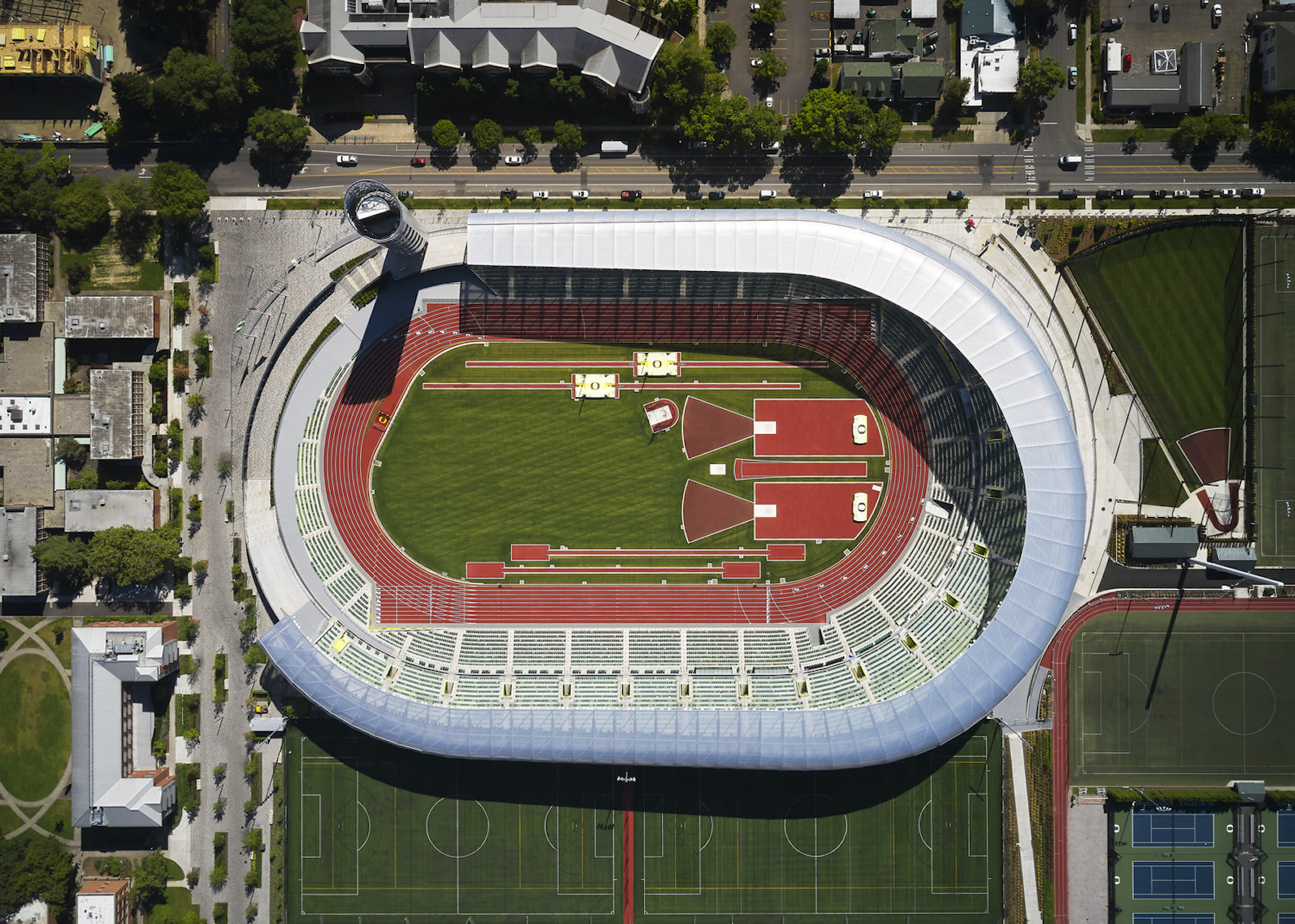
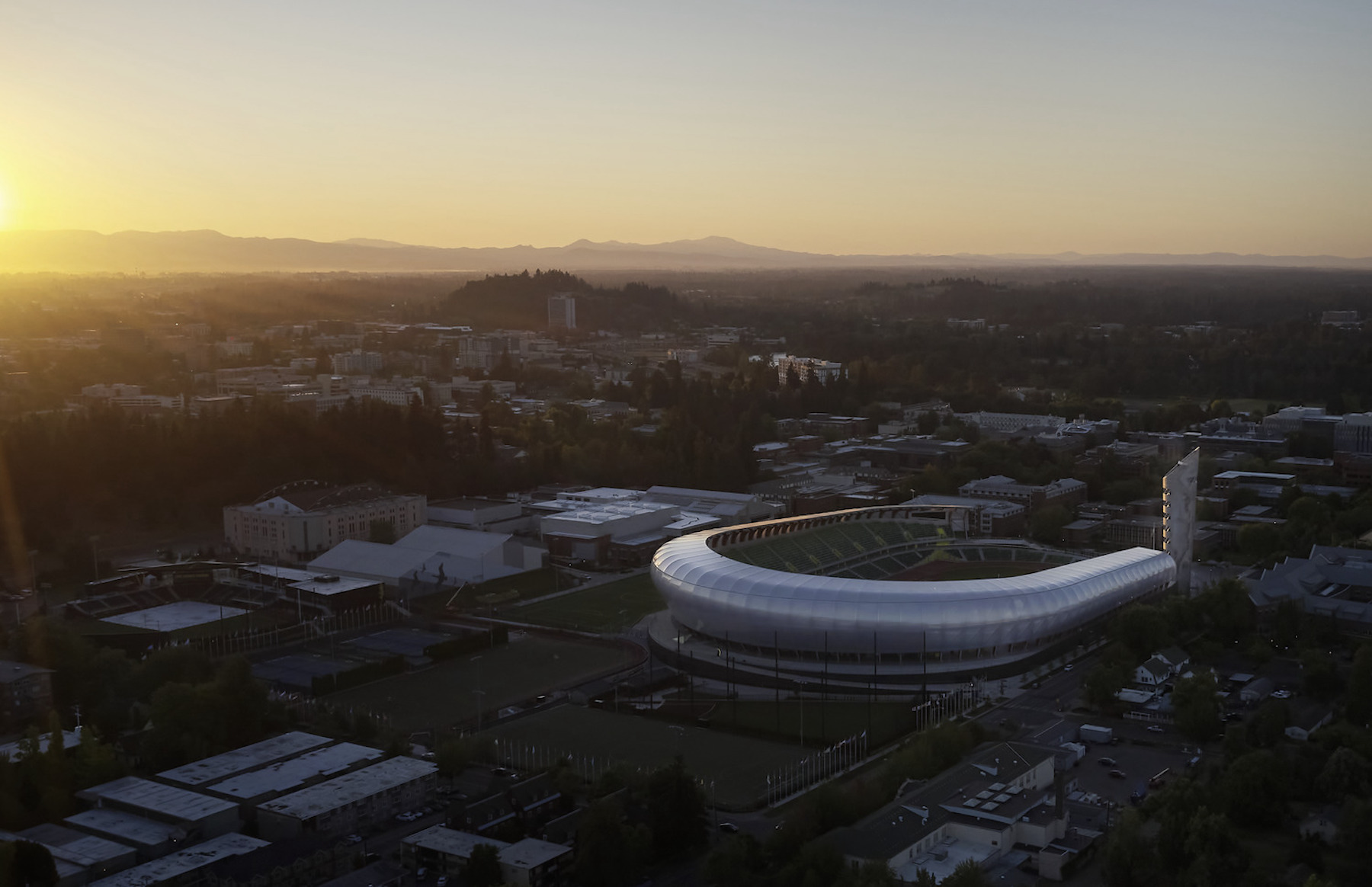
The renovation of the University of Oregon’s Hayward Field had the goal of creating the “finest track and field facility in the world.” The two-year project revamped both the athlete’s and spectator’s experience. It included comfortable seating for every patron, a diversity of in-stadium food and beverage amenities, great sight lines, and close proximity to athletes and the competition. An 8,600 sf museum dedicated to the history of Oregon track & field tells the story of legendary coach Bill Bowerman and the birthplace of Nike.
Beneath the stadium is nearly 40,000 sf dedicated to training and recovery. Team amenities include: an indoor practice area (including a six-lane, 140-meter straightaway and two-story interior space for long jump, triple jump, throws, and pole vault); 100-seat team auditorium; team locker rooms, lounge and shared study spaces; weight training; equipment work-space, offices, storage and check-out; sports medicine and active/passive recovery; hydrotherapy, training and treatment; anti-gravity treadmills; nutrition station; and barber shop.
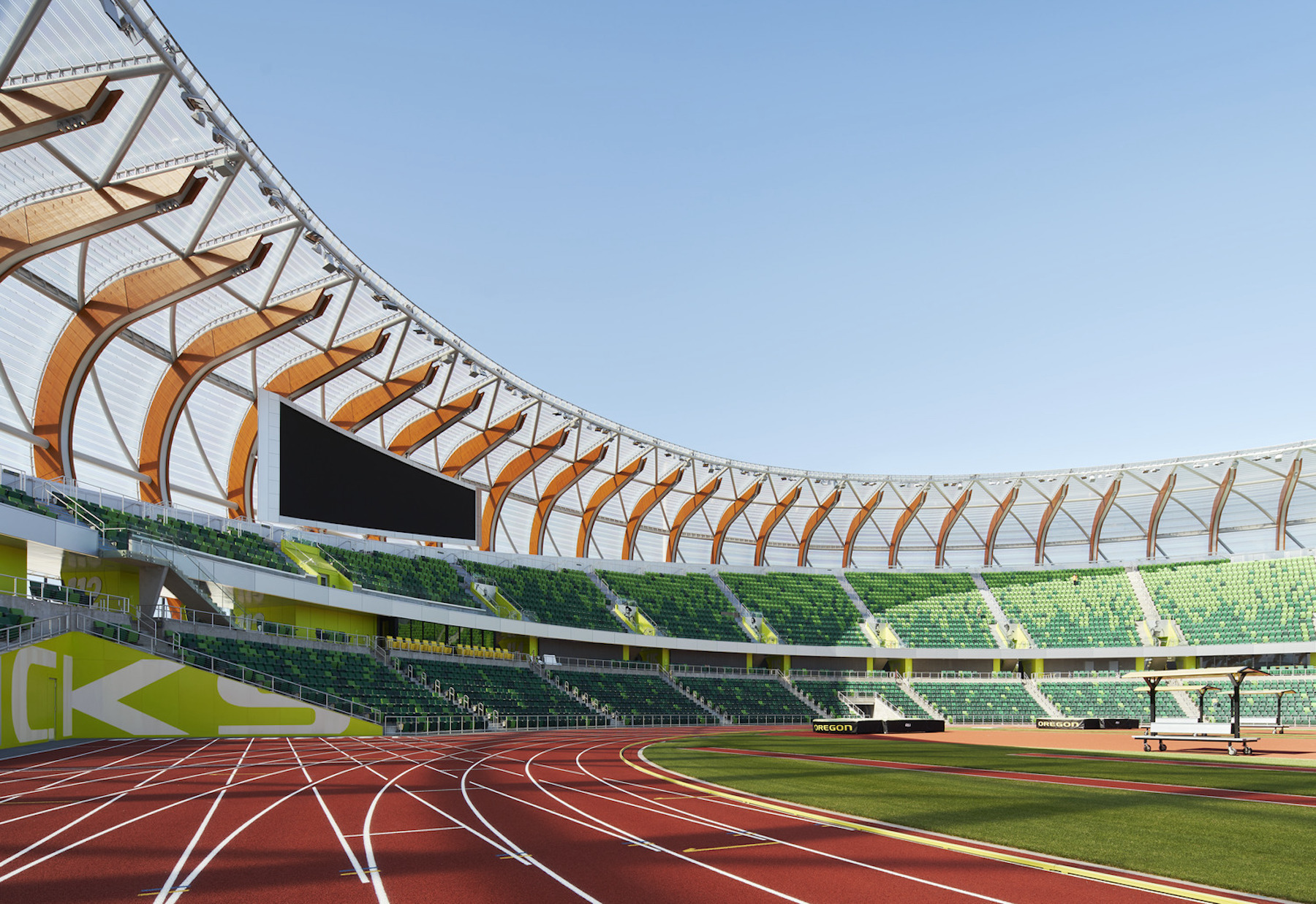
The seating bowl and roof are flowing and asymmetrical, growing in height to the southwest corner of the building. The form of the building appears to be in motion, and also enhances athlete and fan experiences by packing the greatest number of seats and stadium amenities nearest the track’s finish line.
The facility is composed of three primary components: the base, the seating bowl, and the roof canopy. The base encloses the training and team facilities and supports the stadium’s main public concourse above. It is clad in trapezoidal precast concrete panels that ground the building visually from all sides. The panel shapes all lean in the direction of the runners on the track—a nod to the theme of movement.
The bowl was raised off the main concourse to maximize fan flow and to open the stadium to views and daylight. Clad with a metal mesh screen on its underside, the bowl became a canvas for branding and connections to the site’s storied history and is visible to all from the public concourse and beyond.
The soaring wood roof canopy structure was inspired by the Pacific Northwest and acknowledges Hayward Field’s historic wooden grandstands. Stadium environments are typically dark and in shadow because of solid roof structures and materials, but this facility’s ETFE roof allows daylight in, while providing rain and wind protection for fans. A powerful metaphor of the stadium as the body of an athlete emerged with the wood canopy structure being the “ribs” that support and protect the heart with a translucent “skin” roof covering.
Given the high-profile events the facility has drawn since it has reopened, including the U.S. Track & Field Olympic Trials and the World Athletic Championships, it has lived up to the project goal of creating a world-class venue.
On the Building Team:
Owner and/or developer: University of Oregon
Design architect: SRG Partnership
Architect of record: SRG Partnership
MEP engineer: PAE Engineers
Structural engineer: MKA
General contractor/construction manager: Hoffman Construction Company


Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Dec 28, 2014
The Big Data revolution: How data-driven design is transforming project planning
There are literally hundreds of applications for deep analytics in planning and design projects, not to mention the many benefits for construction teams, building owners, and facility managers. We profile some early successful applications.
| Dec 28, 2014
AIA course: Enhancing interior comfort while improving overall building efficacy
Providing more comfortable conditions to building occupants has become a top priority in today’s interior designs. This course is worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW.
| Nov 26, 2014
U.S. Steel decides to stay in Pittsburgh, plans new HQ near Penguins arena
The giant steelmaker has agreed to move into a new headquarters that is slated to be part of a major redevelopment.
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
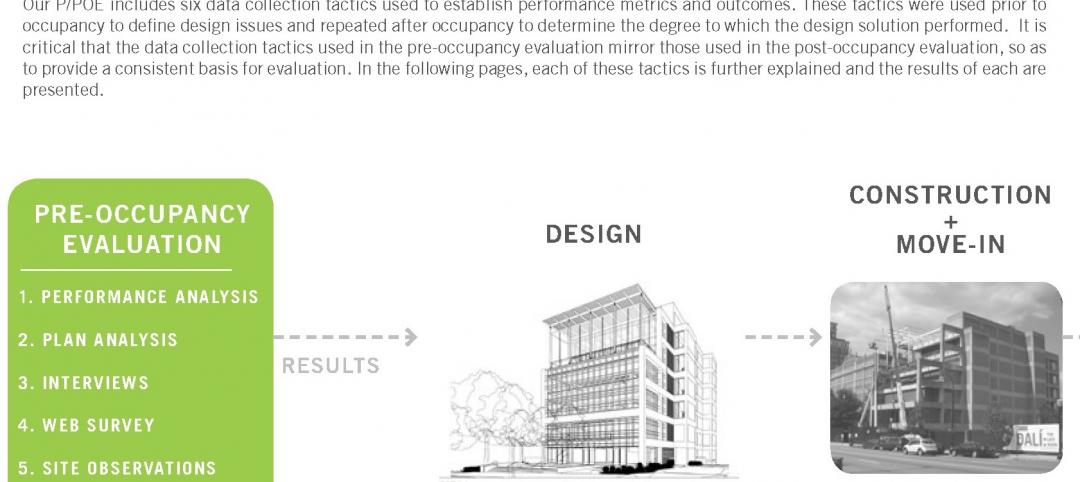
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.
| Sep 15, 2014
Ranked: Top international AEC firms [2014 Giants 300 Report]
Parsons Brinckerhoff, Gensler, and Jacobs top BD+C's rankings of U.S.-based design and construction firms with the most revenue from international projects, as reported in the 2014 Giants 300 Report.