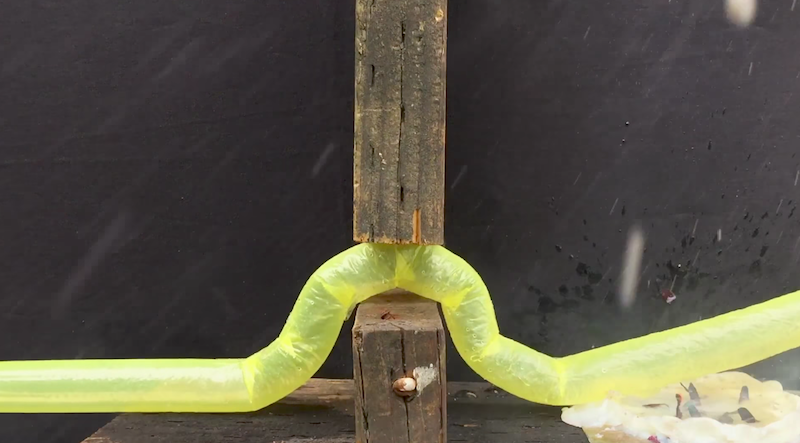
Like a game Snake come to life, a new robot being developed at Stanford grows like a vine and has the ability to weave through tight spaces to provide applications from disaster relief to simplifying construction projects.
The main idea behind the robot is uncomplicated; the “snake” is a tube of soft thin plastic that is folded inside itself. As the material is forced out, either pneumatically or hydraulically, the robot grows longer. According to Stanford, the robot’s design is so useful because the tip moves and results in growth while the body remains stationary, making it incredibly difficult for the robot to become stuck.
“The body can be stuck to the environment or jammed between rocks, but that doesn’t stop the robot because the tip can continue to progress as new material is added to the end,” says Elliot Hawkes, a visiting Assistant Professor from the University of California, Santa Barbara in a Stanford article on the robot.
As the robot grows, it can pull cables along, which means it could be used in the construction industry to help wire new and renovated buildings by traveling in the walls, floors, or ceilings. The robot can make turns via a control system that differentially inflates the body and a software system bases direction decisions on images received from a camera at the tip, so pipes or other obstacles already located in the wall, ceiling, or floor space become non-issues.
Other applications include scaling the robot up for search and rescue operations, growing vertically to act as an antenna, or being used to deliver materials, such as water, to hard to reach places.
The robot is detailed in a Science Robotics paper published on June 19.
Related Stories
| Apr 23, 2014
Experimental bot transfers CAD plans onto construction sites
The Archibot is intended to take technical data and translate it into full-scale physical markings on construction sites.
Sponsored | | Apr 23, 2014
Ridgewood High satisfies privacy, daylight and code requirements with fire rated glass
For a recent renovation of a stairwell and exit corridors at Ridgewood High School in Norridge, Ill., the design team specified SuperLite II-XL 60 in GPX Framing for its optical clarity, storefront-like appearance, and high STC ratings.
| Apr 9, 2014
Steel decks: 11 tips for their proper use | BD+C
Building Teams have been using steel decks with proven success for 75 years. Building Design+Construction consulted with technical experts from the Steel Deck Institute and the deck manufacturing industry for their advice on how best to use steel decking.
| Apr 2, 2014
8 tips for avoiding thermal bridges in window applications
Aligning thermal breaks and applying air barriers are among the top design and installation tricks recommended by building enclosure experts.
| Apr 2, 2014
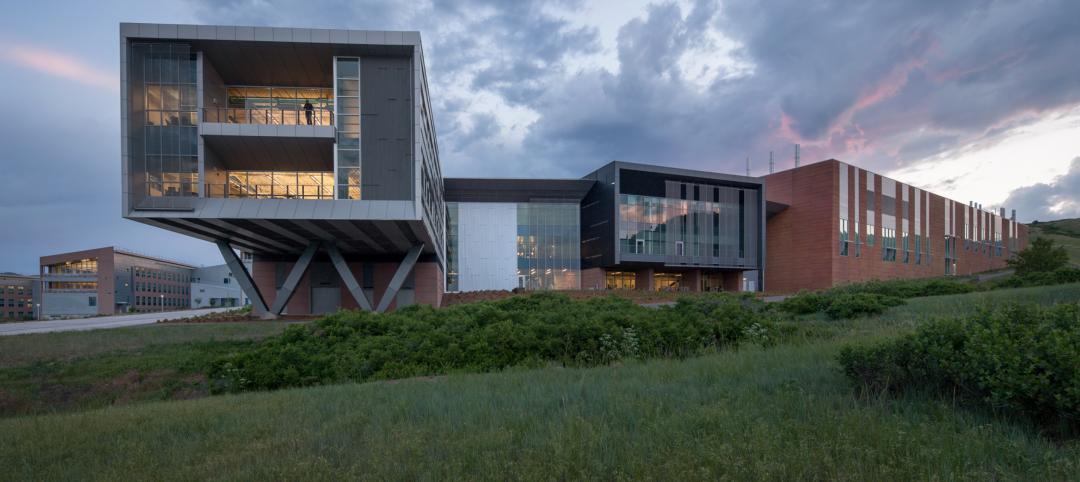
Check out the stunning research facility just named 2014 Lab of the Year [slideshow]
NREL's Energy Systems Integration Facility takes top honors in R&D Magazine's 48th annual lab design awards.
| Mar 26, 2014
Callison launches sustainable design tool with 84 proven strategies
Hybrid ventilation, nighttime cooling, and fuel cell technology are among the dozens of sustainable design techniques profiled by Callison on its new website, Matrix.Callison.com.
| Mar 26, 2014
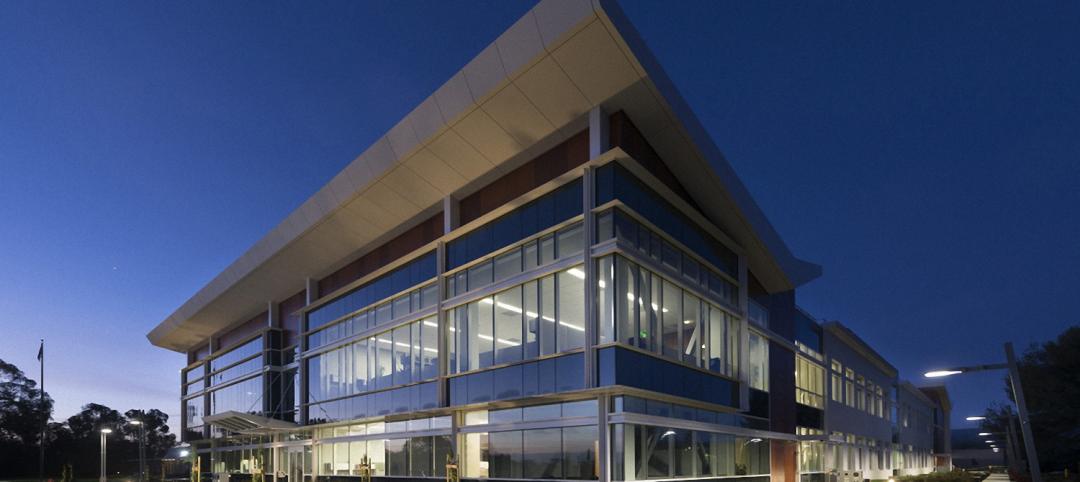
First look: Lockheed Martin opens Advanced Materials and Thermal Sciences Center in Palo Alto
The facility will host advanced R&D in emerging technology areas like 3D printing, energetics, thermal sciences, and nanotechnology.
| Mar 21, 2014
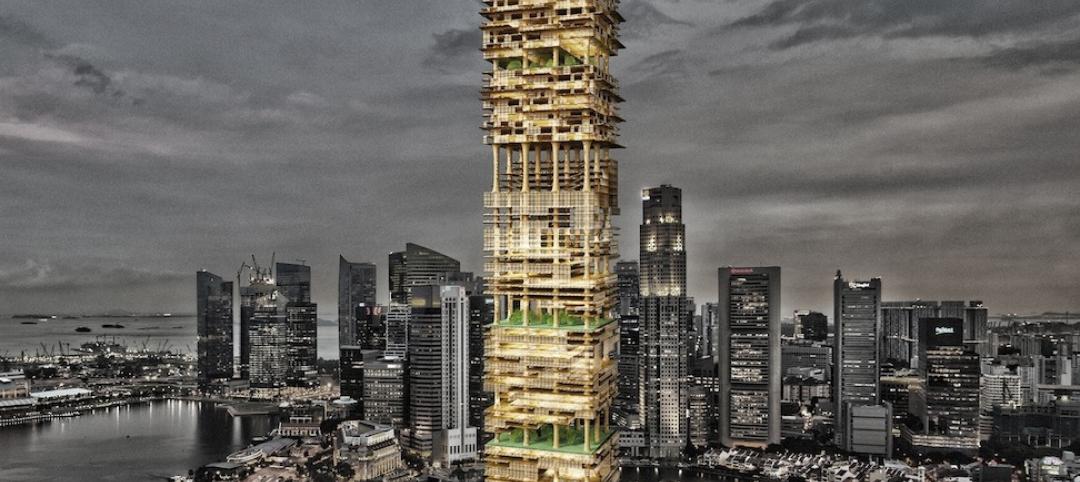
Forget wood skyscrapers - Check out these stunning bamboo high-rise concepts [slideshow]
The Singapore Bamboo Skyscraper competition invited design teams to explore the possibilities of using bamboo as the dominant material in a high-rise project for the Singapore skyline.
| Mar 20, 2014
Common EIFS failures, and how to prevent them
Poor workmanship, impact damage, building movement, and incompatible or unsound substrate are among the major culprits of EIFS problems.
| Mar 13, 2014
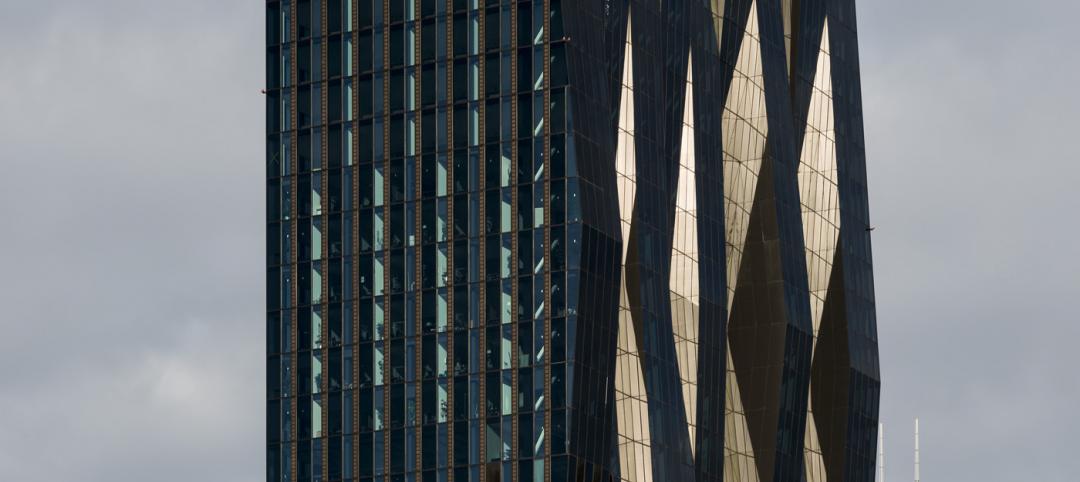
Austria's tallest tower shimmers with striking 'folded façade' [slideshow]
The 58-story DC Tower 1 is the first of two high-rises designed by Dominique Perrault Architecture for Vienna's skyline.