Project Tango may sound like an underground dance movement in South America that’s packed to the gills with Latin flair while emanating the sounds of Carnivàle, but as fun as that sounds, it’s not what this Project Tango is about at all.
This Project Tango is more technological in nature. It is a platform that uses computer vision to give devices the ability to understand their position relative to the world around them. The platform looks to do this by combining three core technologies: motion tracking, area learning, and depth perception.
The motion tracking is implemented using visual-inertial odometry to estimate where a device is relative to where it started. Visual-inertial odometry uses inertial motion sensors that can track a device’s rotation and acceleration so that the device can estimate its orientation and movement within a 3D space with greater accuracy, even when used indoors.
The second core technology is area learning. The technology used in Project Tango has the ability to take note of key visual features of a physical space so that it can recognize them again at a later time.
The third and final core technology used in Project Tango deals with depth perception. Project Tango devices use a depth sensor that projects infrared light to estimate depth based on how the light is shaped by objects in the environment. This technology makes 3D room-scanning applications possible, but it also allows you to interact with the physical environment by using virtual objects.
You might be asking yourself, but what does all of this have to do with the AEC market? That’s a good question, and while currently the uses are somewhat limited, the potential is tantalizing.
Sure, this technology might seem to be more readily useful for creating video games and other sources of entertainment of that nature, but who would have thought something like virtual reality would have become such a useful tool for architects and designers?
For example, looking at an image of something and trying to determine how large it will actually appear in a given space can be very difficult. Something like a refrigerator or a stove might fit in theory, but can dominate a space when it is actually moved in. Some retailers, such as Lowe’s, are offering the ability to virtually place an exact 3D replica of a refrigerator or stove in the space the actual physical appliance would occupy. You can then walk around and look at it from various views to make sure everything is to your liking. In the future, it may also be possible to open and close the doors and all of the drawers to make sure the needed clearance is there.
Similarly, Tango devices can be used to place markers on various services in a given area. Combined with the future possibility of tagging information to these markers, such as specific information about the floors, cabinets, or paint colors used on a project, an augmented reality is created where clients can walk through a given space and see all of the information they might be curious about on their screens.
There is also an app titled Project Tango Constructor that allows for real-time 3D mapping and modeling of a given area. All it requires is to open the app, hold the device, and begin walking around the space that is to be mapped. The app provides first person, third person, and top down views of the area.
This can be taken a step further and can actually be integrated with the Unity game engine, again, in real-time, and can provide the geometry of a given space. The technology can sense things like corners and changes in elevation from doing nothing more than simply walking around and pointing the device.
This technology is still in the very early stages of its life, and it needs to evolve further before the true extent of its usefulness in the AEC market can be determined, but from what has been shown off so far, it doesn’t take an imagination like that of Willy Wonka to think of all the ways this could be used to improve both the speed and precision at which things are done.
You can watch the entire Vision Summit 2016 Project Tango presentation here.
Related Stories
Sustainability | May 1, 2023
Increased focus on sustainability is good for business and attracting employees
A recent study, 2023 State of Design & Make by software developer Autodesk, contains some interesting takeaways for the design and construction industry. Respondents to a survey of industry leaders from the architecture, engineering, construction, product design, manufacturing, and entertainment spheres strongly support the idea that improving their organization’s sustainability practices is good for business.
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
AEC Tech Innovation | Apr 27, 2023
Does your firm use ChatGPT?
Is your firm having success utilizing ChatGPT (or other AI chat tools) on your building projects or as part of your business operations? If so, we want to hear from you.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Resiliency | Apr 18, 2023
AI-simulated hurricanes could aid in designing more resilient buildings
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have devised a new method of digitally simulating hurricanes in an effort to create more resilient buildings. A recent study asserts that the simulations can accurately represent the trajectory and wind speeds of a collection of actual storms.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
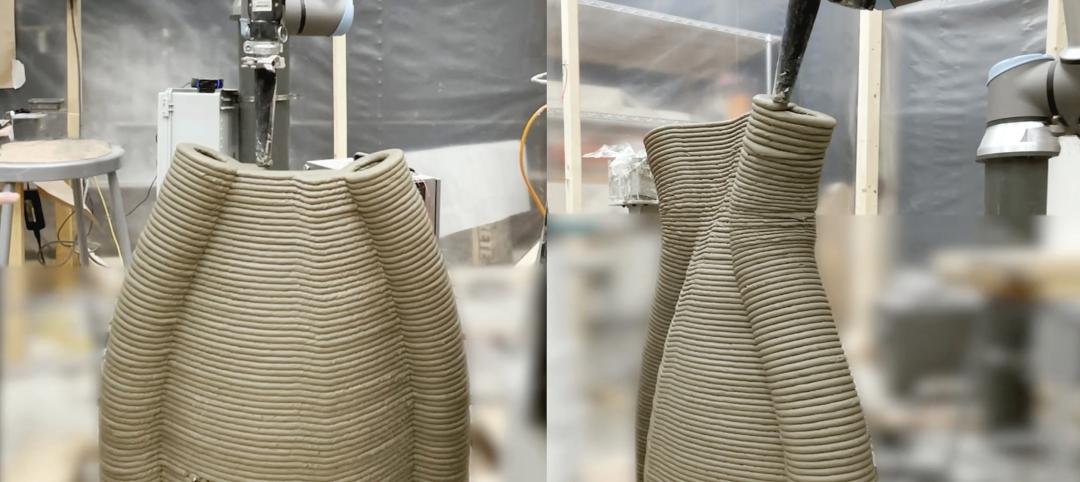
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.
AEC Tech | Mar 14, 2023
Skanska tests robots to keep construction sites clean
What if we could increase consistency and efficiency with housekeeping by automating this process with a robot? Introducing: Spot.
Modular Building | Mar 3, 2023
Pallet Shelter is fighting homelessness, one person and modular pod at a time
Everett, Wash.-based Pallet Inc. helped the City of Burlington, Vt., turn a municipal parking lot into an emergency shelter community, complete with 30 modular “sleeping cabins” for the homeless.