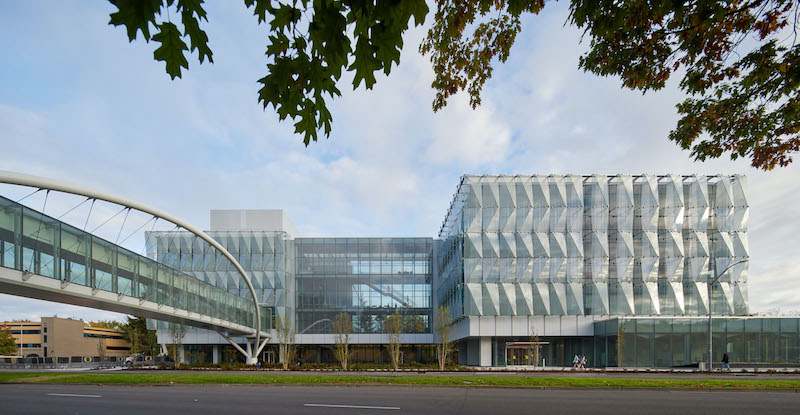
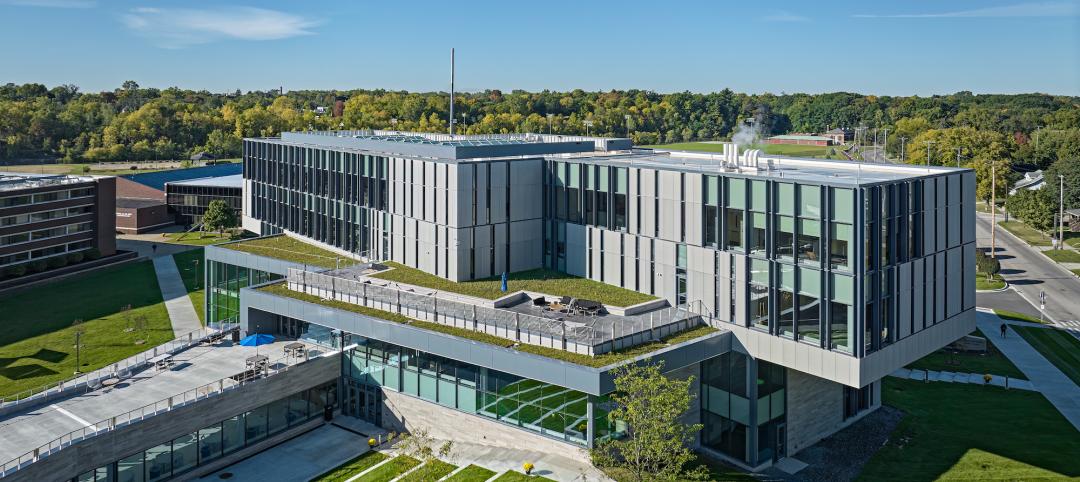
Earlier this month, the University of Oregon in Eugene opened the Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact. The 160,000-sf complex, which consists of two facing L-shaped towers, supports a mission to shorten the timeline between discovery, development, and deployment by bringing together engineering, applied science, business innovations, and culture. Its environment priorities revolve around wellness, human performance, and community. (The Campus’s tagline is “Science Advancing Society.“)
Phil Knight, co-founder and chairman emeritus of Nike, donated $500 million for this project. “Phil was most interested in the mission” of acceleration, Todd Schliemann, FAIA, Design Partner at Ennead Architects, tells BD+C. The Campus’s current focus is bioengineering, and OU partners with Oregon State University to offer a PhD program in that discipline.
Ennead Architects was this project’s design architect, Portland, Ore.-based Bora Architecture & Interiors was its AOR and designed some of the interiors, and Hoffman Construction built the campus.
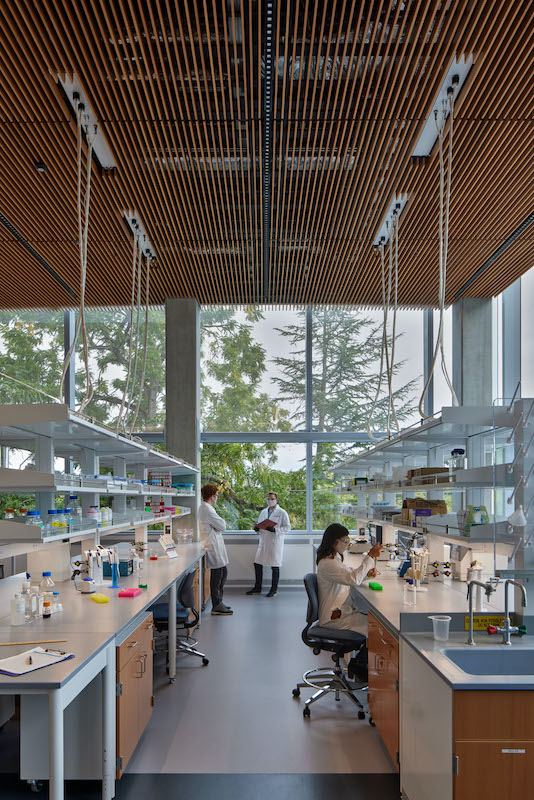

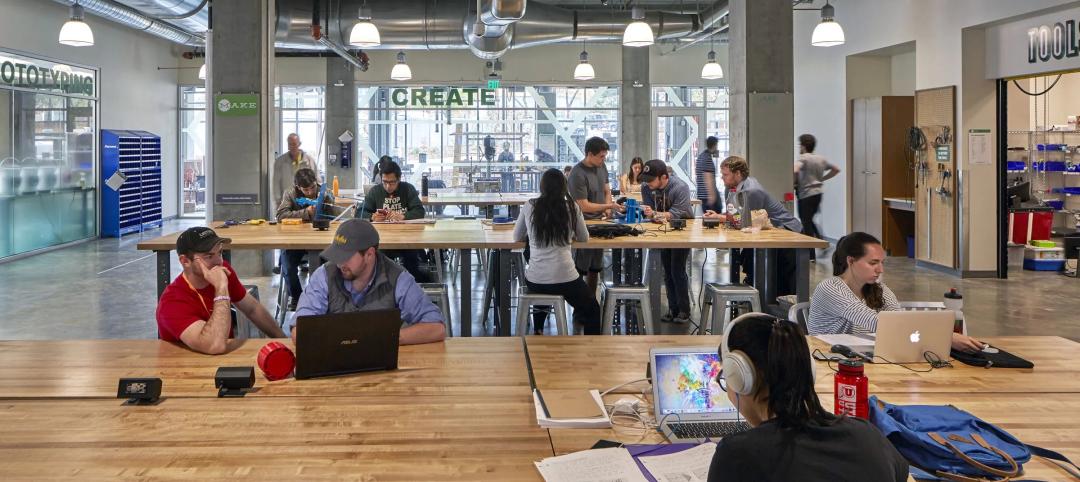
Lab space (above) and work space (below) intersect in the campus's buildings. Mass timber was applied throughout the Campus, including the labs' ceiling.

Built on land where a Domino’s Pizza, a mini-mall and parking lot once stood, the Knight Campus is situated between the University of Oregon’s main campus and parkland straddling the Willamette River. A 190-ft-long, 48-ft-wide enclosed bridge, stretching 35 ft above street traffic, connects Knight Campus to Oregon’s existing campus.
Schliemann says the university is positioning the Knight Campus—which he calls a “humanistic research machine”— as a “gateway building” to a possible future research complex.
During the design process, the university hadn’t decided what disciplines these towers would house. So before designing the Knight Campus, representatives from the design team visited several other universities, including MIT’s Media Lab, Harvard, Stanford, and University of California at San Francisco. What they all have in common, says Schliemann, are collaborative spaces where knowledge can be shared. Stanford’s engineering complex, he adds, is noteworthy for how much natural light it lets inside.
‘NEIGHBORHOODS’ BRING RESEARCHERS TOGETHER
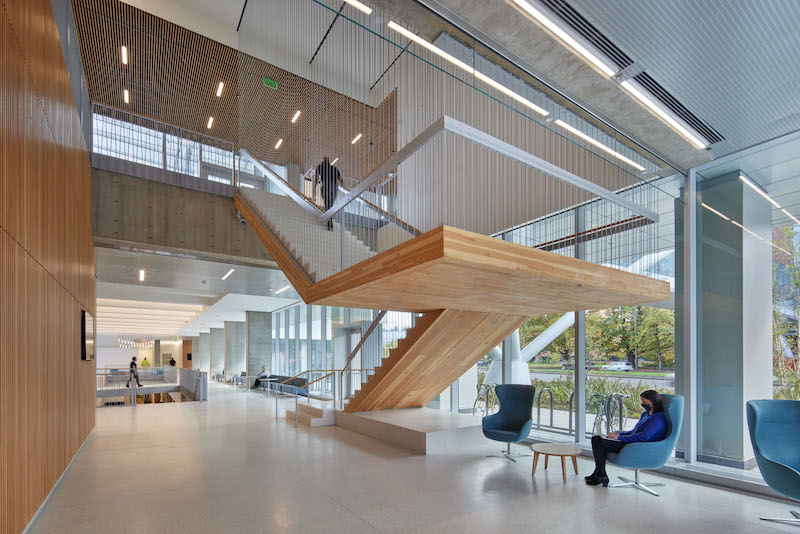

Staircases made from cross-laminated timber connect the floors.
The Knight Campus has several distinguishing characteristics:
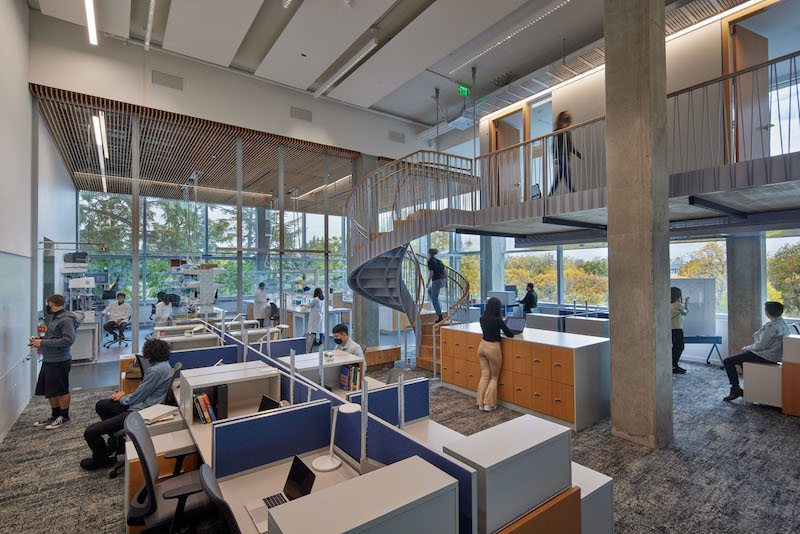
•Its two upper floors include four research “neighborhoods” that each has a wet bench area, computational space, and offices where Principal Investigators work. Schliemann contends that this is one of the first lab buildings in the U.S. where PIs are this visible to other research teammates.
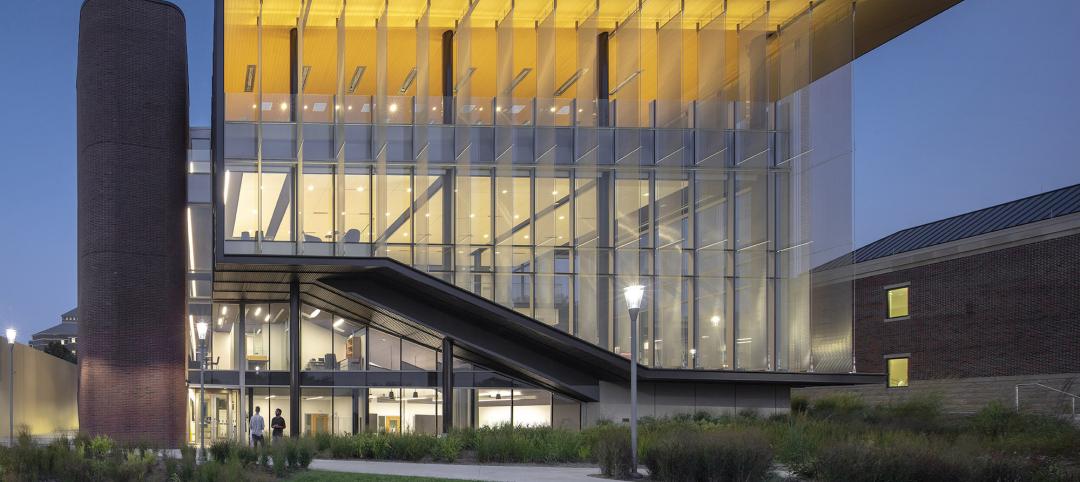
•The Campus’s double-skinned façade showcases an outer wall consisting of 650 glass panels and designed to resemble water flowing over rocks. This cascading wall is stabilized by an inner curtainwall made up of 900 glass panels. Schliemann says that this design and materials were chosen to let more natural light and panoramic exterior views into the building (which, he contends, improves working conditions), and for passive energy performance (the inner wall of the façade never gets exceedingly warm).
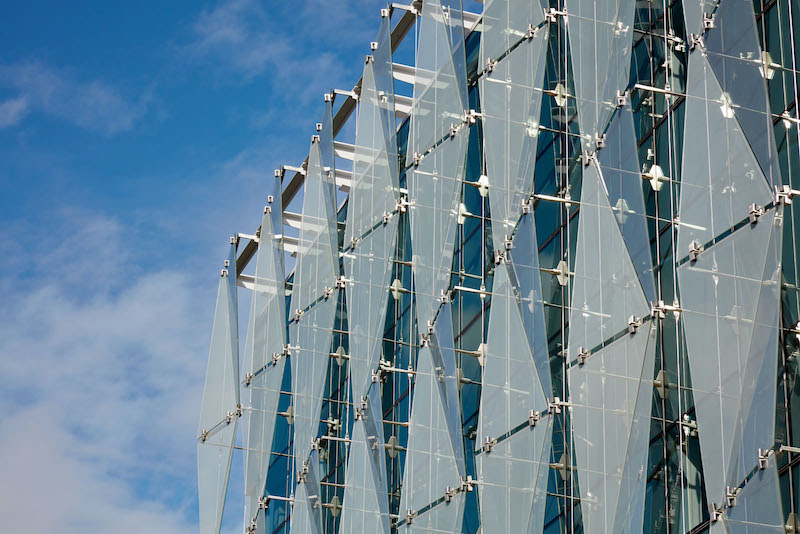

The Campus's double-skinned facade lets more natural light into the buildings and keeps heat from penetrating the inner curtainwall.
The wall structure was light enough to be hung from the roof component.
•Mass timber is prevalent throughout the Knight Campus, whose construction used 20,500 sf of cross-laminated timber that includes 180 CLT panels and 4,000 lbs of wood for each of the building’s staircases. The 21-foot floor-to-floor height allows for suspended mezzanine structures of mass timber containing offices for faculty, creating a new level of connectivity to their labs and graduate students.
Mass timber “is one of the most sustainable ways to construct a building” says Schliemann. (The Knight Campus is targeting LEED Gold certification.) Using mass timber also supports Oregon’s local economy. While vibration prevents a lab space from being made entirely with mass timber, “we could use it for offices, stairs, ceilings and bridges. Plus, we didn’t have to sheetrock the ceilings, as fire codes have finally caught up with mass timber” as a fireproofing agent.
Also see: Researchers use U. of Arkansas buildings as testbed for CLT panels.
SPACES FOR FORMAL OR RELAXED INNOVATION AND INTERACTION
Among the Knight Campus’s amenities are a 6,000-sf Innovation Center and 1,000-sf Wellness Center. While the Innovation Center might seem small when compared to other university research facilities, Schliemann counters that its scale is deceptive. “It gets innovators out into the real world.” He adds that all Knight Campus labs are leasable and tenant-adaptable.
The Wellness Center started out as a locker room with showers. Then spaces for yoga and other exercise regimens were included. Schliemann says the campus has a program where students can take bike rides with researchers.
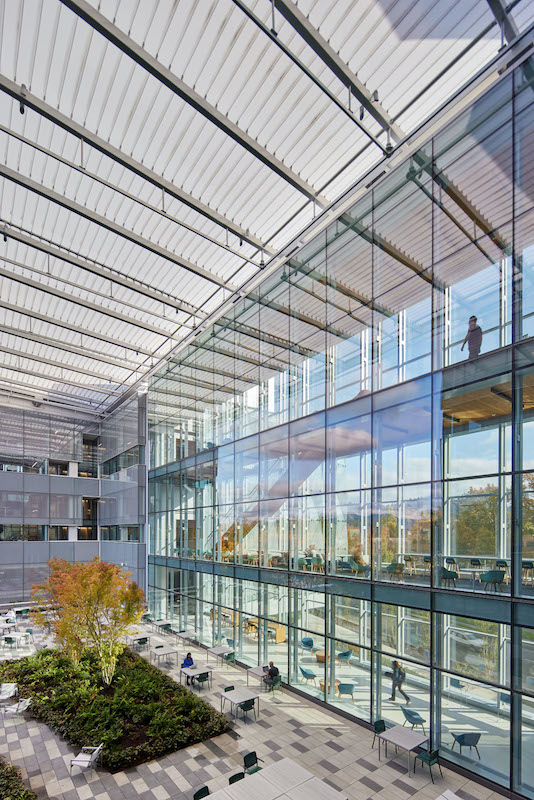

An elevated terrace and courtyard between the Campus's two buildings is covered with a canopy made from ETFE.
Between the Campus’s two buildings is an elevated terrace and courtyard, protected by a transparent plastic canopy, where students and faculty can relax, socialize, and connect with nature, as the terrace overlooks landscaping and the tree-covered Coburg Hills.
Related Stories
University Buildings | Feb 9, 2023
3 ways building design can elevate bold thinking and entrepreneurial cultures
Mehrdad Yazdani of CannonDesign shares how the visionary design of a University of Utah building can be applied to other building types.
Giants 400 | Feb 9, 2023
New Giants 400 download: Get the complete at-a-glance 2022 Giants 400 rankings in Excel
See how your architecture, engineering, or construction firm stacks up against the nation's AEC Giants. For more than 45 years, the editors of Building Design+Construction have surveyed the largest AEC firms in the U.S./Canada to create the annual Giants 400 report. This year, a record 519 firms participated in the Giants 400 report. The final report includes 137 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
University Buildings | Feb 8, 2023
STEM-focused Kettering University opens Stantec-designed Learning Commons
In Flint, Mich., Kettering University opened its new $63 million Learning Commons, designed by Stantec. The new facility will support collaboration, ideation, and digital technology for the STEM-focused higher learning institution.
University Buildings | Feb 7, 2023
Kansas City University's Center for Medical Education Innovation can adapt to changes in medical curriculum
The Center for Medical Education Innovation (CMEI) at Kansas City University was designed to adapt to changes in medical curriculum and pedagogy. The project program supported the mission of training leaders in osteopathic medicine with a state-of-the-art facility that leverages active-learning and simulation-based training.
Giants 400 | Feb 6, 2023
2022 Reconstruction Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. building reconstruction and renovation sector
Gensler, Stantec, IPS, Alfa Tech, STO Building Group, and Turner Construction top BD+C's rankings of the nation's largest reconstruction sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2022 Giants 400 Report.
Steel Buildings | Feb 3, 2023
Top 10 structural steel building projects for 2023
A Mies van der Rohe-designed art and architecture school at Indiana University and Morphosis Architects' Orange County Museum of Art in Costa Mesa, Calif., are among 10 projects to win IDEAS² Awards from the American Institute of Steel Construction.
Sports and Recreational Facilities | Feb 1, 2023
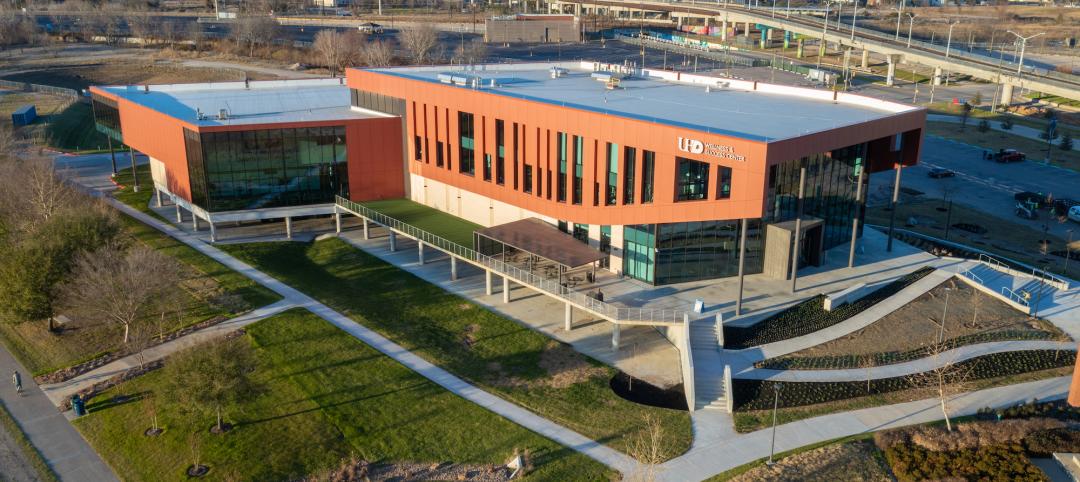
University of Houston opens 'game changer' wellness center at downtown campus
The University of Houston-Downtown (UHD) recently opened its new Wellness & Success Center (WSC). The $39 million, 75,000 sf facility greatly improves the quality of the school’s exercise programs and areas dedicated to them. It also establishes a dynamic core and recognizable landmark for fostering and nurturing an on-campus community, according to a news release from SmithGroup, which designed the building along with HarrisonKornberg Architects.
University Buildings | Jan 30, 2023
How wellness is reshaping college recreation centers
Moody Nolan, a specialist in the design of college recreation centers, has participated in the evolution toward wellness on college campuses.
University Buildings | Jan 27, 2023
Ozarks Technical Community College's advanced manufacturing center is first-of-a-kind in region
The new Robert W. Plaster Center for Advanced Manufacturing at Ozarks Technical Community College in Springfield, Mo., is a first-of-a-kind educational asset in the region. The 125,000-sf facility will educate and train a new generation in high tech, clean manufacturing and fabrication.
Student Housing | Jan 26, 2023
6 ways 'choice architecture' enhances student well-being in residence halls
The environments we build and inhabit shape our lives and the choices we make. NAC Architecture's Lauren Scranton shares six strategies for enhancing well-being in residence halls.