Every year, BuildingGreen names the ten best green building products that, as the publication states, “transform the design and construction industry” by helping to solve environmental problems, from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to finding durable and safe materials.
A urinal, bike rack, ventless dryer, and a chair made of mushroom roots made the cut. For more on this year’s list, click here. Here are the 2014 and 2015 editions.
Honeywell’s Solstice Liquid Blowing Agent — Based on hydrofluoroolefin technology, it replaces a high global warming potential blowing agent, HFC-245fa, found in spray polyurethane foam. Solstice has a 100-year GWP of 1, which means it is equal to carbon dioxide in terms of global warming potential. The product is used by Whirlpool in appliance lines, as well as for Lapolla’s Foam-Lok 2000 4G SPF wall insulation, and Henry-West Development Group’s 3012-EB-3 SPF roof insulation.
Whirlpool HybridCare Ventless Clothes Dryer — The ventless heat-pump dryer improves efficiency by using a refrigeration loop that condenses moisture from the drum and returns excess heat energy. HybridCare saves on HVAC energy, providing 40% energy savings over a standard dryer.
Sloan Hybrid Urinal — The urinal uses a water-free cartridge and automatic rinser to keep it clean and odor-free. The unit’s Velocity cartridge pumps liquid through it and out the drainpipe, lessening buildup, while a water solution called Jetrinse is flushed every 72 hours to keep solids from forming in the housing and drain line.
Gunlocke Savor Guest Chair with Ecovative MycoBoard Backing — This guest chair is made from an engineered-wood alternative made from mushroom mycelium, a root, and is as strong and stable as a standard plywood- or particleboard-backed chair.
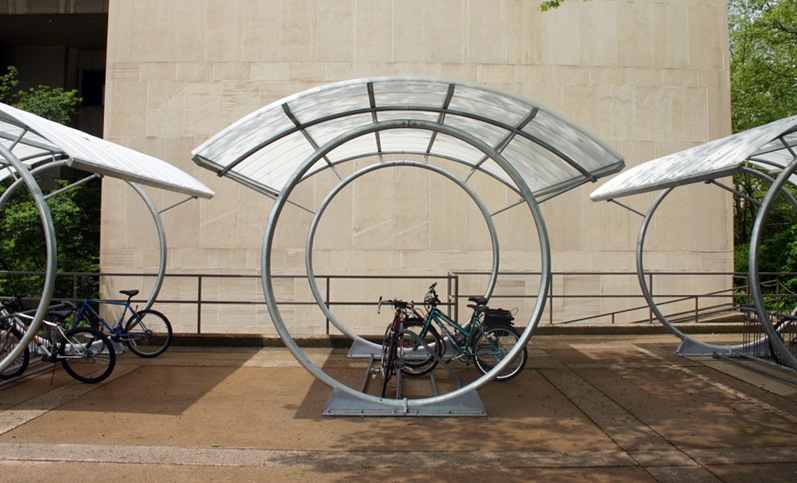
Duo-Gard Bike Racks and Shelters — The racks can be incorporated into a building to help it achieve LEED status. The shelters’ roofs are made of standing-seam metal or polycarbonate, and walls are made of polycarbonate, safety glass, perforated metal, or steel or aluminum mesh. Photovoltaic panels and LED lighting can also be included.
NuLED Power over Ethernet (PoE) Low-Voltage LED Lighting — The system uses DC power from a standard PoE network, and it can monitor and control LED power consumption and color temperature, all with less energy loss than AC systems.
Personal Comfort Systems Hyperchair — When HVAC systems can’t accommodate everyone’s preferred indoor temperature, this office chair provides personal heating and cooling powered by a lithium ion phosphate battery and controlled by a panel on chair’s arm.
Unity Homes High-Performance Panelized Homes — The high-performance panelized home system uses computer numeric control equipment to help create panelized wall systems and small prefab room modules to minimize thermal bridging. Unity Homes use energy-saving insulation and FSC-certified wood with low-VOC finishes.
Sanden Heat Pump Water Heater with CO2 Refrigerant — This heat-pump water heater uses CO2 as a refrigerant and creates water temperatures high enough for hydronic heating. It can deliver around 16,000 Btu/hr and can produce 149°F water.
Tesla Powerwall and Powerpack Onsite Energy Storage — The rechargeable lithium-ion battery system incorporates liquid thermal management, battery management, and a DC–DC converter. It has a 10 kWh unit optimized for weekly or backup use and a 7 kWh unit for daily use.
 Tesla’s Powerwall and Powerpack. Photo: Tesla (via BuildingGreen).
Tesla’s Powerwall and Powerpack. Photo: Tesla (via BuildingGreen).
Related Stories
| Oct 14, 2013
Computer simulation aids design of Vermont ski area net-zero lodge and fitness center
The Craftsbury (Vermont) Outdoor Center has broken ground on a new activity lodge and fitness center. An energy modeling computer simulation was used to optimize solar orientation, insulation values, and the form of the building.
| Oct 10, 2013
Carnegie Mellon study looks at impact of dashboards on energy consumption
A recent study by Carnegie Mellon took a look at the impact of providing feedback in an energy dashboard form to workers and studying how it impacted overall energy consumption.
| Oct 7, 2013
Geothermal system, energy-efficient elevator are key elements in first net-zero public high school in Rhode Island
The school will employ a geothermal system to heat and cool a portion of the building. Other energy-saving measures will include LED lighting, room occupancy sensors, and an energy-efficient elevator.
| Oct 4, 2013
Sydney to get world's tallest 'living' façade
The One Central Park Tower development consists of two, 380-foot-tall towers covered in a series of living walls and vertical gardens that will extend the full height of the buildings.
| Sep 30, 2013
Smart building systems key to new Wisconsin general aviation terminal’s net zero target
The Outagamie County Regional Airport’s new 8,000 sf general aviation terminal was designed to achieve net zero.
| Sep 26, 2013
Sheep's wool insulation, bio-brick among Cradle to Cradle product innovation finalists
Ten finalists are competing for $250,000 in prizes from the Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute and Make It Right.
| Sep 24, 2013
8 grand green roofs (and walls)
A dramatic interior green wall at Drexel University and a massive, 4.4-acre vegetated roof at the Kauffman Performing Arts Center in Kansas City are among the projects honored in the 2013 Green Roof and Wall Awards of Excellence.
| Sep 23, 2013
After retrofit and PV array project, N.Y. beverage distributor gets to net-zero
Queens, N.Y.-based beverage distributor Big Geyser’s energy efficiency retrofit project and rooftop solar array installation have positioned the company’s facility to achieve net-zero power.
| Sep 19, 2013
What we can learn from the world’s greenest buildings
Renowned green building author, Jerry Yudelson, offers five valuable lessons for designers, contractors, and building owners, based on a study of 55 high-performance projects from around the world.
| Sep 16, 2013
Passive solar, enhanced envelope crucial to Univ. of Illinois net-zero project
Passive solar strategies and an enhanced envelope are keys to achieving net-zero on the new 230,000 sf Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering building at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.