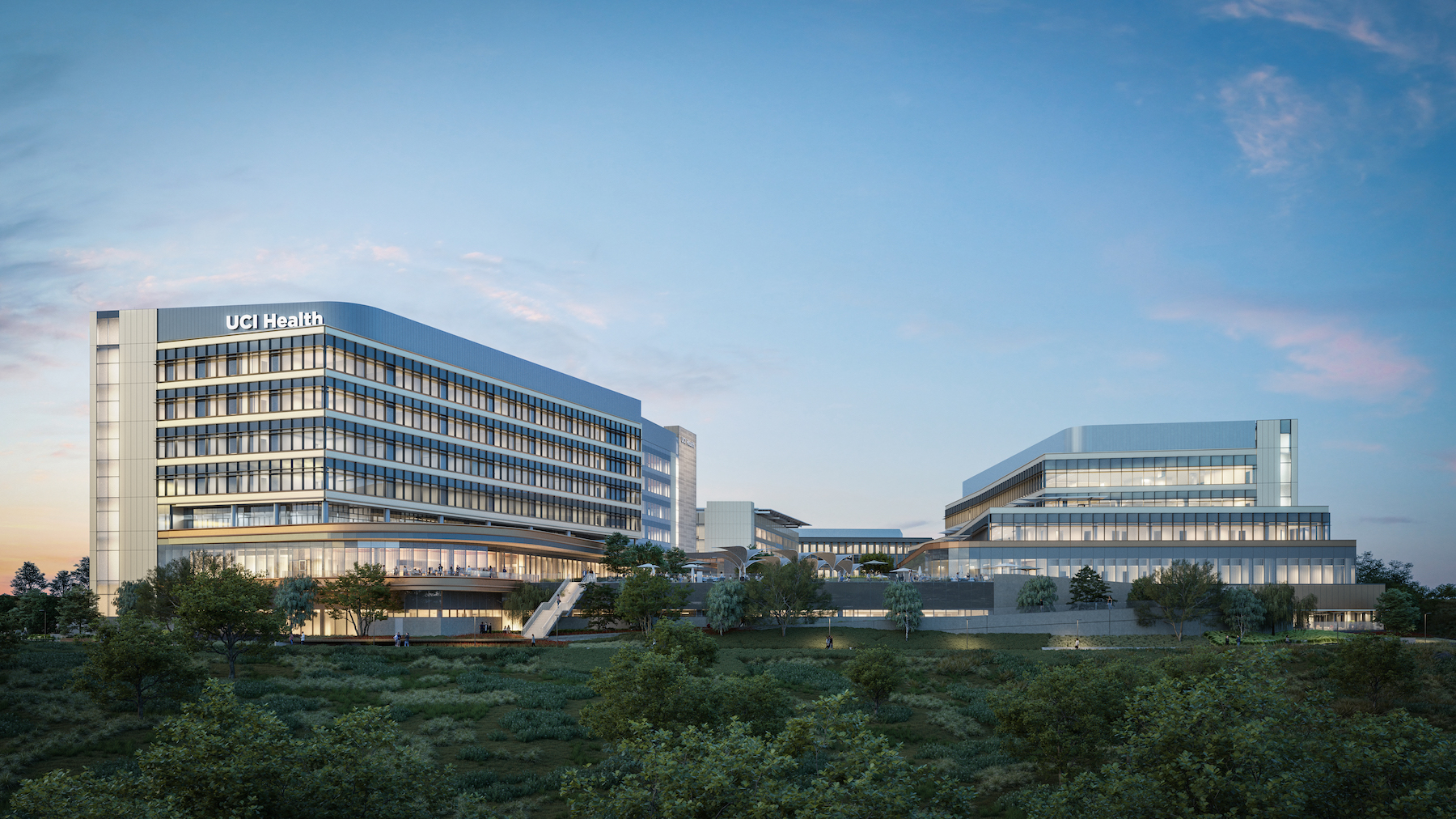
The University of California at Irvine (UCI) has a track record for sustainability. It recently received LEED Platinum certification for its 23rd campus building. Its under-construction UCI Medical Center is designed, positioned, and built to preserve the nearby San Joaquin Marsh Reserve, to reduce the facility’s solar gain by 85%, and to be the first medical center in the country to operate on an all-electric central plant.
The University of California’s system favors sustainable solutions, including its requirement that new construction be all-electric. Instead of filing for a waiver, UCI determined that it could meet that requirement “at only a modest premium,” says Brian Pratt, UCI Campus Architect and Associate Vice Chancellor. (The premium would be around $2.5 million on a project whose construction cost is $770 million and all-in cost will be over $1 billion.)
UCI Medical Center will consist of a four-story, 357,000-sf hospital with 144 beds, operating rooms, 20 Emergency Department beds, and 16 acute observation beds; a 223,000-sf Comprehensive Cancer and Ambulatory Care Center with 36 exam rooms, outpatient surgery, labs, and a pharmacy; a 35,000-sf central plant; and a parking structure with 1,340 spaces.
The parking structure was completed last year, and the outpatient building and central plant are scheduled for completion next year. The hospital should be done in 2025. To meet California and national code requirements, the power system will be backed up by diesel fuel generators (see Editor's note below).

Electrification without compromise
The decision to go all-electric was made early in the design process, recalls Khristina Stone, Preconstruction Manager for the GC Hensel Phelps, which with CO Architects leads the Progressive Design-Build team on this project. Nick Spady, Hensel Phelps’ Operations Manager, says that installing the buildings’ electrical infrastructure and emergency generators pose the greatest challenges in an all-electric environment.
The bridging documents actually described an electric heating system that allowed for the use of natural gas for steam. But ultimately the design-build team and the university decided to dispense with steam boilers altogether, says Roger Carter, CEO and Senior Principal of tk1sc, the project’s MEP engineer.

Carter notes that state codes now require hospital rooms to have constant air volume, which can impact the heating system’s’ load. An all-electric system will allow UCI’s hospital to leverage the central plant’s heat-recovery chillers to manage the building’s energy performance. Indeed, going all-electric is not expected to compromise the medical center’s operations, whose universal design allows for all patient rooms to be converted to intensive care units.
UCI Medical Center is being built under a Progressive Design-Build contract, which Pratt says has been the university’s bid-out preference for decades. He notes that hospital projects are complicated with many stakeholders, and a Progressive Design-Build agreement “allows for expert feedback earlier in the project.”
He notes, parenthetically, that prior to construction UCI had worked with the architect HOK for a year on the medical center’s programming. “This put up guardrails on the project, but with enough room for flexibility.” Gina Chang, CO Architects’ Principal and Healthcare Team Lead, says there was also a program alignment period, during which the team could receive comment and suggestions from UCI and the hospital’s users.
“The bridging documents weren’t overly heavy, so the contract set up a more positive relationship [with UCI] for flexibility and creativity,” says Stone.
The rest of the Progressive Design-Build team includes Degenkolb (SE), Stantec (CE), Ridge Landscape Architects (LA), Newson Brown Acoustics (acoustical engineer), and Colin Gordon Associates (acoustical vibration).
Indoor and outdoor wellness
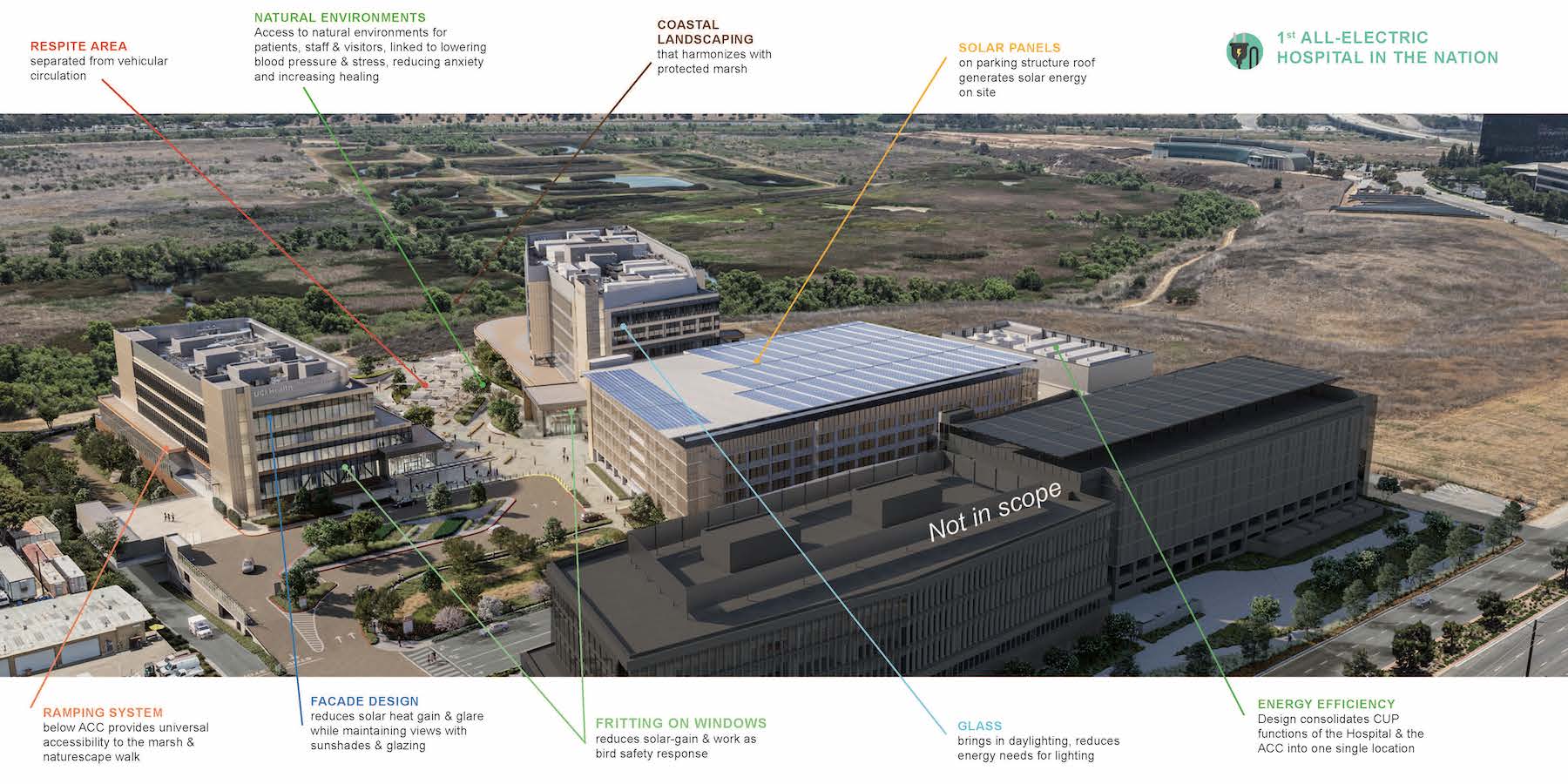
Aside from its electrification, UCI Medical Center features other sustainable elements. For example, the choice of brace framing, which Pratt says was “rooted in resilience,” reduces the project’s measurable embodied carbon by 20 percent. CO’s Chang further explains: “We implemented the lightest structural system possible (BRBF buckling restrained braced frame) to reduce the embodied carbon footprint. Though we sought for carbon reduction also with the concrete design, the site had high levels of methane and other greenhouse gasses that needed to be contained, so a larger, mat footing was utilized to mitigate that problem.”
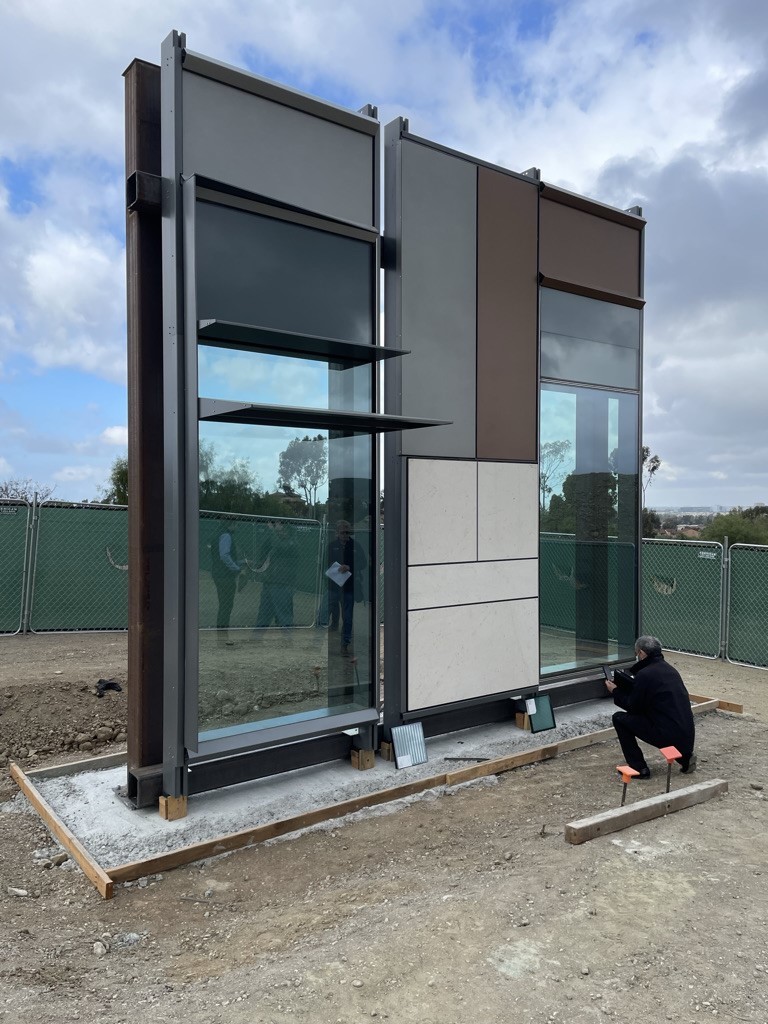

After conducting several frit and shading studies, the design team optimized the building’s envelope to reduce its solar gain by 85 percent, and to minimize bird strikes.
The medical center will also tap into the city of Irvine’s robust recycled water infrastructure.
Chang says the marsh—which is managed by UCI biologists—drove the massing and position of the buildings. “We took seriously being a good neighbor to the marsh,” adds Pratt. The construction site includes a turtle fence. And the biologists said that runoff from the site was fine as long as it was treated.
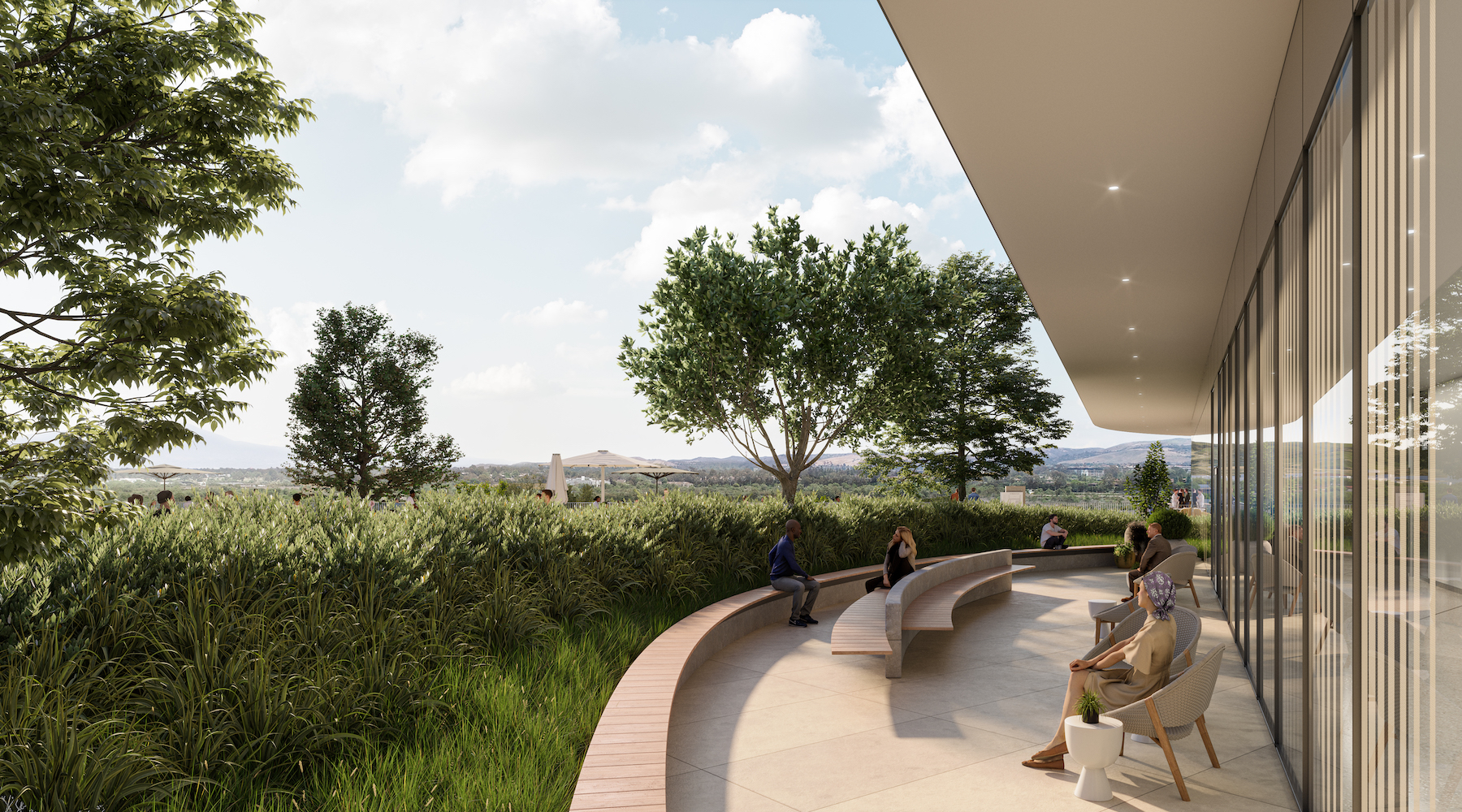

Like most healthcare facilities, UCI Medical Center is placing a premium on wellness. It has multiple areas for gathering outdoors, including walkable pathways and so-called healing gardens that offer views of the landscaping. (The outside plaza between the hospital and outpatient buildings brushes up against the edge of the marsh.)
“The landscape design and plant palette matter,” says Pratt. “And the marsh in the differentiator.” Indoors are numerous terraces, and other places of respite that include “lavender” rooms where staff members under stress can retreat.
________
Editor's note: After this story was posted, Ray Swartz, an engineer and Senior Principal with tk1sc, the project's MEP engineer, responded to a reader's question about the Medical Center's backup power source in the event of an electrical outage:
Swartz said that California's Department of Health Care Access and Information enforces a minimum of 72 hours of fuel storage for a new NPC-5 building, not the 96 hours required by NFPA 110. However, NFPA 110 requires the main fuel tank(s) to have a minimum capacity of at least 133 percent of the quantity needed by CEC 700.12 (B) (2) Exception 1 or 2. Therefore, for NPC-5 buildings, the minimum capacity requirement is 133 percent of the 72-hour fuel supply, equating to 96 hours.
The UCI Medical Center project includes four 3,000-kW generators operating in parallel. The capacity is adequate to service the campus in a 100 percent business-as-usual format. The generators are diesel fuel type, and the campus has an underground fuel storage capacity of 65,000 gallons. If, in an emergency, refueling the tanks is feasible, the campus could operate continuously under generator power.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
MOB added to new hospital project
A late-2009 ground breaking is planned for a $20 million medical office building on the grounds of the $211 million, 106-bed Loma Linda University Medical Center in Murrieta, Calif., which itself is under construction. Minneapolis-based Frauenshuh HealthCare Real Estate Solutions is developing the five-story, 160,000-sf MOB, which will accommodate 60 physician offices.
| Aug 11, 2010
Rehabilitation center helps patients transition
Construction is under way on the Polytrauma Transitional Rehabilitation Center on the VA Medical Center campus in Richmond, Va. The $8 million, 22,000-sf facility will provide physical therapy, housing, and education to veterans as part of their transition back into their communities. The center was designed by HDR, Alexandria, Va.
| Aug 11, 2010
Medical office building planned in Fort Worth, Texas
Dallas-based TGS Architects has unveiled its design for the five-story, 130,000-sf Plaza Medical Office Building, planned for Fort Worth, Texas. The Class A development will include space for orthopedic care, surgery, breast center, diagnostic imaging, cardiovascular, and rehabilitation therapy services.
| Aug 11, 2010
Philadelphia cancer center seeks LEED certification
The New York office of Thornton Tomasetti provided structural engineering services for the Ruth and Raymond Perelman Center for Advanced Medicine in Philadelphia, a $232 million medical research center and advanced treatment center for cancer and cardiovascular disease. Designed by a joint venture of Perkins Eastman Architects and Rafael Vinõly Architects, the 340,000-sf facility will hous...
| Aug 11, 2010
High-level NICU opens in Washington, D.C.
Design to the highest distinction available by the American Academy of Pediatrics, the new Level IIIC neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at Children's National Medical Center in Washington D.C., is equipped to care for the sickest premature babies, including those that require open-heart surgery. The 54-bed facility, designed by Karlsberger with KLMK Group as space planner, is four times large...
| Aug 11, 2010
San Bernardino health center doubles in size
Temecula, Calif.-based EDGE was awarded the contract for California State University San Bernardino's health center renovation and expansion. The two-phase, $4 million project was designed by RSK Associates, San Francisco, and includes an 11,000-sf, tilt-up concrete expansion—which doubles the size of the facility—and site and infrastructure work.
| Aug 11, 2010
New hospital expands Idaho healthcare options
Ascension Group Architects, Arlington, Texas, is designing a $150 million replacement hospital for Portneuf Medical Center in Pocatello, Idaho. An existing facility will be renovated as part of the project. The new six-story, 320-000-sf complex will house 187 beds, along with an intensive care unit, a cardiovascular care unit, pediatrics, psychiatry, surgical suites, rehabilitation clinic, and ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Manhattan's Gouverneur Healthcare Services tops out renovation, expansion
One year after breaking ground, the Building Team for the renovation and expansion of the Gouverneur Healthcare Services facility on Manhattan's Lower East Side topped out the $180 million project. Designed by New York-based RMJM, the development involves a 316,000-sf renovation and 108,000-sf addition that will house a 295-bed nursing facility and five-story ambulatory care center.
| Aug 11, 2010
Decline expected as healthcare slows, but hospital work will remain steady
The once steady 10% growth rate in healthcare construction spending has slowed, but hasn't entirely stopped. Spending is currently 1.7% higher than the same time last year when construction materials costs were 8% higher. The 2.5% monthly jobsite spending decline since last fall is consistent with the decline in materials costs.
| Aug 11, 2010
Construction under way on LEED Platinum DOE energy lab
Centennial, Colo.-based Haselden Construction has topped out the $64 million Research Support Facilities, located on the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) campus in Golden, Colo. Designed by RNL and Stantec to achieve LEED Platinum certification and net zero energy performance, the 218,000-sf facility will feature natural ventilation through operable ...







