When it comes to the building of the future, every material used in construction needs to pull its weight. For a building to become as sustainable, environmentally friendly, and as comfortable as possible, there can be no slackers on the materials front.
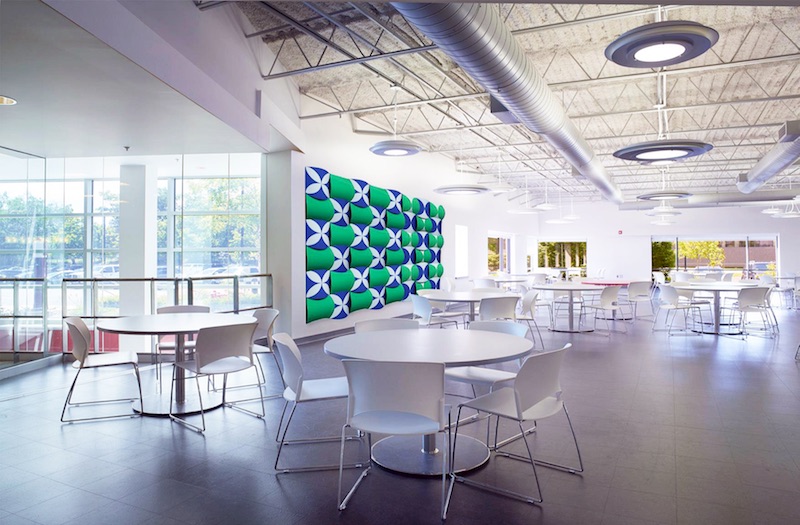
Take the newest offering from E Ink. Using the same E Ink bi-stable ink technology found in its current line of eReaders and wearables and integrating it with traditional architectural materials, E Ink Prism creates a new way for commercial spaces such as large hotel lobbies, office complexes, and airports to change the aesthetics of the space without resorting to a large LCD or LED screen—and the light pollution and higher energy demands that come with it.
E Ink Prism has a paint-like appearance and a wide-ranging compatibility with various materials and shapes that make it highly suitable for architectural applications. E Ink Prism comes in seven different colors—Voyage (dark blue), Daydream (cyan), Blush (red), Sprout (green), Zest (yellow), Harvest (brown) and Waltz (black)—and can be sized to be compatible with most configurations, patterns, and materials.
The film can be programmed to dynamically switch colors in nearly any pattern, shape, speed, and sequence. During these visual changes, E Ink Prism only requires ultra-low power and never requires the use of electrical outlets. The film does not provide any illumination and, as with paint, its visibility is based on ambient light.
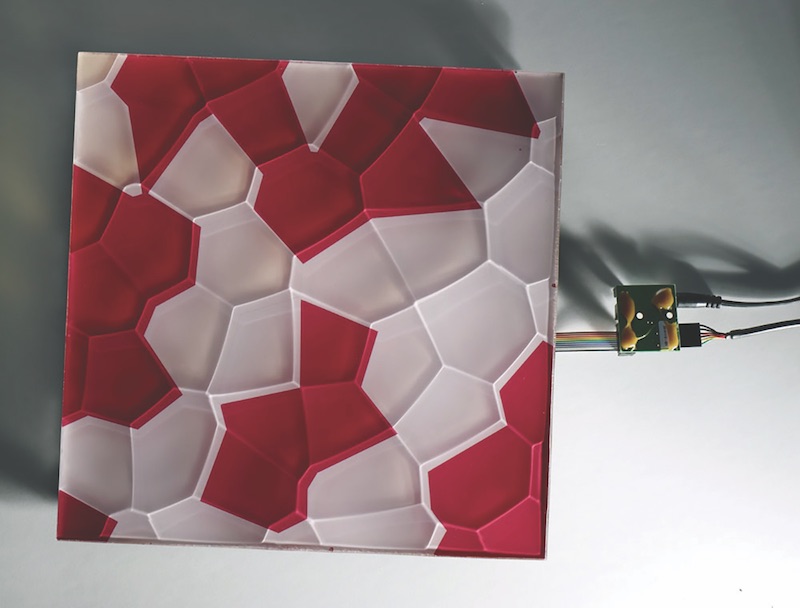 Courtesy of E Ink.
Courtesy of E Ink.
Recent developments are beginning to point to a much more utilitarian future for paint. Researchers at RMIT University, Melbourne, have developed a paint that can absorb water vapor and use solar energy to split it and generate hydrogen. Hydrogen, which is often referred to as the cleanest source of energy, can be used in fuel cells or in conventional combustion engines as an alternative to fossil fuels.
The paint contains synthetic molybdenum sulfide, a new material that acts as a semiconductor and catalyses the splitting of water atoms into hydrogen and oxygen, according to RMIT. All that is needed for the paint to produce fuel is solar energy and moist air.
Applied to a brick wall of a building, the paint instantly converts the wall into an energy-harvesting, fuel-production space. Areas with humid climates provide ideal applications for the paint. But its developers say the material can also be used in applications in very dry, hot climates near oceans. As the seawater is evaporated, the paint will absorb the vapor and produce fuel.
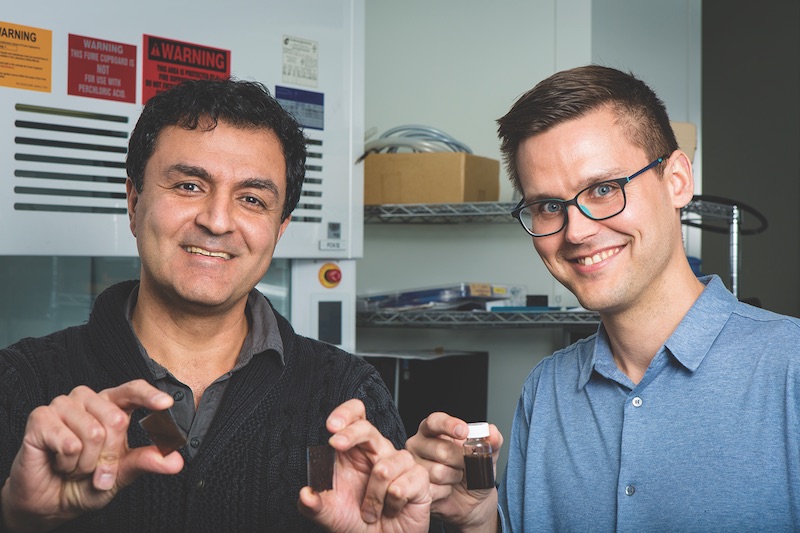 Courtesy of RMIT University.
Courtesy of RMIT University.
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Apr 5, 2018
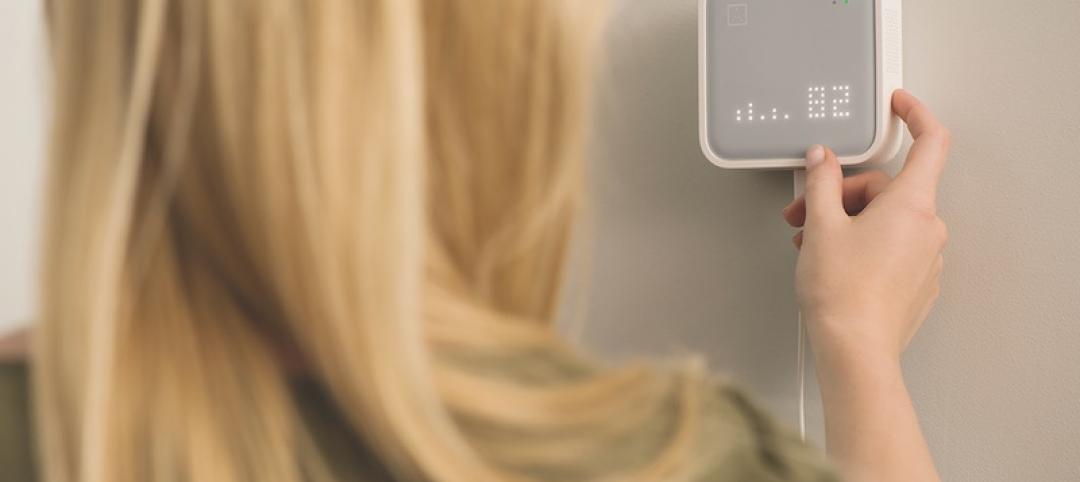
IAQ monitoring for all
San Francisco startup Bitfinder debuts a commercial-grade version of its air quality monitoring system.
Great Solutions | Mar 9, 2018
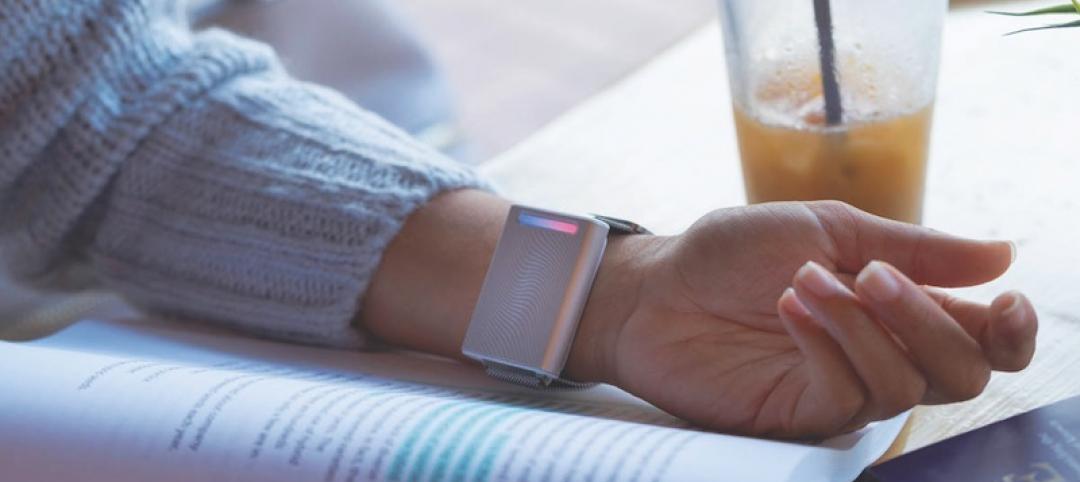
Forget the wall thermostat: Wear one on your wrist instead
The Embr Wave Wristband acts like a personal thermostat and could become a user-friendly component in building energy-saving strategies.
Great Solutions | Feb 8, 2018
Stackable steel modules speed building core construction
With this patented, steel-and-concrete hybrid system, the service core will no longer be the schedule bottleneck on new construction projects.
Great Solutions | Jan 10, 2018
Blue lagoon technology brings the beach anywhere in the world
From coastal resorts to inner cities, these large-scale clear-water lagoons offer a slice of paradise.
Great Solutions | Oct 17, 2017
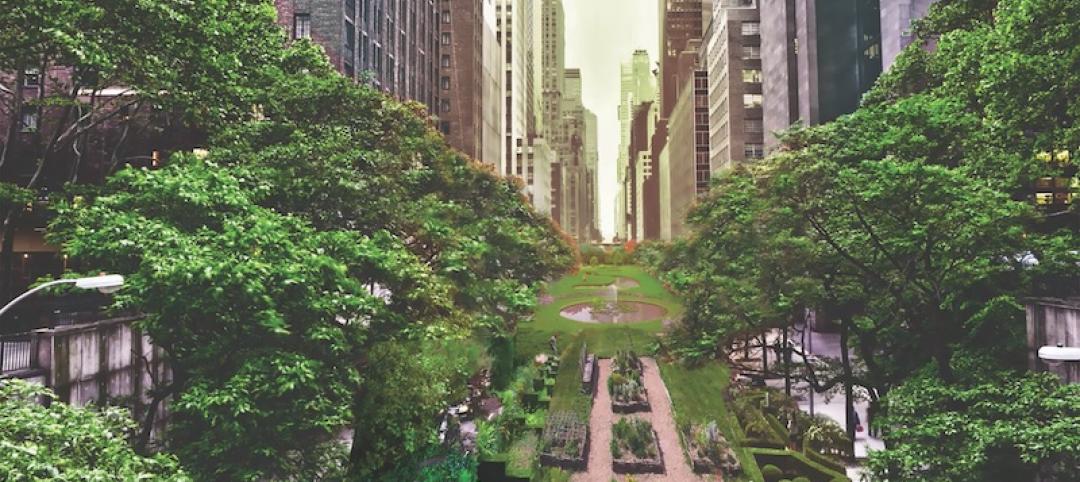
Loop NYC would reclaim 24 miles of park space from Manhattan’s street grid
A new proposal leverages driverless cars to free up almost all of Manhattan’s Park Avenue and Broadway for pedestrian paths.
Great Solutions | Sep 14, 2017
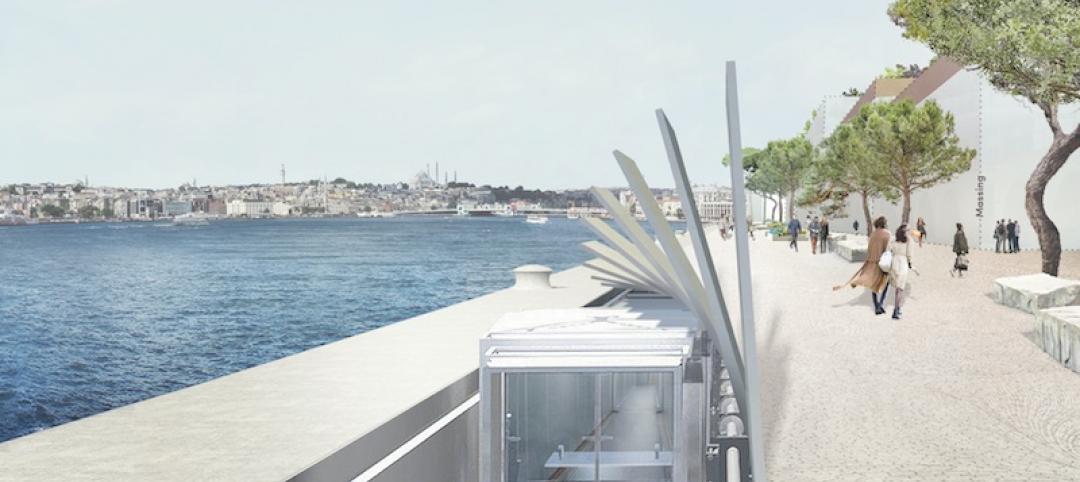
Hydraulic underground boardwalk and gangway system reunites the public with the coastline in Istanbul
The bespoke system is part of a master plan by Dror and Gensler that creates the world’s first underground cruise operation.
Great Solutions | Jul 12, 2017
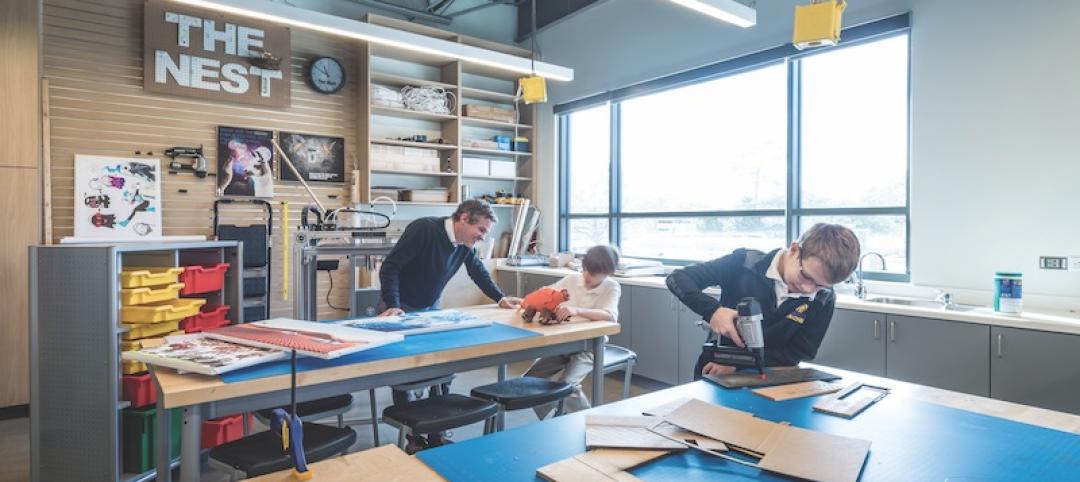
The writing on the wall: Maker spaces encourage students to take an active role
Maker spaces, dry-erase walls, and flexible furniture highlight Kinkaid’s new Learning Center.
Great Solutions | Jun 6, 2017
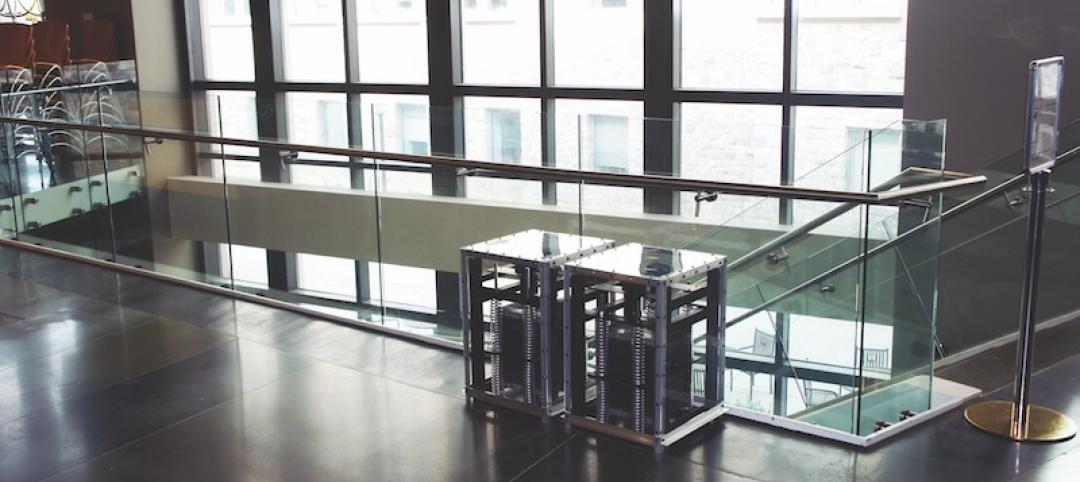
Good vibrations: Portable tuned mass damper provides lightweight, cost-effective way to reduce structural vibrations
Developed by a team at Virginia Tech, the PTMD has been shown to reduce vibrations by as much as 75%.
Great Solutions | May 5, 2017
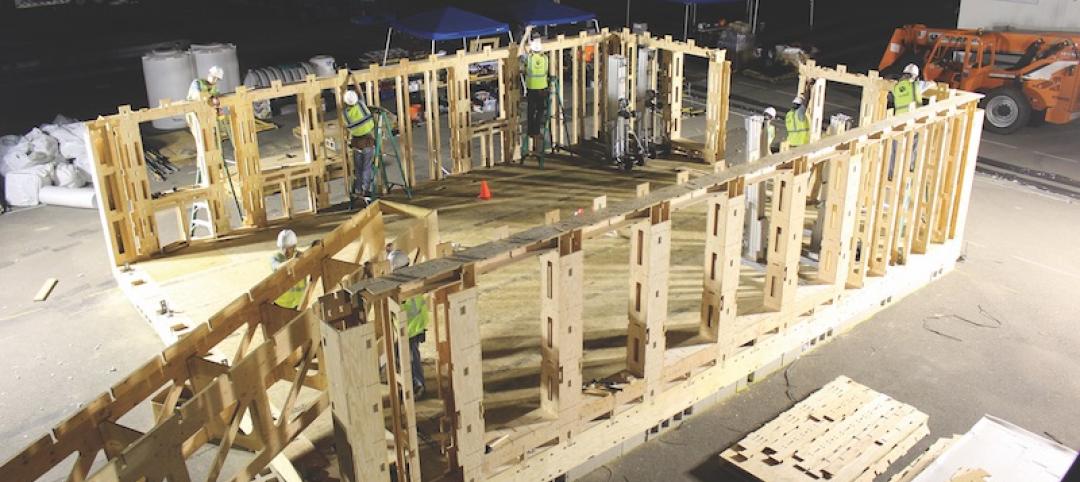
No nails necessary: Framing system comes together with steel zip ties and screws
Clemson University’s School of Architecture develops a patent-pending construction method that is gaining attention for its potential use in rapid, low-tech sustainable housing.
Great Solutions | Apr 6, 2017
Phone booths for the 21st century
Spotting a phone booth on a public street may not become any less rare, but they may soon become fixtures in the modern office.

















