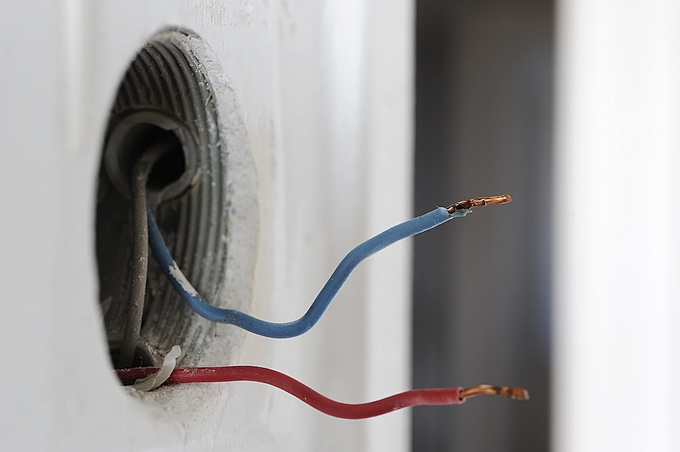
Low-smoke halogen-free (LSHF) cables have been on the market for decades, yet there are still many misconceptions about the application and definition of test requirements/methods for these cables.
Generally speaking, traditional halogenated cables, when compared to LSHF cables, produce more toxic and corrosive smoke in the event they are burned.
LSHF cables first originated in the 1970s in Europe and the U.S., and began being used in underground structures by London Underground and North Sea offshore drilling platforms in the 1980s. These cables have traditionally been used in enclosed spaces, such as subway systems, tunnels, submarines, ships, and mines. Today, LSHF cables are also being used for life safety and mission critical applications, including hospitals and data centers.
“Traditionally, where LSHF cables are used, the application of these cables were in enclosed spaces,” says Robert Bellassai, senior staff engineer at certification company UL. “So, if you had a space that was not exposed to or installed in outside air, that’s where these cables would be used. But the use of LSHF cables is rapidly expanding.”
Wire and cables, which are essential to any building, structure, or product, generally consist of insulated copper conductors or buffered/unbuffered optical fibers, and are covered by a protective outer jacket. Cables may also contain other polymetric materials, such as fillers, tapes/wraps (e.g., PET, fiberglass, polyester, etc.), ripcords, shields (e.g., aluminum-PET, copper-PET, etc.), and color concentrates.
In the case of halogenated cables, the polymetric materials of which they are manufactured contain one or more halogenated elements, such as chlorine, bromine, fluorine, iodine, or less likely astatine.
Halogenated elements serve a purpose when used in polymetric materials. In most applications, they are in the form of chlorinated and brominated flame retardants to inhibit flame propagation of the cable when burned. However, the cable will emit smoke that is toxic and corrosive, and that contain higher amounts of carbon monoxide (CO).
One study from the University of Lancashire in the U.K. found evidence that suggests combustion products can be potentially hazardous to people if they cannot easily evacuate from the area. The cables studied contained brominated or chlorinated flame retardants, which produced significantly higher levels of CO gas during combustion.
Additionally, when mixed with water, hydrogen halides form hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, or hydrobromic acid, which can damage and destroy critical structures, components, and equipment, due to the corrosive nature of the combustion product.
Installing LSHF cables significantly reduces the risk of toxic and corrosive smoke being emitted in case of a fire.
Ideal for subterranean and mission critical applications, such as subway tunnels and data/emergency call centers, LSHF cables can be called other acronyms, such as LSZH, HFFR, LSF, and LS0H. These acronyms have been developed by manufacturers to characterize (self-certify) their products for smoke generation and halogen content.
Each self-certification acronym is associated with industry standards that were not always directly applicable for the characterization of smoke and halogen content. Also, each cable and material manufacturer doesn’t always associate the same standards with the same acronym.
“Low-smoke” refers to the amount of smoke that a complete cable construction produces upon combustion. “Halogen-free” refers to the amount of individual halogen elements that are present in each combustible cable component.
The dangers of not installing LSHF cables are potentially deadly, as evidenced by the Jan. 12, 2015, fire at Washington, D.C. Metro’s L’Enfant Plaza Station.
There, an electrical malfunction caused a fire which filled up the subway tunnels with toxic smoke. In total, 86 people were injured from smoke-related injuries and one person died.
D.C. Metro, and other transit agencies, had been advised by the National Transportation Safety Board in July 2014 to replace and update its cables to better protect them from fires. Metro had been in the process of installing new cables for over a year, but had not yet finished the project when the June 2015 fire broke out.
According to the Washington Post, multiple lawsuits filed by transit riders alleged that Metro created unsafe conditions in the tunnels, in addition to delaying evacuation efforts.
While some suits have been settled out of court, others, including a suit filed by the family of the person who died, are expected to go to trial this fall.
Installing LSHF cables not only protects employees and customers, but they can also increase the value of the structure in which they’re installed.
The U.S. Green Building Council recognizes four levels of LEED certification: Certified (40-49 points), Silver (50-59 points), Gold (60-79 points), and Platinum (80+ points). Having LSHF cables installed counts as points toward certification and can increase the financial value of the property and save owners money in decreased operational costs.
“Certified LEED green buildings are very efficient, resulting in decreased operational costs due to lower utility and maintenance expenses,” says Bellassai.
The high safety standards associated with LSHF cables are environmentally friendly and cost effective.
Additionally, LSHF cables have been proposed to be included in the 2020 version of the National Electrical Code. The proposal, submitted by Mexichem, seeks to add HF and LSHF optional markings so contractors, architects, specifiers, and users can specify HF and LSHF cables. It would give these end users a standards-based Mark brought to you by an independent third-party laboratory such as UL LLC.
If approved by the NFPA for the 2020 NEC, this will give Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) an easy way to identify HF and LSHF products for applications that would benefit from the reduced toxicity and corrosivity of these cables, and from a trusted third-party independent test laboratory like UL LLC.
Download UL LLC's free white paper on this topic, Clearing Misconceptions About Low-Smoke, Halogen-Free Cables.
Related Stories
Codes | Jul 10, 2023
Water Demand Calculator outperforms traditional plumbing codes for energy, carbon, and water savings
Using IAPMO’s Water Demand Calculator tool can result in energy, carbon, and water savings as compared to using traditional plumbing specification methods in plumbing codes, according to a study by Arup.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Energy-Efficient Design | Jun 5, 2023
Implementing an ‘asset drawdown strategy’ for site decarbonization
Solidifying a decarbonization plan via an “asset drawdown strategy” that carefully considers both capital and operating costs represents a game-changing opportunity for existing properties to compete with new projects.
Office Buildings | May 15, 2023
Sixteen-story office tower will use 40% less energy than an average NYC office building
This month marks the completion of a new 16-story office tower that is being promoted as New York City’s most sustainable office structure. That boast is backed by an innovative HVAC system that features geothermal wells, dedicated outdoor air system (DOAS) units, radiant heating and cooling, and a sophisticated control system to ensure that the elements work optimally together.
Digital Twin | May 8, 2023
What AEC professionals should know about digital twins
A growing number of AEC firms and building owners are finding value in implementing digital twins to unify design, construction, and operational data.
K-12 Schools | Apr 18, 2023
ASHRAE offers indoor air quality guide for schools
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) has released a guide for educators, administrators, and school districts on indoor air quality. The guide can be used as a tool to discuss options to improve indoor air quality based on existing HVAC equipment, regional objectives, and available funding.
Codes | Mar 2, 2023
Biden Administration’s proposed building materials rules increase domestic requirements
The Biden Administration’s proposal on building materials rules used on federal construction and federally funded state and local buildings would significantly boost the made-in-America mandate. In the past, products could qualify as domestically made if at least 55% of the value of their components were from the U.S.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 31, 2023
How to solve humidity issues in hospitals and healthcare facilities
Humidity control is one of the top mechanical issues healthcare clients face. SSR's Lee Nordholm, PE, LEED AP, offers tips for handling humidity issues in hospitals and healthcare facilities.
Mass Timber | Jan 27, 2023
How to set up your next mass timber construction project for success
XL Construction co-founder Dave Beck shares important preconstruction steps for designing and building mass timber buildings.