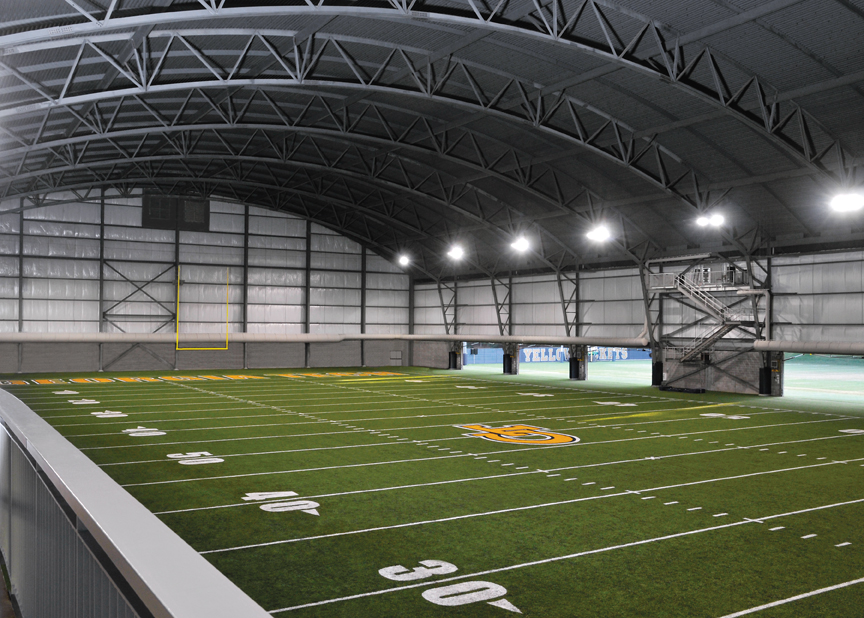
Last fall, the design-build team for Georgia Tech’s new indoor football practice facility was given just 40 weeks to design and construct the John and Mary Brock Football Facility in Atlanta. The design-build team led by project management firm Barton Malow won the job on October 15, 2010, and the 88,000-sf facility had to be ready by August 1, 2011 in time for the new season of Yellow Jackets’ Football. The $9.75 million new practice facility would also have to be accessible to Georgia Tech officials, boosters, and recruits considering committing to the program the summer before it opened.
“Our sole focus was minimizing risk to deliver the project on schedule,” said Jason McFadden, project manager for Barton Malow. “We weren’t using BIM to show clash detection or make a pretty model.”
At the kickoff meeting last October, Barton Malow and other members of the Building Team—architect Knight Architects of Atlanta, structural engineer Walter P Moore, and owner representatives from Georgia Tech and construction partner May Moeller Purcell—signed memos that committed each discipline to specific completion dates for the various phases of the project. They also set up a workflow where the entire team had to go through the BIM model together on a weekly basis. Most important, the team agreed on a set of tools to model in, collaborate, and deliver closeout documents—a combination of Tekla Engineer and Detailing packages and Tekla for Construction Management to manage and track project status, including submittals, RFIs, and scheduling. Subsequently, TeklaBIMsight for collaboration was added.
At that initial meeting, the Building Team decided that designing a building that was mostly structural steel (rather than a prefabricated metal building) would be the only way to deliver on the tight schedule. Shortly thereafter, Barton Malow published an RFP for steel fabricators challenging them to explain how their system would most benefit the project. The Atlanta office of SteelFab won the project and committed to using Tekla for direct design-to-fabrication as outlined in the RFP.
Walter P Moore started development of the steel model in Tekla Structures in early December. By December 8, 2010, the first model was out to the Steelfab team. The process ran smoothly from that initial model exchange, since both the engineer and fabricator were using native Tekla Structures files. The final, fully detailed design model was approved by Walter P Moore on January 8, 2011. Only 12 weeks separated the start of steel design to the start of steel erection.
Truss sections were determined by what could be shipped and built on the tight site on Georgia Tech’s campus. Each 228-foot truss was divided into six equal sections, which were delivered and bolted together on the ground at the site. The stair tower and camera platform, including rails, were all fully modeled in Tekla.
“The key was continuous back-and-forth information exchange,” McFadden said. Steelfab suggested several fabrication techniques that really allowed us to achieve our schedule goals.
The Tekla Model Reviewer was used early in the steel design, but once TeklaBIMSight was released last February, the Building Team quickly adopted it as its collaboration tool. Ambassador Steel of Waukesha, Wis., was chosen as the concrete rebar fabricator; however, the concrete foundation design was delayed because a geotechnical report was not delivered until December 7. That cut the team’s schedule to three weeks for completion of concrete design and one week to complete the reinforcing bar detail shop drawings.
“We gambled a little bit with publishing approved rebar shop drawings prior to the concrete subcontract award,” McFadden said. “That’s not yet very common in the eastern part of the country but Ambassador Steel really came through.”
Ambassador and Walter P Moore delivered a full rebar model for the foundation by December 30. It took only eight days from the time the concrete subcontract was awarded to get rebar on site. The structural engineer modeled all concrete reinforcement and shared it with Ambassador Steel in Tekla to streamline the rebar detailing process. Ambassador also produced reinforcing bend diagrams directly from the model. The concrete model was integrated with the steel and electrical model by late January. By that time TeklaBIMsight was being used as the collaboration tool and model viewer of choice. Tekla BIMsight was also taken out into the field in tablet computers to match up the model to work in the field. With both rebar and steel design, the model exported directly to the fabricator’s production equipment.
The integrated models were used for scheduling and erection planning sequencing with Tekla’s Construction Management solution, which also provided a tool to evaluate erection plan and sequence.
CREATING A VISUAL REPRESENTATION
To coordinate the schedule, the Barton Malow team used model-based color-coded timelines for scheduling and just-in-time delivery. The Suretrak schedule was integrated with the Tekla task manager to provide a visual representation of all completed and upcoming construction tasks. Custom reports were created using the BIM model to streamline a two-week look-ahead for installation of each component of the building. No paper approval documents were used on the project until file record copies were needed.
The Tekla Model Reviewer and BIMsight from tablets and computers in the field were used to document and discuss all construction problems in the field. Thanks to the weekly meetings and detailed project memos from design to construction there were no clashes at any point in construction. Last August 1, the new practice facility opened on time and on budget.
“We’re not necessarily trying to have every project engineer or project manager or superintendent having to learn a particular BIM software, but for every project team to be using BIM technology in the way that’s right for their job,” said Phil Kirby, Barton Malow’s senior vice president. “We don’t have a one-size-fits-all solution because every job is different. What we have found is that prefabrication can be applied to most jobs, and choosing the right tool to enable that is what worked at Georgia Tech.” BD+C
--
Contributing Editor Jeff “BIMBoy” Yoders blogs on BIM and related IT topics at www.BDCnetwork.com.
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 35 Veterans Affairs Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
LEO A DALY, Page Southerland Page, Guidon, and HDR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest Veterans Affairs facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 40 Military Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
Michael Baker International, HDR, Whitman, Requardt & Associates, and Stantec top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest military facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Office Buildings | Dec 12, 2023
Transforming workplaces for employee mental health
Lauren Elliott, Director of Interior Design, Design Collaborative, shares practical tips and strategies for workplace renovation that prioritizes employee mental health.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 150 Local Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HOK, Stantec, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest local government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 90 State Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Page Southerland Page, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Stantec, and NORR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest state government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Codes and Standards | Dec 11, 2023
Washington state tries new approach to phase out fossil fuels in new construction
After pausing a heat pump mandate earlier this year after a federal court overturned Berkeley, Calif.’s ban on gas appliances in new buildings, Washington state enacted a new code provision that seems poised to achieve the same goal.
Green | Dec 11, 2023
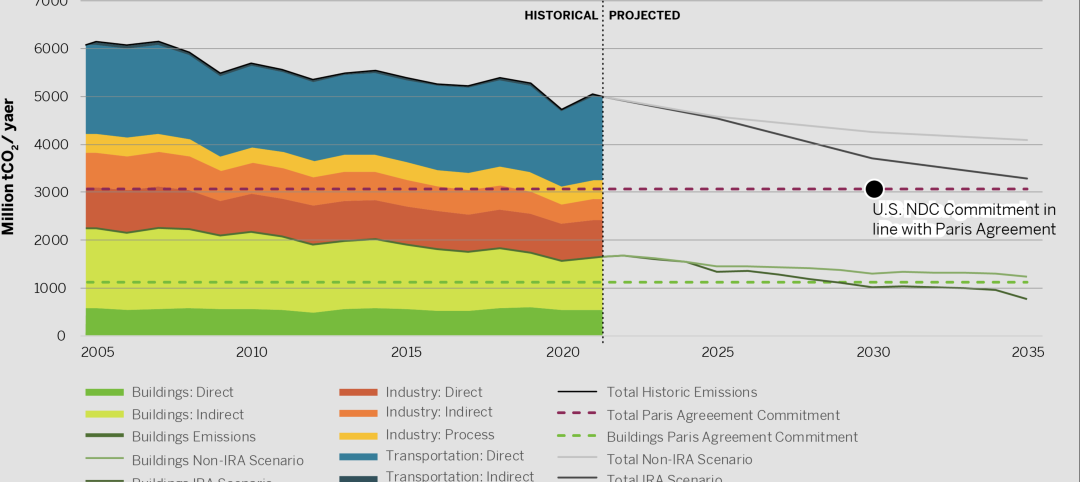
U.S. has tools to meet commercial building sector decarbonization goals early
The U.S. has the tools to reduce commercial building-related emissions to reach target goals in 2029, earlier than what it committed to when it signed the Paris Agreement, according to a report by the U.S. Green Building Council.
MFPRO+ News | Dec 11, 2023
U.S. poorly prepared to house growing number of older adults
The U.S. is ill-prepared to provide adequate housing for the growing ranks of older people, according to a report from Harvard University’s Joint Center for Housing Studies. Over the next decade, the U.S. population older than 75 will increase by 45%, growing from 17 million to nearly 25 million, with many expected to struggle financially.
Office Buildings | Dec 11, 2023
Believe it or not, there could be a shortage of office space in the years ahead
With work-from-home firmly established, many real estate analysts predict a dramatic reduction in office space leasing and plummeting property values. But the high-end of the office segment might actually be headed for a shortage, according to real estate intelligence company CoStar Group.
University Buildings | Dec 8, 2023
Yale University breaks ground on nation's largest Living Building student housing complex
A groundbreaking on Oct. 11 kicked off a project aiming to construct the largest Living Building Challenge-certified residence on a university campus. The Living Village, a 45,000 sf home for Yale University Divinity School graduate students, “will make an ecological statement about the need to build in harmony with the natural world while training students to become ‘apostles of the environment’,” according to Bruner/Cott, which is leading the design team that includes Höweler + Yoon Architecture and Andropogon Associates.