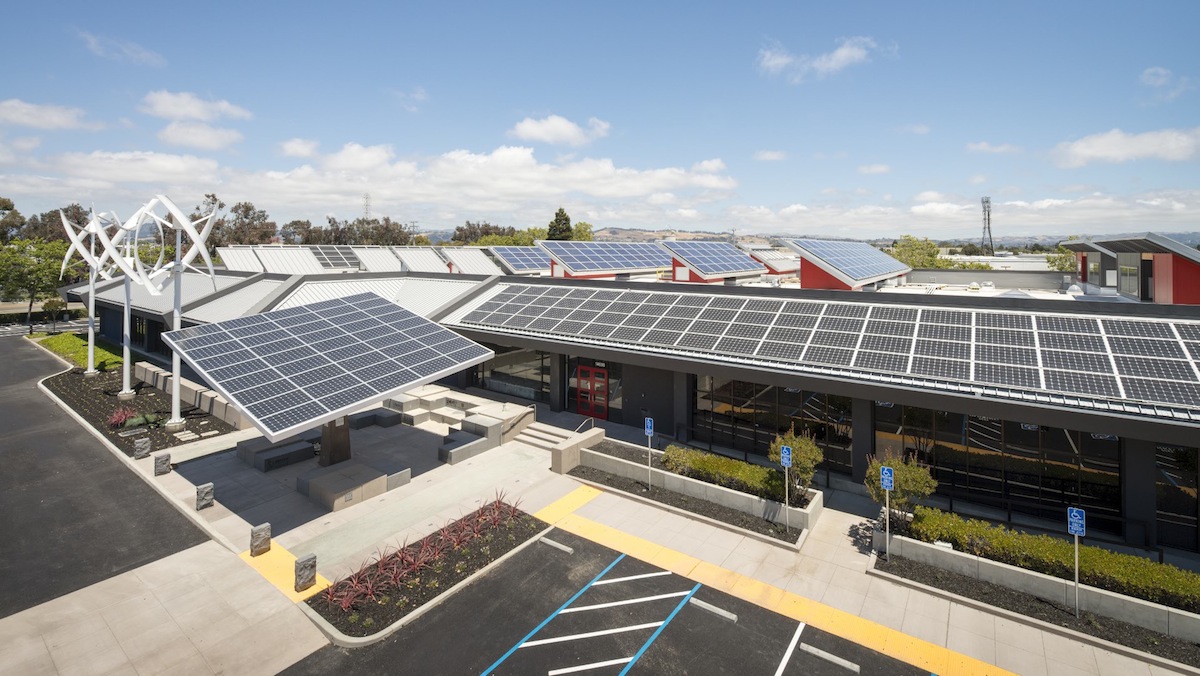
Construction has begun Los Angeles County on what is being called the nation’s largest Net Zero Plus retrofit of a commercial building.
The transformation of the 142,000-sf Electrical Training Center—which was formally announced 11 months ago—should be completed by Spring 2016. (Its grand opening is scheduled for April 21—Earth Day of that year.)
It will be renamed the Net Zero Plus Electrical Training Institute, and the building will demonstrate the future of smart energy efficiency, microgrid system integration, energy storage solutions, resiliency in the wake of a natural disaster or grid interruption, and advanced lighting controls and automated building management systems.
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 11, with more than 13,000 members; and the Los Angeles Chapter of the National Electrical Contractors Association, which represents more than 400 electrical contractors in Los Angeles and Ventura Counties, are investing $13 million into this retrofit. The General Contractor on this project is Santa Fe Springs, Calif.-based PDE Total Energy Solutions, and the Electrical Contractor is Chatsworth, Calif.-based O’Bryant Electric.
California’s latest construction codes call for all new commercial buildings to be built to net zero standards by 2030. To that end, the union and association have also launched their Net Zero Plus initiative to accelerate the shift toward a clean-energy economy. This initiative is intended to help the building industry improve grid reliability, implement energy storage solutions, as well as advance energy independence, security, and building control. The initiative also aims at reducing the environmental impacts of commercial buildings, reduce electricity costs, and provide better analytics.
The Training Center instructs over 4,000 apprentices and journeymen electricians annually. The retrofitted facility “will set the standard for training as a replicable model for other electrical training centers around the country,” said Marvin Kropke, the Local’s business manager.
Den Henrich, president of PDE Total Energy Solutions, estimates that the retrofit would reduce the building’s energy consumption by between 15% and 30%. The retrofit will include the installation of one megawatt of solar photovoltaic panels, with two arrays on the roof and two solar shade systems with a charging station in the parking lot.
The energy usage reduction is projected to be 250,000 kWh per year, and the building will have the capacity to produce about one megawatt of energy. The building is also expected to achieve a 28.5-ton annual reduction in CO2 emissions.
The training center is working with the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power to develop, test, and implement strategies that lead to the adoption of energy efficient technologies with the utility’s customers, said David Jadot, PE, LADWP’s director.
Related Stories
Green | Jun 22, 2022
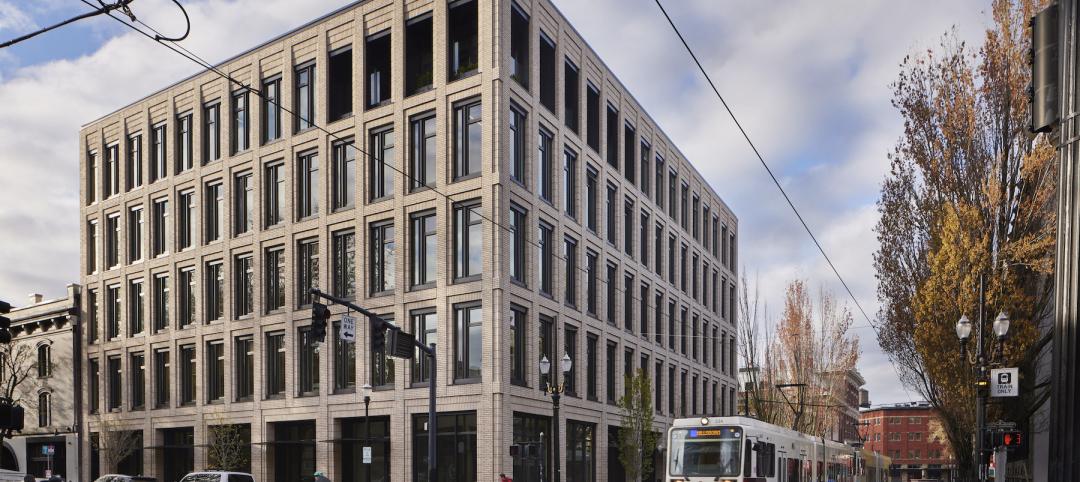
World’s largest commercial Living Building opens in Portland, Ore.
The world’s largest commercial Living Building recently opened in Portland, Ore.
Coronavirus | May 20, 2022
Center for Green Schools says U.S. schools need more support to fight COVID-19
The Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council released a new report detailing how school districts around the country have managed air quality within their buildings during the second year of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Green Specifications | May 12, 2022
MG2’s Sustainable Materials Evaluation System
Learn how MG2’s Sustainable Materials Evaluation System helps clients, prospects, and staff choose the most environmentally feasible materials for their building projects. Candon Murphy, LEED GA, Assoc. IIDA, Design Lab Manager and Materials & Sustainability Specialist with MG2, speaks with BD+C Executive Editor Rob Cassidy.
Sponsored | Healthcare Facilities | May 3, 2022
Planning for hospital campus access that works for people
This course defines the elements of hospital campus access that are essential to promoting the efficient, stress-free movement of patients, staff, family, and visitors. Campus access elements include signage and wayfinding, parking facilities, transportation demand management, shuttle buses, curb access, valet parking management, roadways, and pedestrian walkways.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | May 3, 2022
For glass openings, how big is too big?
Advances in glazing materials and glass building systems offer a seemingly unlimited horizon for not only glass performance, but also for the size and extent of these light, transparent forms. Both for enclosures and for indoor environments, novel products and assemblies allow for more glass and less opaque structure—often in places that previously limited their use.
Codes and Standards | May 2, 2022
Developer Hines, engineer MKA develop free embodied carbon reduction guide
Real estate management and investment firm Hines has released the Hines Embodied Carbon Reduction Guide. The free guide, produced with Magnusson Klemencic Associates (MKA), is the result of a two-year effort, relying on MKA’s industry-leading knowledge of carbon accounting and involvement in programs such as the Embodied Carbon in Construction Calculator (EC3) Tool.
Codes and Standards | Apr 28, 2022
Architecture firm Perkins&Will to deliver ‘carbon forecasts’ for clients
Global architecture firm Perkins&Will says it will issue its clients a “carbon forecast” for their projects.
Green | Apr 26, 2022
Climate justice is the design challenge of our lives
As climate change accelerates, poor nations and disadvantaged communities are suffering the first and worst impacts.
Architects | Apr 22, 2022
Top 10 green building projects for 2022
The American Institute of Architects' Committee on the Environment (COTE) has announced its COTE Top Ten Awards for significant achievements in advancing climate action.
Building Team | Apr 20, 2022
White House works with state, local governments to bolster building performance standards
The former head of the U.S. Green Building Council says the Biden Administration’s formation of the National Building Performance Standards Coalition is a “tremendous” step in the right direction to raise building performance standards in the U.S.