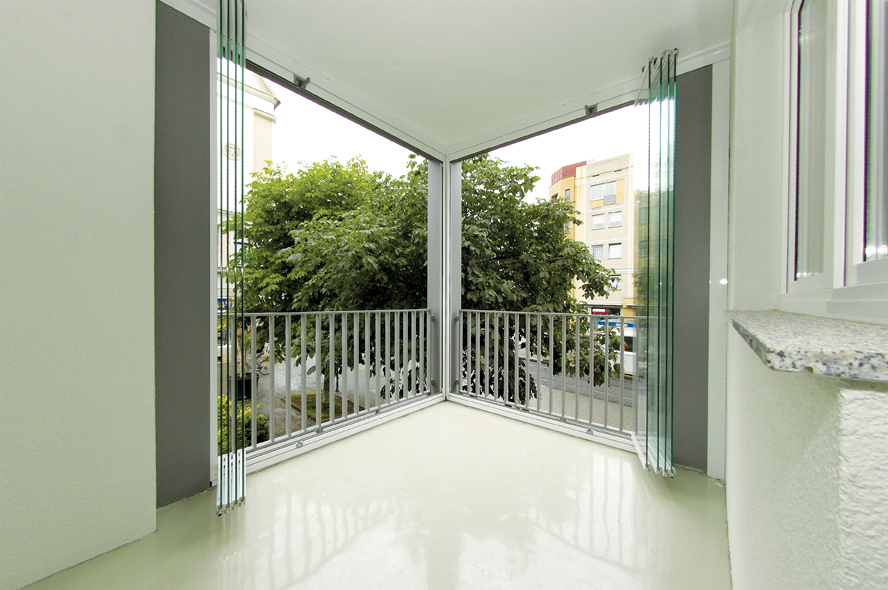
What if you could squeeze a few dozen extra square feet of usable space out of an existing apartment or condo unit? Instead of unsightly balconies that often store bicycles and Weber grills, what if they were converted from the largely unusable space into attractive space that could be functional to occupants for most of the year?
At the Elm Park residential project in Dublin, Ireland, operable glass balcony glazing systems are also being used to create an intelligent, user-controlled building envelope that reduces energy consumption while increasing the comfort level of occupants.
Globally, the trend to install operable glass balcony glazing systems into residential and commercial applications for both new structures as well as reconstructed buildings has been on the upswing. Though balcony glazing systems have been primarily installed on an international basis, Building Teams and owners in North America are beginning to embrace the technology.
For either new construction or the reconstruction of an existing building, the use of glass is an effective way to maximize the connection between indoor and outdoor spaces, while also adding unconditioned space that was previously lost to inclement weather or the winter season. As a result of a glazing system installation, occupants can now use this space year-round regardless of the weather.
Owners of residential buildings recognize value in the escalated usable square footage as well as the increase to the building’s curb appeal by adding aesthetic enhancements.
INCREASING ENERGY EFFICIENCY
Whether the project is residential- or commercial-based, pumping up the energy efficiency is an essential element in the design strategy incorporated by Building Teams. Energy savings may be as much as a 60% reduction for heating for residential or commercial structures that include glazed balconies, according to the report “Nature & Nurture, the Sustainable Benefits of All-glass Operable Double-wall Systems,” by Celeste Allen Novak, AIA, LEED AP.
Glazed balconies save the most energy in a sunny and cold climate. Acting as a double-skin layer to the structure, the system reduces the wind pressure on an adjacent room, reducing heat losses due to infiltration of outside air. In a windy but cloudy climate or in a heating-dominated climate, savings typically range between 10-25%.
4 ADVANTAGES of Balcony Glazing Systems for Building Owners
1. Energy savings, as solar energy is used to preheat the ventilation air and reduce heat loss.
2. An extra room that can be used in the spring, summer, and autumn.
3. Control of solar heat gain in the summer by using ventilation devices and solar shading.
4. Ventilation devices can be used to prevent drafts and save energy.Orientation is also an important consideration. To save the most energy, glazed balconies should have an orientation between southeast and southwest. A north-oriented balcony is also an energy saver—though not as much as a south-oriented balcony—because the glazed balcony creates a buffer zone between the unit and the exterior.
In some cases, the glazed balconies provide natural cooling through cross-ventilation. Solar energy can preheat ventilation air in a balcony. Glazed balconies reduce transmission and ventilation losses. Part of the heat loss is recovered from incoming ventilation air.
SAFETY ASPECTS OF GLAZING SYSTEMS
Depending on the structural design wind load requirements, glass thickness ranges from 5/16 inch to ½ inch. Glazing systems are engineered to handle high wind loads up to 80 stories in 90 mph wind zones, depending on building location. A design pressure rating of +40 psf / -45 psf per ASTM E330 structural load testing has been achieved with half-inch-thick panels measuring two feet, seven inches by seven feet, eight inches.
When the windows are open, horizontal twin ball-bearing runner carriages with a high load-bearing capacity keep the structural load within the plane of the opening. Typically, one roller is situated within the track at all times, keeping the panels secure even when opened. A pin and socket locking system provides security and protection from forced entry.
In terms of maintenance, the glass surfaces can be cleaned from the inside due to the laterally secured panels.
The glazing system has an impact on structural maintenance as well. In a white paper entitled “Effect of Balcony Glazing on the Durability of Concrete Structures in a Nordic Climate” (www.irbdirekt.de/daten/iconda/CIB11652.pdf), Jussi S. Mattila, ScD, at the Tampere University of Technology, in Finland, examined how equipping aging balconies with glazing can lessen moisture content and water collection, reducing the corrosion rates of steel and the disintegration of concrete.
According to the study, “The efficiency of moisture protection by the glazing was measured by monitoring the corrosion rate of reinforcement in carbonated concrete sensors, which were installed both in glazed and open balconies. The results showed that glazing changes the micro-climate in the balcony so the hygrothermal conditions turned unfavorable to degradation resulting in an increase in service-life of concrete structures.”
As for exterior noise, balcony glazing systems can reduce street noise pollution. When the windows are shut, there is only a 1/8-inch gap between the panels. Measuring a sound transmission class (STC) value of 17, a glazing system reduces most noise from street level, resulting in a quieter indoor environment. Thicker or laminated glass produces even higher STC values.
RESIDENTIAL AND COMMERCIAL APPLICATIONS
In 2008, construction was completed on the Elm Park residential complex in the Irish capital. This six-building complex includes apartments, a hotel, restaurants, a clinic, a leisure center, and parkland. Designed by Bucholz McEvoy Architects, Dublin, the project utilized 665 panels of the SL 25 glazing system by NanaWall, Mill Valley, Calif. The frameless slide-and-turn system offers versatility of balcony use for most of the year while providing a uniform façade grid that accentuates the structure.
A recent commercial application in the Netherlands includes folding glass doors with wooden frames in the interior and a glass slide-and-turn glazing system on the exterior of structure. Combined, this double façade creates an accessible façade corridor that encircles the entire building. Both façade layers can be completely opened, allowing manual regulation of room temperature depending on weather conditions.
The completely closed double-skin façade offers thermal insulation. The outer skin functions as a solar heat collector. As higher temperatures are generated in the façade space, occupants can open the inner façade to allow a fresh supply of pre-warmed air to enter the building. When the weather is hot, the outer skin can be opened to prevent overheating in the façade corridor. BD+C
Related Stories
| May 25, 2011
Developers push Manhattan office construction
Manhattan developers are planning the city's biggest decade of office construction since the 1980s, betting on rising demand for modern space even with tenants unsigned and the availability of financing more limited. More than 25 million sf of projects are under construction or may be built in the next nine years.
| May 25, 2011
Olympic site spurs green building movement in UK
London's environmentally friendly 2012 Olympic venues are fuelling a green building movement in Britain.
| May 25, 2011
TOTO tests universal design at the AIA conference
If you could be 80 years old for 30 minutes—and have to readjust everything you think you know about your own mobility—would you do it?
| May 20, 2011
Hotels taking bath out of the bathroom
Bathtubs are disappearing from many hotels across the country as chains use the freed-up space to install ever more luxurious showers, according to a recent USAToday report. Of course, we reported on this move--and 6 other hospitality trends--back in 2006 in our special report "The Inn Things: Seven Radical New Trends in Hotel Design."
| May 19, 2011
BD+C’s "40 Under 40" winners for 2011
The 40 individuals profiled here are some of the brightest stars in the AEC universe—and they’re under the age of 40. These young architects, engineers, contractors, designers, and developers stood out among a group of 164 outstanding entrants in our sixth annual “40 Under 40” competition.
| May 18, 2011
Sanford E. Garner on the profitability of being diverse
Sanford E. Garner, AIA, NOMA, LEED AP ND, NCARB, founding partner and president of A2SO4 Architecture, LLC, Indianapolis, on gentrification, the profitability of being diverse, and his goals as NOMA president.
| May 18, 2011
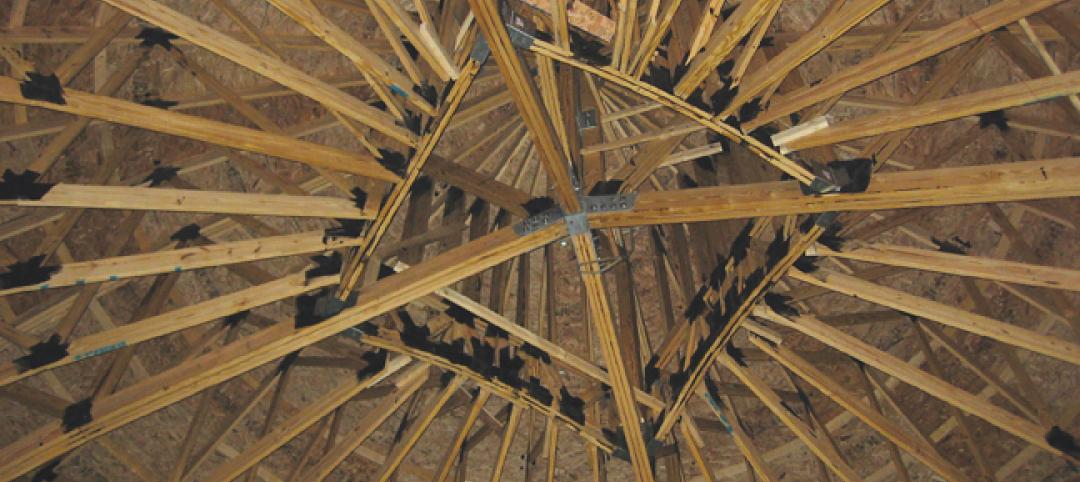
8 Tips for Designing Wood Trusses
Successful metal-plate-connected wood truss projects require careful attention to detail from Building Team members.
| May 18, 2011
Major Trends in University Residence Halls
They’re not ‘dorms’ anymore. Today’s collegiate housing facilities are lively, state-of-the-art, and green—and a growing sector for Building Teams to explore.
| May 18, 2011
Former Bronx railyard redeveloped as shared education campus
Four schools find strength in numbers at the new 2,310-student Mott Haven Campus in New York City. The schools—three high schools and a K-4 elementary school—coexist on the 6.5-acre South Bronx campus, which was once a railyard.