metal, terra cotta, and precast concrete. The owner is seeking LEED Gold certification.
“Moisture can get in behind the terra cotta wall panels, but it drains out at the bottom,” explains Sam Dettore, a senior project manager with Columbia. “The spray-on insulation, which becomes inert—a block of insulation behind that terra cotta—is preferable because it’s resistant to any kind of moisture that might get into the wall.”
Dettore says two different methods were used to apply the NCFI product. For the metal exteriors, foam was sprayed onto an air and vapor barrier and the metal panels were installed over that. Sanford Contracting, North Billerica, Mass., prefabricated the wall panels for the terra cotta exteriors. “Sanford assembled the walls and applied the foam and terra cotta in their warehouse, then delivered the panels to the job site and hung them in place on the steel superstructure of the building,” says Dettore.
A recent inspection by Columbia Construction showed that InsulBloc is living up to expectations. “We’ve gone through an entire cycle of weather that you can have in New England, and it’s resisted any kind of cracking or twisting,” says Dettore.
MORE DEMAND FOR LOW-PRESSURE FOAM
In commercial buildings, contractors use high-pressure foam—sprayed out of a rig at more than 1,000 psi—to create a monolithic exterior insulation layer. But low-pressure foam also has its uses in commercial construction, says Tom Fishback, vice president of R&D for Fomo Products, whose spray foam is dispensed from portable kits at 200 psi.
“Probably the greatest demand for low-pressure spray foam in commercial buildings, both new construction and retrofit, is at the roof/wall juncture,” says Fishback. “That juncture is often not air-sealed. Even in new buildings, the usual practice is to stuff fiberglass insulation into the cavity in a non-fire-rated wall. The width of that gap can be six inches, and it allows cold air and pollutants to come through from outside.”
Fishback says some contractors have started sealing roof/wall junctures with Fomo’s low-pressure foam, dispensing it to a depth of two inches. He says this results in an R-value of 12.
The retrofit market is another strong one for low-pressure foam. In New York City, for example, old factories and warehouses are being converted to loft condominiums and the exterior cladding of old public schools is being stripped off and replaced. Low-pressure foam has proven very effective in sealing the gaps between windows and walls. Those gaps, which can be up to four inches wide, are one of the greatest ingress points for moisture and air, Fishback says. Applying a Class A, two-component spray foam to the gaps gives the insulation an R-value of 6.2 per inch.
One more benefit of spray foam insulation: acoustics. SPF has proven to be an effective sound barrier in office conference rooms where noisy presentations or webcasts may take place. “There’s a lot of noise emanating from those rooms to adjacent offices,” says Fishback. “Open-cell foam is very easy to apply, and it creates a good monolithic layer on interior walls.”
Related Stories
Sponsored | | Mar 25, 2014
Johns Hopkins chooses SLENDERWALL for a critical medical facility reconstruction
After decades of wear, the hand-laid brick envelope of the Johns Hopkins nine-story Nelson/Harvey inpatient facility began failing. SLENDERWALL met the requirements for renovation.
| Mar 21, 2014
Forget wood skyscrapers - Check out these stunning bamboo high-rise concepts [slideshow]
The Singapore Bamboo Skyscraper competition invited design teams to explore the possibilities of using bamboo as the dominant material in a high-rise project for the Singapore skyline.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 20, 2014
13 dazzling wood building designs [slideshow]
From bold structural glulam designs to striking textured wall and ceiling schemes, these award-winning building projects showcase the design possibilities using wood.
| Mar 19, 2014
Federal agency gives thumbs up to tall wood buildings
USDA's support for wood projects includes training for AEC professionals and a wood high-rise design competition, to launch later this year.
| Mar 17, 2014
Rem Koolhaas explains China's plans for its 'ghost cities'
China's goal, according to Koolhaas, is to de-incentivize migration into already overcrowded cities.
| Mar 12, 2014
14 new ideas for doors and door hardware
From a high-tech classroom lockdown system to an impact-resistant wide-stile door line, BD+C editors present a collection of door and door hardware innovations.
| Mar 10, 2014
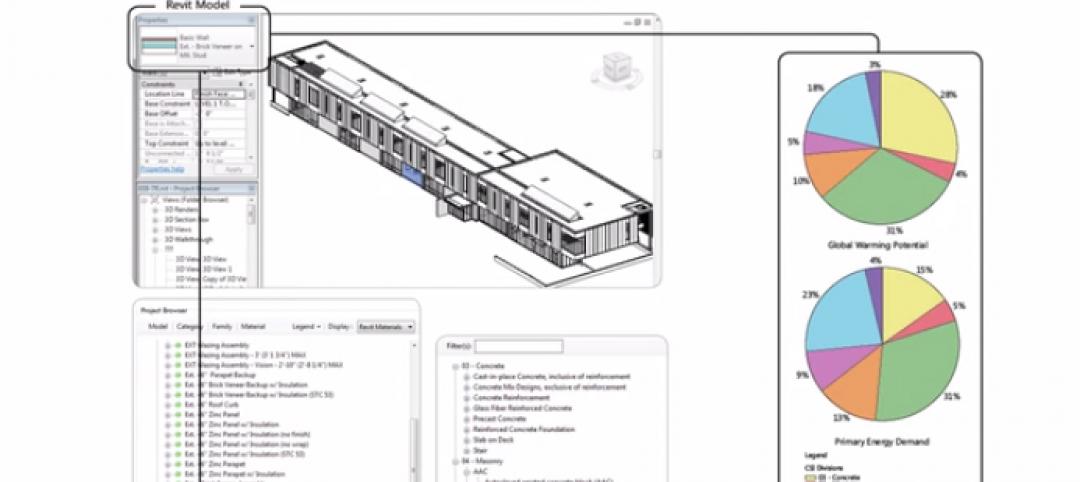
Meet Tally – the Revit app that calculates the environmental impact of building materials
Tally provides AEC professionals with insight into how materials-related decisions made during design influence a building’s overall ecological footprint.
| Mar 5, 2014
5 tile design trends for 2014
Beveled, geometric, and high-tech patterns are among the hot ceramic tile trends, say tile design experts.
| Mar 4, 2014
How EIFS came to America
Design experts from Hoffmann Architects offer a brief history of exterior insulation and finish systems in the U.S.