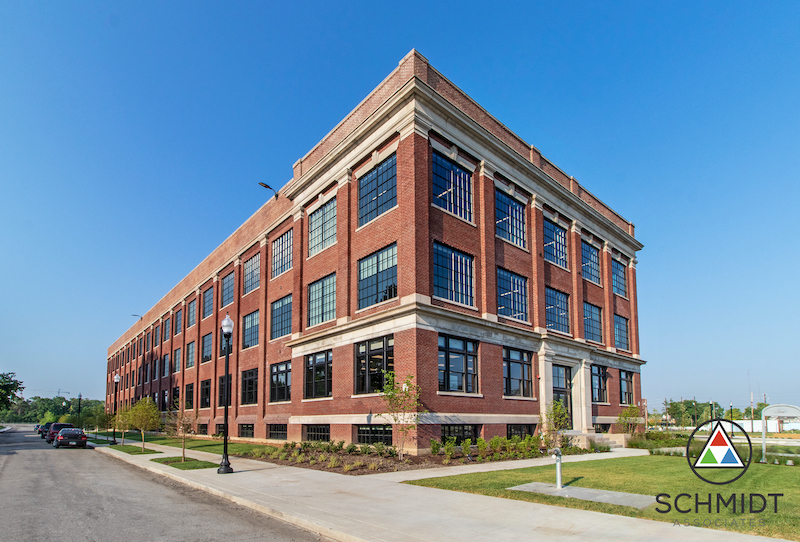
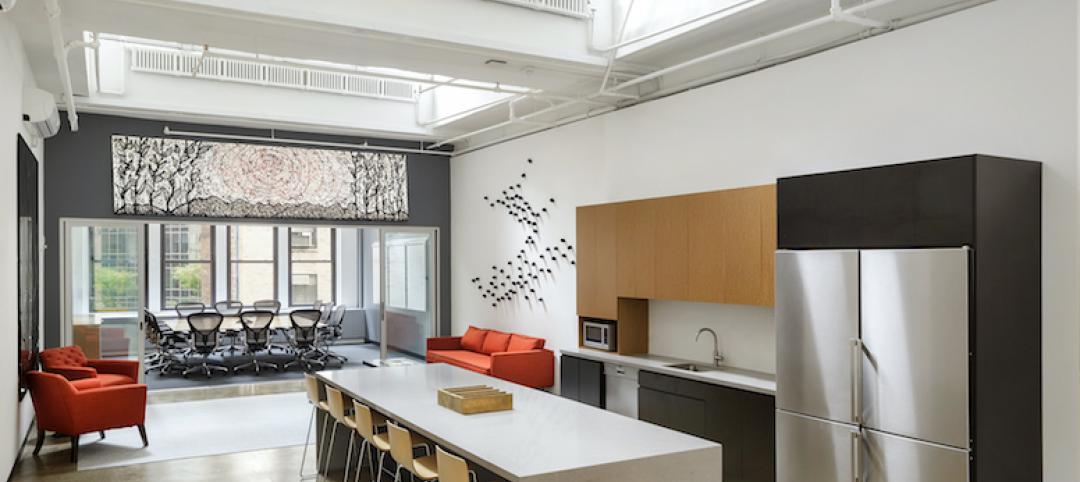
The P.R. Mallory Building in Indianapolis was once where the Duracell battery was invented and patented. Vacant for decades, the 100-year-old building has been jolted back to life through an adaptive reuse project that converted the facility into new homes for the STEM-focused public charter school Purdue Polytechnic High School and Paramount Englewood Middle School.
The building team—AE firm Schmidt Associates, Brandt Construction, and landscape designer Anderson + Bohlander—was instrumental in helping Englewood Community Development and John Boner Neighborhood Centers, the building’s owners since 2018, to realize their vision.
“We were able to help the owners take something old and dilapidated, and turn it into something new and innovative that will improve lives long into the future,” says Lisa Gomperts, FAIA, LEED AP, Principal and Project Manager with Schmidt Associates.
REUSE DESIGN COMPLICATED BY NATIONAL REGISTRY

A before-and-after look at one of the building's areas. Large floor plates gave the design team lots of room for their ideas.
Adaptive reuse and historic preservation are among Schmidt’s specialties. For example, last year the firm converted an abandoned 62,000-sf strip mall in Shelbyville, Ind., into Golden Bear Preschool, a $13 million project that encompasses a SENSES gym for children with special needs, 15 classrooms, a cafeteria, and outdoor play area. The school’s administrative office is located inside what had been a bank at the end of the shopping center.
The Indianapolis schools, which opened last week, are contained within 114,256 sf over four floors. The project’s total cost was $38 million, of which $23.4 million was construction.
Click here to see an architectural tour of the building
The adaptive reuse presented some challenges. During the design phase, the owners initiated the process of putting the building on the National Register of Historic Places, which meant that any proposed designs needed approval from the National Parks Service, the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, and the city.
It took 23 months to get the building’s 206 historically accurate windows approved. The building itself also had an undocumented tunnel system that had to be filled in. And because that had once been a battery plant, environmental remediation was a given to make the space safe for students and faculty.
The building’s original wood columns and ceilings were stripped and restored, and other original elements were retained such as a catwalk and roof monitors, steel doors of the elevator and vaults, and the factory’s smokestack for future renovation. The original terrazzo tile that adorned the building’s north entryway was restored.
Also see: Hastings Architecture creates its new HQ from a former Nashville public library building
ARCHITECT HAD LOTS OF SPACE TO WORK WITH
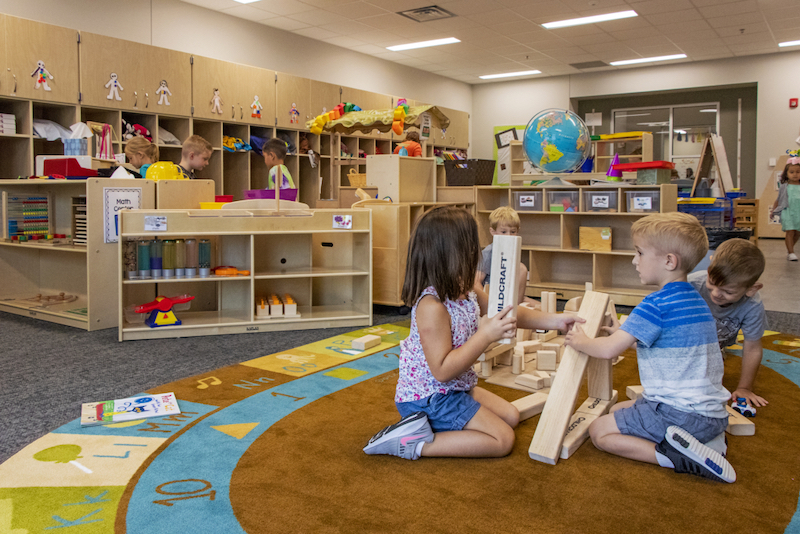

Another of Schmidt Associates' adaptive reuse projects is Golden Bear Preschool, inside what once was a shopping mall in Shelbyville, Ind.
The nontraditional curricula of the educational tenants, and their relationship, drove the reuse design. The two institutions will be integrated with each other and Purdue University; for example, a middle-school student would receive priority admittance to Purdue Polytechnic, whose students receive direct admittance upon graduation to Purdue University.
The building has 56 classrooms: 31 for the high school including labs and a career readiness center; and 25 for the middle school.
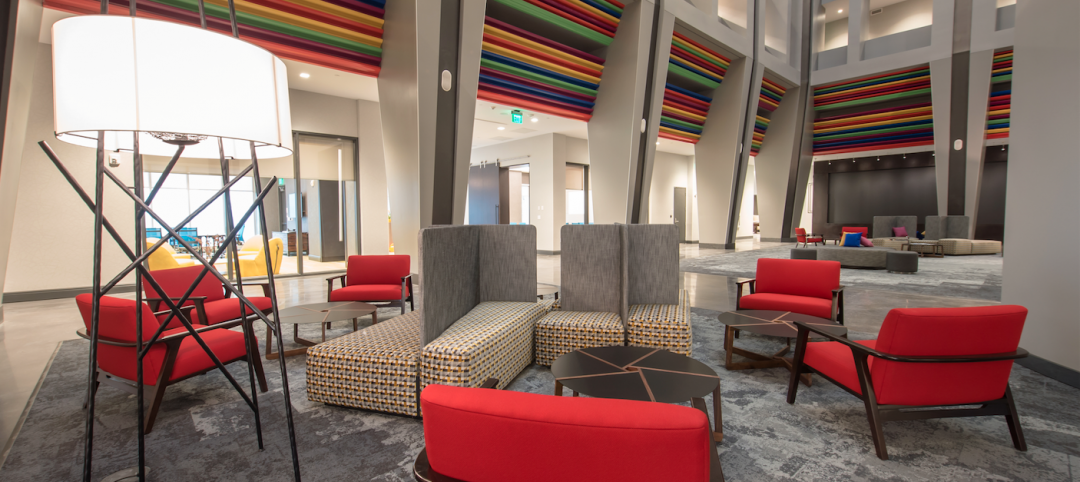
The building’s expansive floor plates gave Schmidt an ample canvas for its design ideas. The building now features collaborative study lounges whose furniture can be broken down into pods; clean and dirty maker spaces; flexible classrooms with garage doors that open up or section off spaces as needed; and communal outdoor gathering areas. There is also a high level of technological integration between the schools.
Related Stories
Adaptive Reuse | Oct 26, 2020
Mall property redevelopments could result in dramatic property value drops
Retail conversions to fulfillment centers, apartments, schools, or medical offices could cut values 60% to 90%.
Adaptive Reuse | Oct 22, 2020
A Los Angeles design firm reimagines urban workplaces, multifamily buildings, and warehouses
Omgivning conjures varieties of adaptive-reuse concepts.
Coronavirus | May 18, 2020
Will empty hotels provide an answer for affordable housing shortage?
A Los Angeles-based startup sees the Midwest as most fertile for adaptive reuse.
Adaptive Reuse | Feb 25, 2020
Hastings Architecture creates its new HQ from a former Nashville Public Library building
The building was originally constructed in 1965.
Mixed-Use | Jul 18, 2019
POST Houston mixed-use development will include a five-acre “skylawn”
OMA is designing the project.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 17, 2019
Boston multifamily development combines a historic warehouse with a new, modern addition
The Architectural Team designed the project.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 11, 2019
The power and possibility of adaptive reuse
Building reuse generally offers greater environmental savings than demolition or new construction.
Adaptive Reuse | Jul 9, 2018
Work, park, live: Inside Cincinnati’s parking garage turned lifestyle hotel
The Summit hotel and conference center is a converted parking garage that was once a factory.
Office Buildings | Jun 6, 2018
Final Cut: Jupiter Entertainment’s new production studio in New York combines office and editing spaces
The project team completed this full-floor renovation in four months.
Adaptive Reuse | Jun 4, 2018
Pop-up retail market on Chicago’s Randolph Street will be made of repurposed shipping containers
Related Midwest will open the market at 725 W. Randolph St. later this week.