More than 49 million students were enrolled in public elementary and secondary schools as of fall 2021, according to the Digest of Education Statistics. Coincidentally, that number (the “49” in 49 million) matches the average age of a main instructional school building in the U.S., according to the National Center for Education Statistics. More alarming, nearly four in 10 schools (38%) were built before 1970—and half of those have never had a major building renovation or addition.
Clearly, too many of the nation’s school districts are having to make it work with less-than-ideal educational facilities. But at what cost to student performance and staff satisfaction?
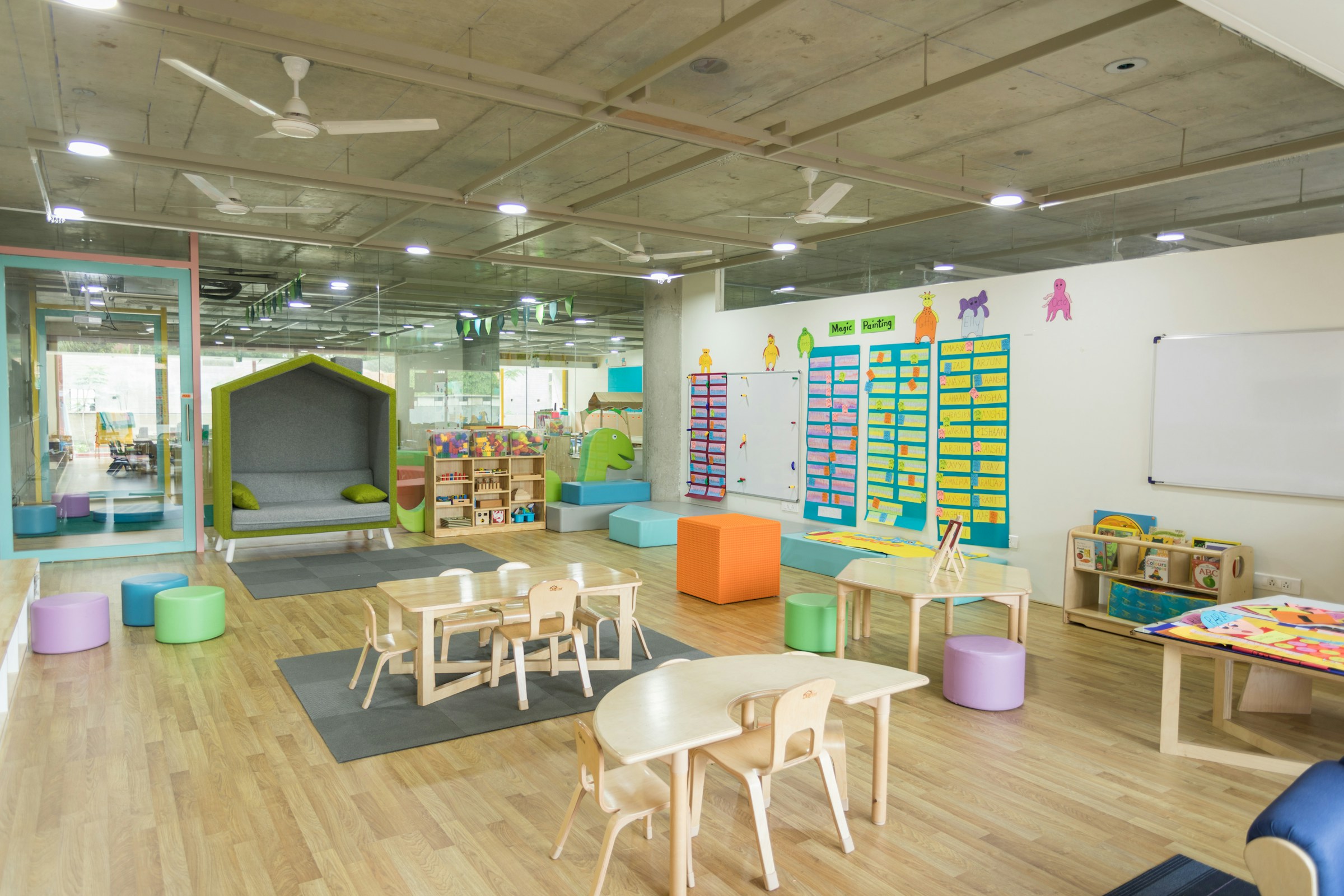
Newly released findings from a 28-school research study by Drexel University and Perkins Eastman reveal a strong correlation between the quality of school building environments and key educational indicators like test scores, graduation rates, enrollment, teacher retention—even community health and wellness.
The study, “Addressing a Multi-Billion Dollar Challenge” (140-page PDF download at BDCnetwork.com/2024-school-study), investigated the differences between modernized and non-modernized elementary, middle, and high schools—17 modernized, 11 non-modernized—throughout Washington, D.C., and Baltimore.
The primary finding: When measuring the educational adequacy of schools, modernized schools outperformed non-modernized schools by a wide margin, representing 13 of the top 15 performers, including the top 11 schools. The research team looked at factors such as instructional space, safety and security, environmental quality, extended learning, assembly, community, organization, and civic presence.
Drexel and Perkins Eastman hope the study will inform school districts on how best to invest limited CapEx funds. Some recommendations from the research:
Upgrades that enhance indoor environmental quality—air quality, lighting, acoustics, and thermal comfort—can positively impact students’ ability to focus and learn.
However, they warn that small incremental upgrades over time to items like HVAC systems can lead to potential detrimental impacts to the learning environments (e.g., unsightly conduit, blockage of windows).
These five areas offer the greatest opportunity for improvement: instructional space ambiance, exterior presence, safety and security, community assembly space, and main office location.
Overall, modernized schools better serve their community by being able to host initiatives like health clinics, food distribution programs, and public recreational facilities.
Download the full report at: BDCnetwork.com/2024-school-study.
Related Stories
| Oct 26, 2014
Study asks: Do green schools improve student performance?
A study by DLR Group and Colorado State University attempts to quantify the student performance benefits of green schools.
| Oct 21, 2014
Check out BD+C's GreenZone Environment Education Classroom debuting this week at Greenbuild
At the conclusion of the show, the modular classroom structure will be moved to a permanent location in New Orleans' Lower 9th Ward, where it will serve as a community center and K-12 classroom.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
Sponsored | | Oct 16, 2014
Mill Brook Elementary School colors outside the lines with creative fire-rated framing solution
Among the building elements contributing to the success of the elementary school’s public learning areas is a fire-rated stairwell that supports the school’s vision for collaboration. HMFH Architects designed the stairwell to be bright and open, reflecting the playful energy of students. SPONSORED CONTENT
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 9, 2014
Regulations, demand will accelerate revenue from zero energy buildings, according to study
A new study by Navigant Research projects that public- and private-sector efforts to lower the carbon footprint of new and renovated commercial and residential structures will boost the annual revenue generated by commercial and residential zero energy buildings over the next 20 years by 122.5%, to $1.4 trillion.
| Sep 29, 2014
Living Building vs. LEED Platinum: Comparing the first costs and savings
Skanska USA's Steve Clem breaks down the costs and benefits of various ultra-green building standards and practices.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
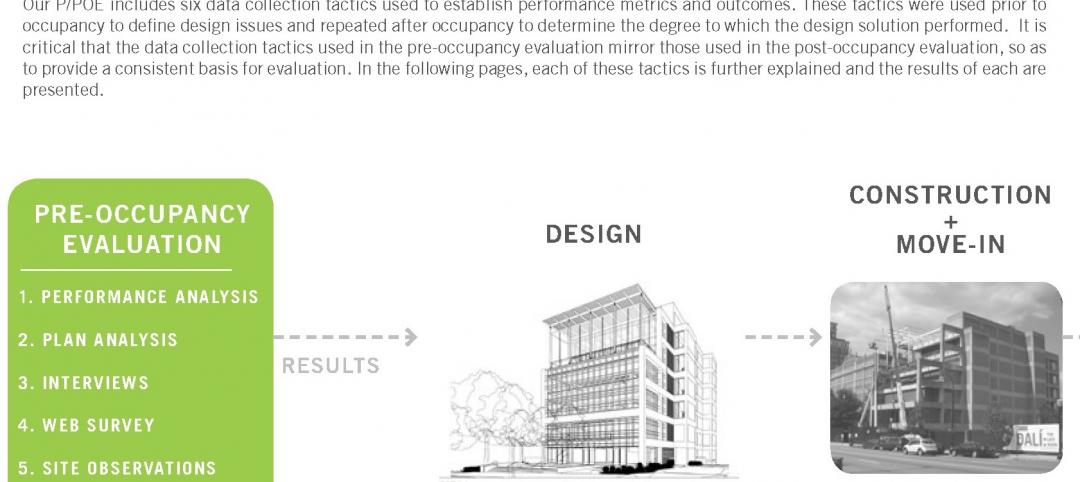
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.