An NFT, or non-fungible token, is a digital object that cannot be duplicated. NFTs allow the owners of digital or intangible assets that can be replicated to assert ownership and, by extension, to commodify and trade those assets. For example, anyone can browse photography of the latest Anish Kapoor, but only one city can make a grand public artwork a tourist calling card. For anyone who has ever experienced the frustration of having an idea copied, NFTs offer a possible solution.
As we know them today, NFTs exist in a world far removed from everyday reality—belonging to an intangible fantasy land pioneered by connoisseurs of computer games and digital art. But the value placed on these digital objects, and the tokens associated, is as real as a coin in your pocket.
Where does design come into the NFT picture? A fundamental value of design is its ingenuity in reimagining a better future. Designs can be abstracted or copied, but the ingenuity lies in the process. The labor in design—the thinking, testing, and problem solving—is what clients are ultimately buying. The building or interior is the product of that process.
6 ways non-fungible tokens (NFTs) could transform the design industry
“Tokenizing” design labor would give clients the opportunity to bid for the time of a designer or firm. By placing a higher value on time, this Token Future would create six compelling outcomes:
1. Complimentary Investment.
When a client invests in design, they invest in the benefits expected from the finished building. Tokenizing design labor would mean that a complimentary investment in the designer’s time is also made. To explain, a labor token could appreciate in value and be traded for profit. A token will appreciate as market demand grows, which is itself fueled by public awareness of quality design. When a token appreciates, both designer and client/investor are rewarded with capital gain.
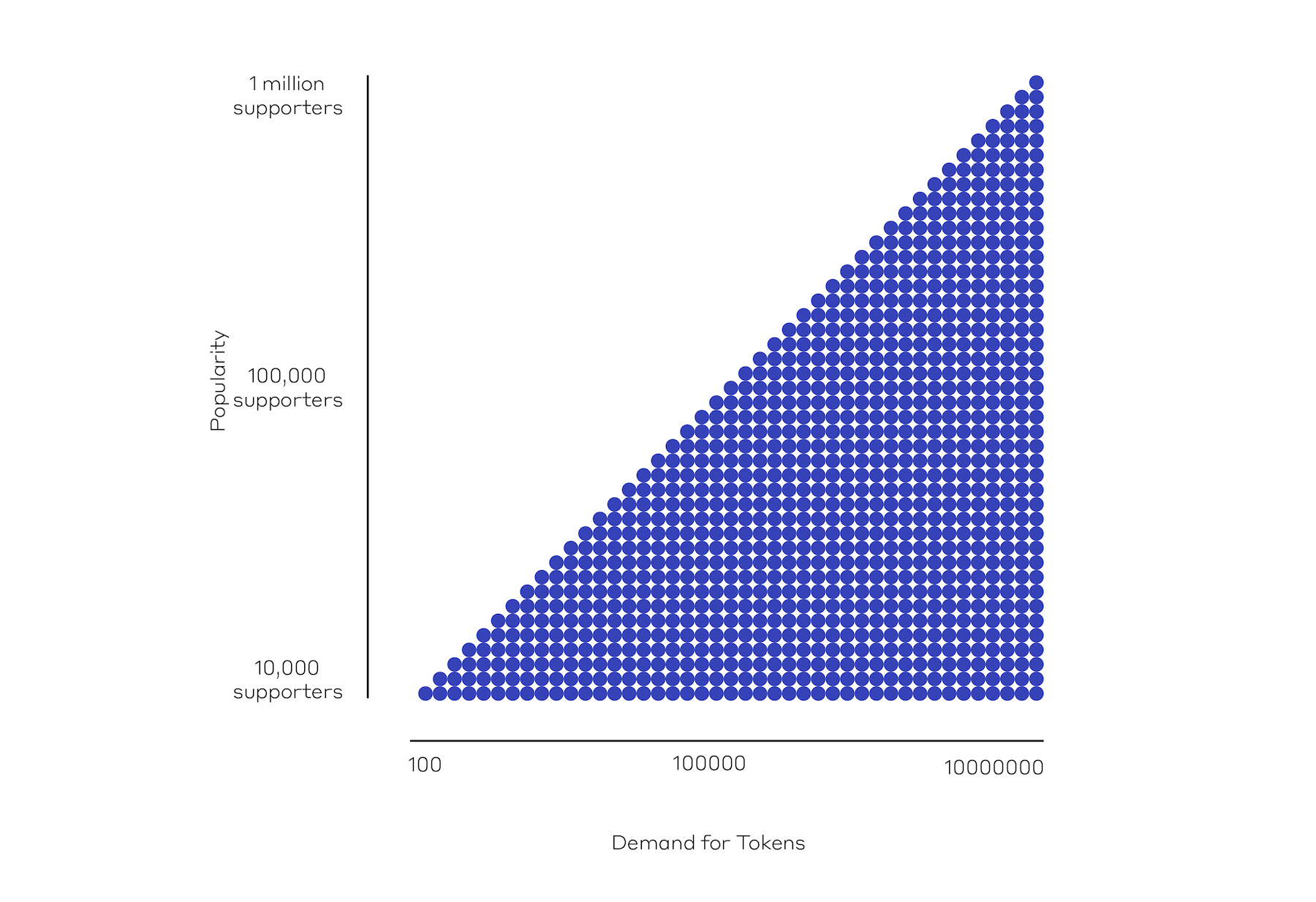
2. Mutually Beneficial Collaboration.
When a client purchases tokens from a designer, they become invested in the ongoing success of that token. The designer becomes a potential source of capital gain, like any other investment—something to be protected and nourished. For a designer, this means a client is more likely to support the process and capacity to perform.
3. Protection of Quality Design Time.
A Token Future should prevent design time from becoming overstretched. It would eliminate the fixed-fee contract, which sees designers at risk of shouldering disproportionate work without compensation—resulting in all-nighters, working weekends and, ultimately, a compromised design. Avoiding these pitfalls is in the best interests of all parties.
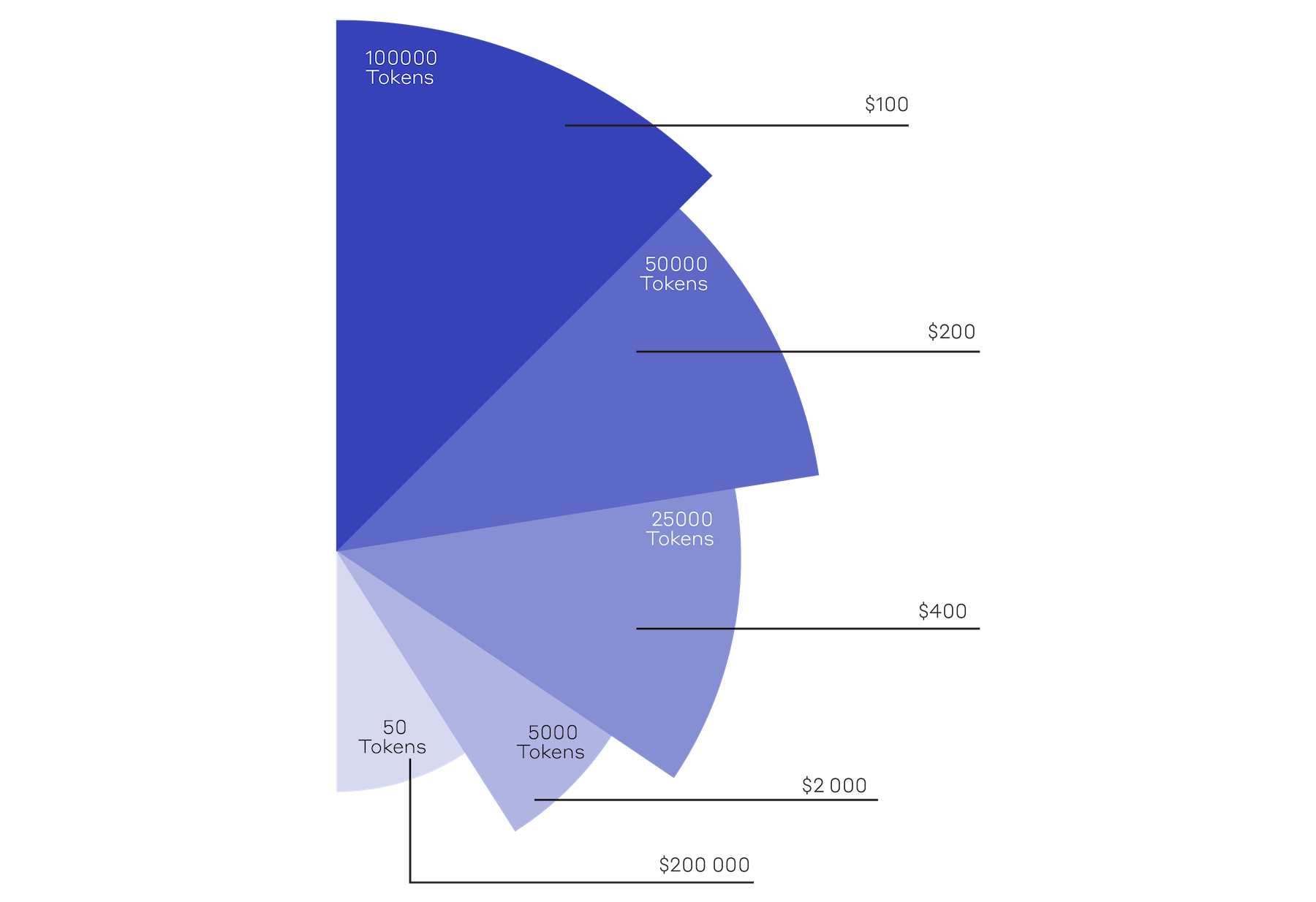
4. Less Money Wasted.
In a case where a client might need to cancel a project, good work and pursuant appreciation of the Token value may result in a financial return on their design investment rather than a write-off.
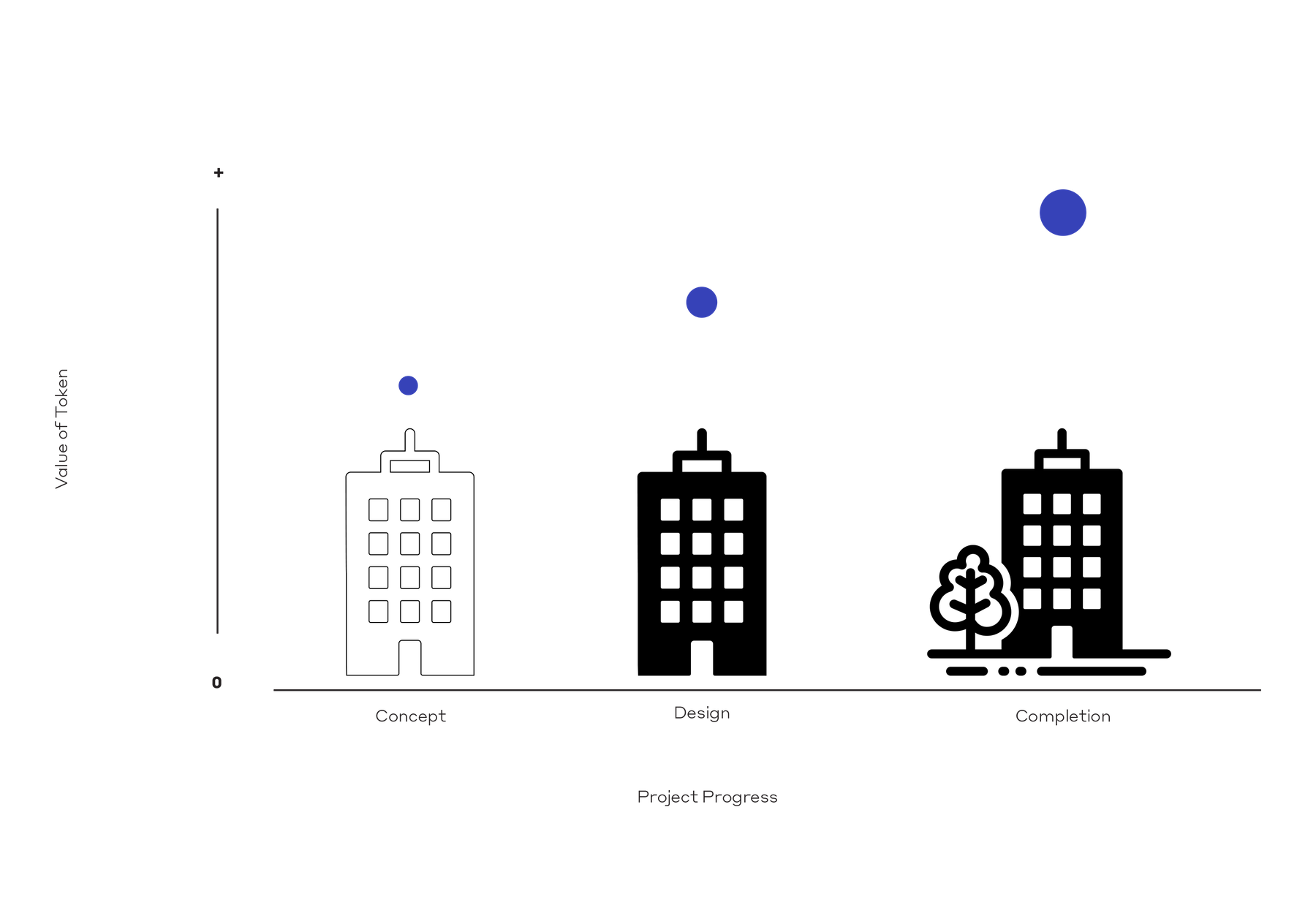
5. A Clearer and More Flexible Market.
The procurement of designers can be opaque and uncertain. Unfamiliar designers with hard-to-understand fee structures may be deemed a risk by clients. A project may need to be put on hold or cancelled. In both scenarios, a regulated and transparent token-based market would afford clients the opportunity to divest as they see fit, with the value of their original investment having appreciated.
6. An Equitable Market for Designers.
In such a system, a designer negotiates the supply of labor in a collaborative manner, only offering services in accordance with their resources. Managed professionally and systematically, design labor could be calibrated not only to a client’s requirements and the designer’s expertise, but also to the mutual financial and cultural benefit of each party—improving life for both parties.
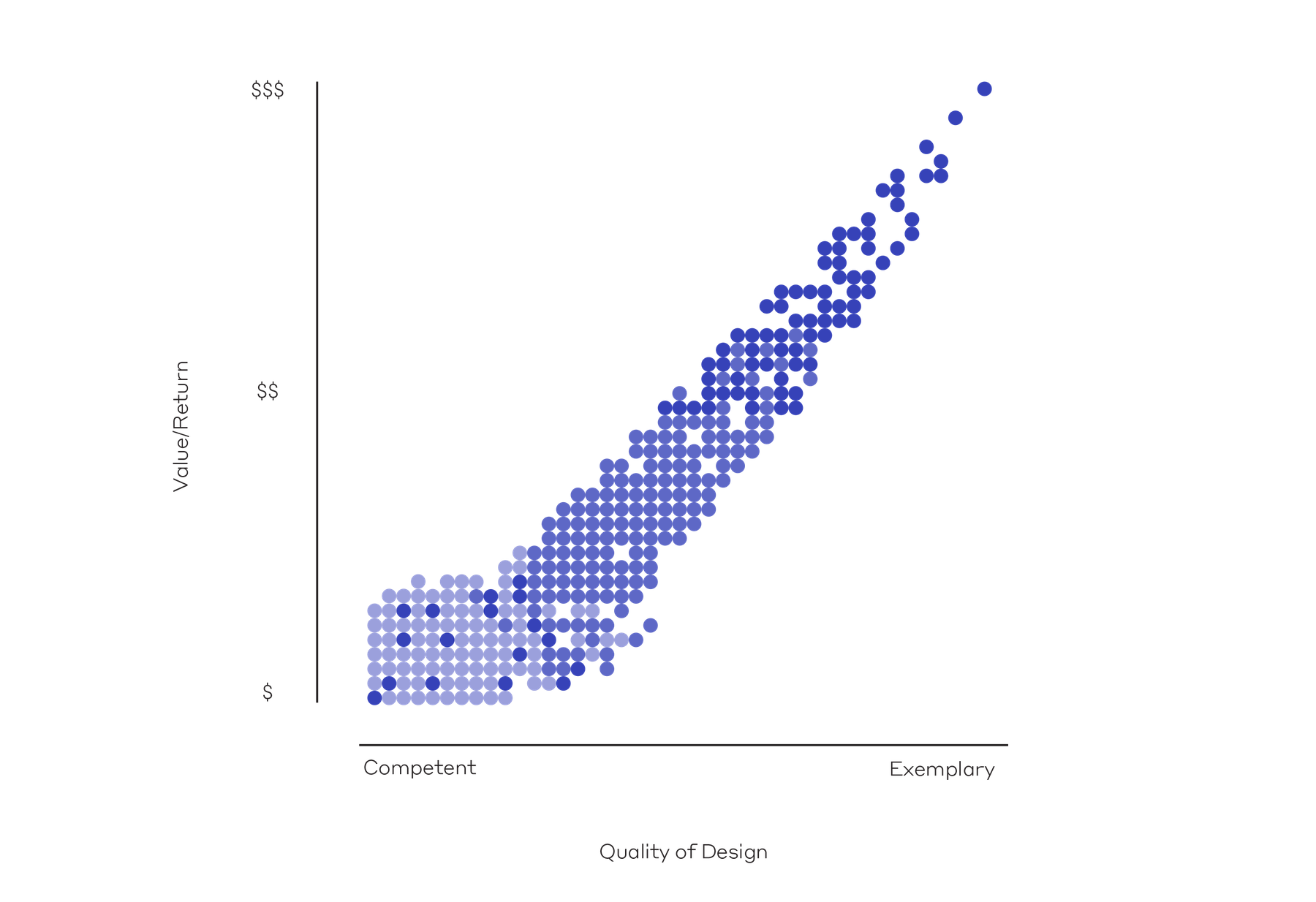
The benefits of a Token Future currently contend with numerous uncertainties and challenges—much like any innovation. Though this concept remains a glimmer on the horizon, NFTs in the design industry promise better welfare, growth, and profit.
As the design industry continues to chart a course toward automated production and an acceleration of the service economy, the rewards of exploring a Token Future for design labor outweigh the risks.
About the author
Jet Geaghan is an Architect based in Woods Bagot’s Sydney studio. For Jet, every building should be conceived with purpose, expertise and wit. Clarity of communication is fundamental to his work, whether it be in a design gesture, construction detail, or cultural testimony. Having completed numerous additions and alterations projects, Jet relishes the complexity and challenges of adapting existing buildings to address evolving demands and unforeseen potential. His experience lends him a broad understanding of the myriad parameters involved in bringing buildings of differing scales to life, which have included the 275 Kent Street redevelopment and the refurbishment of InterContinental Hotel Sydney. Jet has extensive experience with planning approvals, design, documentation, construction delivery, digital modeling, as well as a passion for the written word.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Oct 16, 2024
How AI can augment the design visualization process
Blog author Tim Beecken, AIA, uses the design of an airport as a case-study for AI’s potential in design visualizations.
3D Printing | Oct 9, 2024
3D-printed construction milestones take shape in Tennessee and Texas
Two notable 3D-printed projects mark milestones in the new construction technique of “printing” structures with specialized concrete. In Athens, Tennessee, Walmart hired Alquist 3D to build a 20-foot-high store expansion, one of the largest freestanding 3D-printed commercial concrete structures in the U.S. In Marfa, Texas, the world’s first 3D-printed hotel is under construction at an existing hotel and campground site.
AEC Tech Innovation | Oct 8, 2024
New ABC technology report examines how AI can enhance efficiency, innovation
The latest annual technology report from Associated Builders and Contractors delves into how artificial intelligence can enhance efficiency and innovation in the construction sector. The report includes a resource guide, a case study, insight papers, and an essay concerning applied uses for AI planning, development, and execution.
AEC Tech | Oct 4, 2024
Publication explores how facility managers can use AI
A new guide, “Gamechanger: A Facility Manager’s Guide to Building a Relationship with AI,” provides a roadmap to understanding and using AI in the built environment.
AEC Tech | Oct 3, 2024
4 ways AI impacts building design beyond dramatic imagery
Kristen Forward, Design Technology Futures Leader, NBBJ, shows four ways the firm is using AI to generate value for its clients.
AEC Tech | Sep 25, 2024
Construction industry report shows increased use of robotics on jobsites
Nearly two-thirds of contractors surveyed, who cited use of robotics on jobsites, are either using monitoring and/or service/labor robotics.
AEC Tech | Sep 24, 2024
Generative AI can bolster innovation in construction industry
Jeff Danley, Associate Technology and Innovation Consultant at Burns & McDonnell, suggests several solutions generative AI could have within the construction industry.
3D Printing | Sep 17, 2024
Alquist 3D and Walmart complete one of the nation’s largest free-standing, 3D-printed commercial structures
Walmart has completed one of the largest free-standing, 3D-printed commercial structures in the US. Alquist 3D printed the almost 8,000-sf, 20-foot-high addition to a Walmart store in Athens, Tenn. The expansion, which will be used for online pickup and delivery, is the first time Walmart has applied 3D printing technology at this scale.
3D Printing | Sep 13, 2024
Swiss researchers develop robotic additive manufacturing method that uses earth-based materials—and not cement
Researchers at ETH Zurich, a university in Switzerland, have developed a new robotic additive manufacturing method to help make the construction industry more sustainable. Unlike concrete 3D printing, the process does not require cement.
AEC Tech | Aug 25, 2024
Are AI opportunities overwhelming design and construction firms?
A new survey of A/E firms found that more than three-fifths of 652 respondents expect AI to improve their operational efficiency. That survey, though, also found that the same portion of respondents wasn’t using AI yet, and two-thirds admitted they were struggling with where and how to apply AI.

















