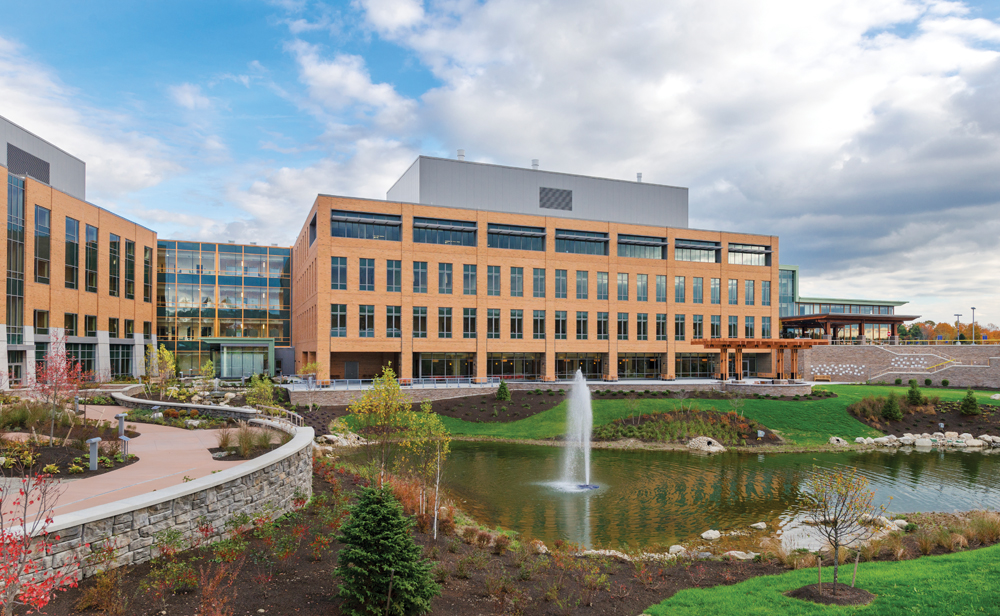
About four years ago, executives at MaineGeneral Health, which has served the people of the Kennebec Valley since 1891, realized that they faced a classic decision: Should they renovate their two primary facilities, one in Augusta, the state capital, the other 20 or so miles north in Waterville, or start all over?
“Just to keep up those two facilities would have cost $100 million, and it would have been another patchwork renovation that could not give us the quality we needed,” recalled MaineGeneral President/CEO Chuck Hays. “To set us up for the future, a new site was the way to go.”
Having successfully built a new cancer center in 2007 under a collaborative project model, Hays, an engineer, and his team set out to build a new hospital at a central location in Augusta, using integrated project delivery. To implement their vision, they asked the Building Team of contractors Robins & Morton and H.P. Cummings Construction and design firms SMRT and TRO JB to enter into an IPD agreement that would guarantee fixed costs and completion imperatives, quality of patient care through evidence-based design (EBD), and operational efficiencies via sustainable design and Lean principles.
GOLD AWARD
Project SummaryAlfond Center for Health
Augusta, MaineBUILDING TEAM
Submitting firm: Robins & Morton (GC), joint venture with H.P. Cummings Construction
Owner: MaineGeneral Medical Center
Architect, interior architect, MEP engineer: SMRT and TRO JB
Structural engineer: SMRTGENERAL INFORMATION
Project size: 644,000 sf
Construction cost: $312,000,000
Construction period: August 2011 to August 2013
Delivery method: Integrated project delivery
It became immediately apparent that the chief stumbling block to the IPD agreement was the insurance. In the words of John Milbrand, PE, Construction Manager for MaineGeneral, “Insurance companies don’t know how to act when the parties agree not to blame each other.” After weeks of negotiation, MaineGeneral put together an owner-controlled insurance policy to cover worker’s compensation and other liabilities.
In early 2011, with the IPD firmly in place, the team began engaging 250 MaineGeneral staff, plus community members, patients, and patient advocates, in design discussions. They toured new hospitals across the country to gather ideas.
Before any work could get started, however, MaineGeneral’s financing was held up, and the Building Team faced the prospect of losing months of warm-weather construction time. Under a typical design-bid-build contract, no work would have been allowed to proceed; but with the IPD, the site work subcontractor was able to start moving dirt without waiting for change orders.
Then, in August 2011, just as crews were starting to roll, Hurricane Irene deluged the site, threatening the protected streams on the property with damage from runoff. The Building Team worked with the state Department of Environmental Protection to pump runoff from containment ponds into tanker trucks and transport it to a DEP-approved disposal area, thereby saving the streams from excess turbidity.
The Building Team’s entrepreneurial creativity, spurred by the IPD and inspired by a forward-thinking client, went well beyond the norm.
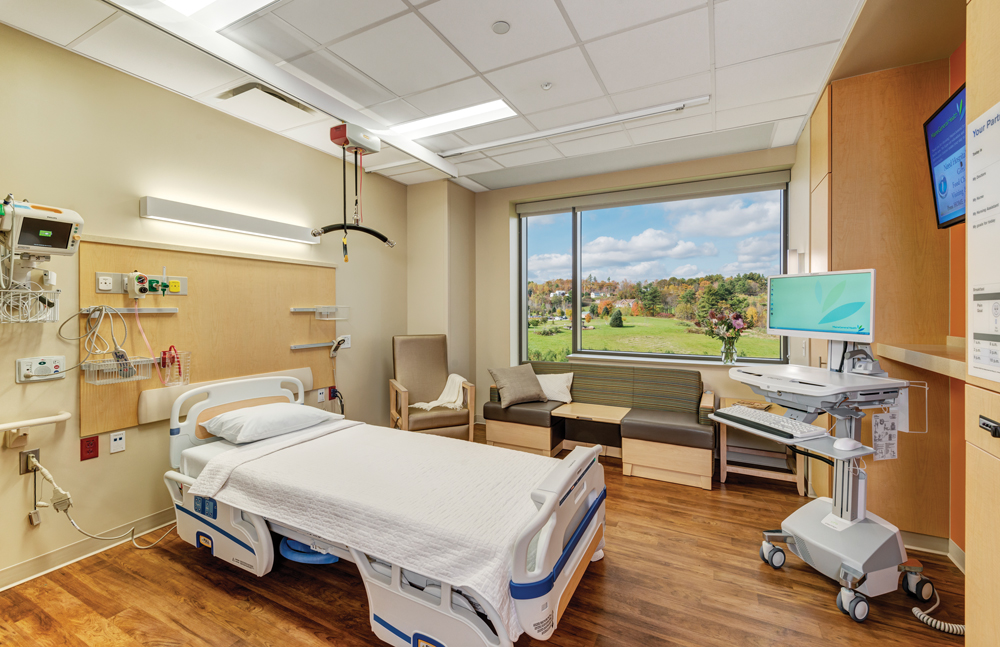
As a key component of evidence-based design, all 192 patient rooms are private to reduce hospital-induced infection. Each room has a family area with a sofa bed and a table that pops up for sharing meals, a patient lift, and a handrail between the bed and the bathroom to prevent falls. PHOTO: ANTON GRASSL/ESTO
For example, when the team put out RFPs for drywall/acoustical ceiling work, it became clear that the four local subcontractors would be bidding against each other on the biggest such job in the state. This put MaineGeneral’s management in an awkward position.
Instead of awarding the job to a single subcontractor, the hospital invited the four companies to operate under a single contract for the drywall work. This had never been done before, and it posed grave financial risk to the companies—not to mention to the hospital—but they made it work. In fact, of $172 million in subcontracts on the hospital, $167 million (97%) went to firms based in Maine, and 90% of the 3,000 jobs created by the project went to state residents.
To gain time and be as lean as possible, the Building Team set up an assembly line in an onsite basement, where they produced headwalls and bathrooms for the patient rooms. This shaved 25% off the delivery time for installing these components versus stick-built construction. Exterior wall panels were prefabbed and shipped in from a warehouse factory 60 miles from Augusta, in Portland, which allowed the building envelope to be closed in early, saving the owner thousands of dollars in temporary heating costs.
Construction of the Alfond Center for Health was completed in 24 months, nine months ahead of schedule, at a price below the validated target cost. Some of the savings went back into the project in the form of value-added improvements, including a 4,000-sf facilities building and a redundant data center.
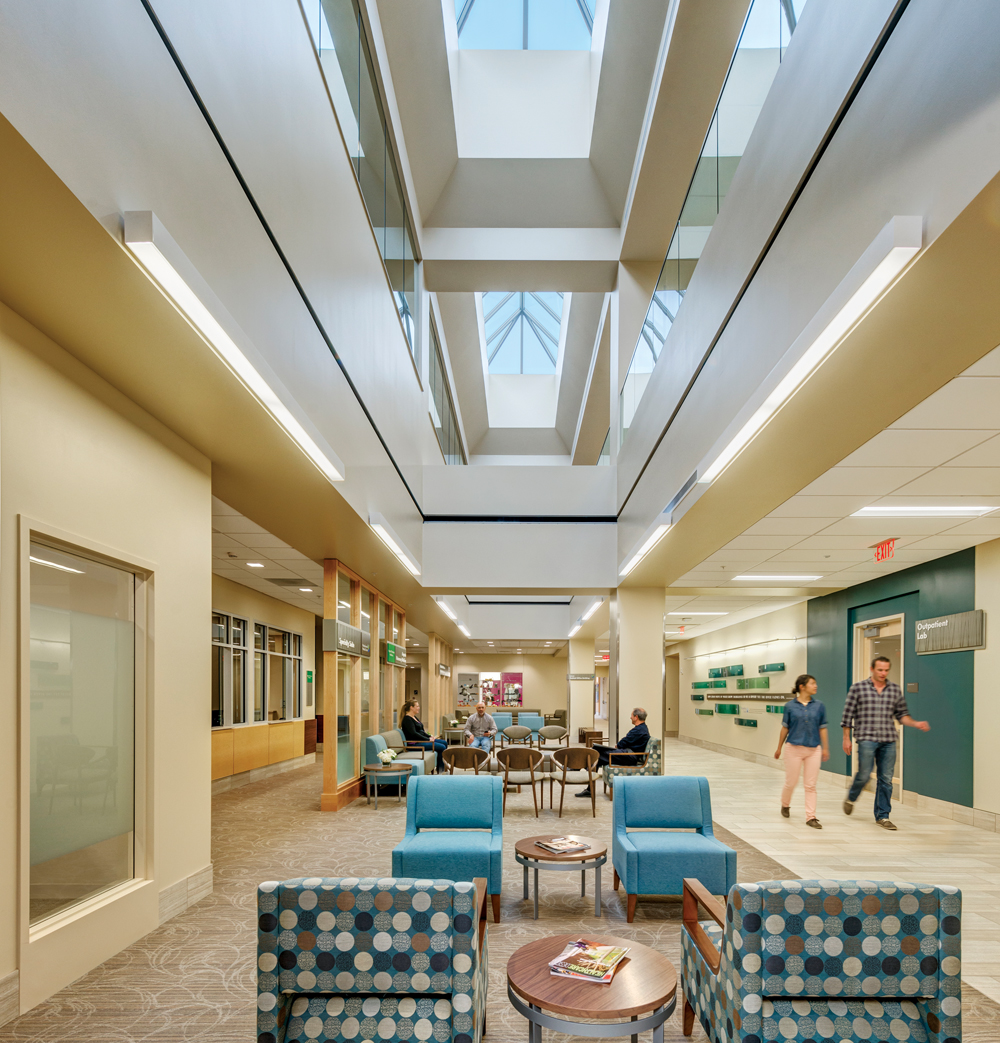

Daylight floods the reception area at the 644,000-sf replacement hospital. It was originally programmed to attain LEED Silver certification, but the Building Team was able to earn it LEED Gold status. Environmental components include a 140,000-sf reflective roof, outdoor healing gardens, rainwater collection, and a heat-recovery system. The Building Team used mockups to test the functionality of patient rooms and exterior façades. PHOTO: ANTON GRASSL/ESTO
At 192 beds—all single-occupancy, a key element of EBD—the $312 million facility surpassed its planned LEED Silver certification to achieve LEED Gold. Sustainable elements include a heat-recovery system, rainwater collection and reuse, ice production to offset peak electrical use, LED lighting, a 140,000-sf white roof, and the use of natural gas instead of fuel oil for heating. Paul Stein, MaineGeneral’s COO, calculates that these initiatives will cut the hospital’s utility bills in half, to $3.27/sf, compared to $7.80/sf at the facilities it replaced.
Building Team Awards jurors appreciated the team’s attention to detail. “The patient rooms were well thought out,” said judge Terry Fielden, LEED AP BD+C, Director of K-12 Education at International Contractors, Inc. Prototype rooms were mocked up so that patients, their families, and hospital staff could make suggestions. Rooms were laid out with a handrail between the head of the bed and the nearby entrance to the bathroom. “You can see the evidence-based design in the patient rooms,” said judge Susan Heinking, AIA, NCARB, LEED AP O+M, VP and Sustainability Leader at VOA Associates.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
SAFTI FIRST hires Tim Nass as National Sales Manager
SAFTI FIRST, a leading USA manufacturer of fire rated glazing and framing systems, is pleased to announce the addition of Tim Nass as National Sales Manager. In his new role, Tim will be working closely with architects and contract glaziers in selecting the appropriate and most economical fire rated glazing solution for their project. He will also be coordinating SAFTI FIRST’s extensive network of architectural representatives throughout the United States.
| Aug 11, 2010
NCARB welcomes new board of directors
The National Council of Architectural Registration Boards (NCARB) introduces its Board of Directors for FY10, who were installed during the culmination of the Council’s 90th Annual Meeting and Conference in Chicago.
| Aug 11, 2010
Berkebile wins $100K award for commitment to environment
Robert Berkebile, the founding principal of BNIM Architects and a founding member of the U.S. Green Building Council, has been selected to receive a $100,000 Heinz Award. The award honors his role in promoting green building design and for his commitment and action toward restoring social, economic, and environmental vitality to America’s communities through sustainable architecture and planning.
| Aug 11, 2010
Polshek Partnership unveils design for University of North Texas business building
New York-based architect Polshek Partnership today unveiled its design scheme for the $70 million Business Leadership Building at the University of North Texas in Denton. Designed to provide UNT’s 5,400-plus business majors the highest level of academic instruction and professional training, the 180,000-sf facility will include an open atrium, an internet café, and numerous study and tutoring rooms—all designed to help develop a spirit of collaboration and team-oriented focus.
| Aug 11, 2010
University of Florida aiming for nation’s first LEED Platinum parking garage
If all goes as planned, the University of Florida’s new $20 million Southwest Parking Garage Complex in Gainesville will soon become the first parking facility in the country to earn LEED Platinum status. Designed by the Boca Raton office of PGAL to meet criteria for the highest LEED certification category, the garage complex includes a six-level, 313,000-sf parking garage (927 spaces) and an attached, 10,000-sf, two-story transportation and parking services office building.
| Aug 11, 2010
Draft NIST report on Cowboys practice facility collapse released for public comment
A fabric-covered, steel frame practice facility owned by the National Football League’s Dallas Cowboys collapsed under wind loads significantly less than those required under applicable design standards, according to a report released today for public comment by the Commerce Department's National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
| Aug 11, 2010
Callison, MulvannyG2 among nation's largest retail design firms, according to BD+C's Giants 300 report
A ranking of the Top 75 Retail Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants







